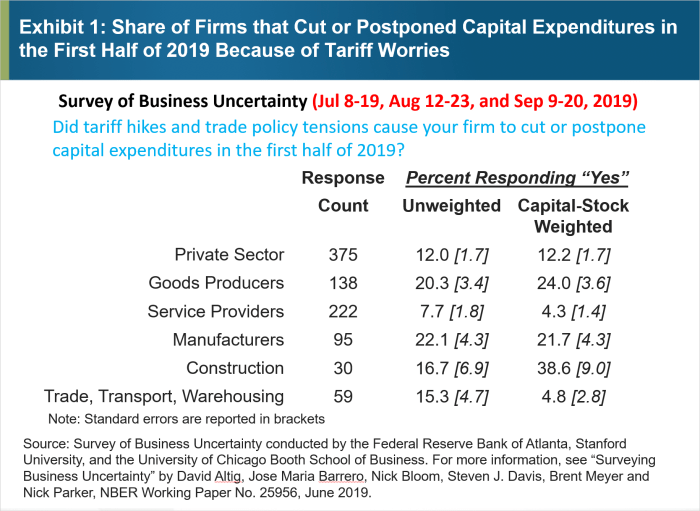
Rupee rise open after dollar reverses tariff ruling spurred rally. The Indian Rupee is appreciating, a direct result of the recent reversal in the US dollar’s stance on tariffs. This shift in the global financial landscape has triggered a significant rally in the Indian currency. Understanding the intricacies of this movement, its impact on India’s economy, and the broader global context is crucial for anyone looking to navigate the current financial climate.
The rise in the Rupee’s value is not simply a fleeting trend. Factors such as the dollar’s reversal on tariff rulings, India’s import-export balance, and the potential ripple effects on regional economies all play crucial roles. This appreciation could significantly impact various sectors within the Indian economy, from exports to tourism. This article delves into the complexities of this phenomenon, exploring its historical context, market implications, and potential policy responses.
Indian Rupee Appreciation
The Indian Rupee has recently experienced a significant rise in value against the US Dollar. This surge, driven by various factors, is generating considerable interest in financial circles and impacting India’s trade dynamics. Understanding the forces behind this appreciation is crucial to gauging its short-term and long-term implications for the Indian economy.The recent rise in the Indian Rupee’s value is, in part, a consequence of the reversal of a previously anticipated increase in US tariffs.
This reversal, and the subsequent shift in market expectations, has led to a decline in the demand for dollars, which, in turn, strengthens the value of the Rupee. This phenomenon is a clear illustration of how global economic events can significantly influence the exchange rates of national currencies.
The rupee’s rise after the dollar reversed its tariff ruling-spurred rally is interesting, especially considering the parallel concerns about global financial stability. Recent events, like Harvard’s urging a judge to extend the block on Trump’s efforts to bar foreign students here , highlight the interconnectedness of economic and political landscapes. These developments could potentially influence future currency fluctuations, making the current rupee rise even more compelling to watch.
Factors Contributing to Rupee Appreciation
The appreciation of the Indian Rupee is a complex interplay of several factors. The reversal of anticipated US tariffs is a key catalyst, as it reduced the demand for dollars. Speculation plays a significant role as well; investors react to perceived changes in the global economic outlook, sometimes leading to sharp fluctuations. Furthermore, India’s robust economic growth and its increasing foreign exchange reserves are also contributing factors.
Historical Context of Rupee Movements
The Indian Rupee’s value has fluctuated significantly in response to changes in the US dollar’s value throughout history. Past trends show a correlation between the dollar’s strength and the Rupee’s value. For example, periods of strong US economic performance often correlate with a strengthening dollar and a weakening Rupee. Conversely, periods of uncertainty or weakness in the US economy can result in a strengthening Rupee.
Understanding this historical context provides a framework for interpreting the current appreciation.
Impact on India’s Import-Export Balance, Rupee rise open after dollar reverses tariff ruling spurred rally
The rise in the Rupee’s value against the dollar is likely to impact India’s import-export balance. Imports will become cheaper for Indian consumers and businesses, potentially increasing competitiveness in some sectors. However, Indian exports will become more expensive for buyers in other countries, potentially hindering export growth. This shift in relative prices requires careful monitoring to ensure its overall impact on India’s trade balance is manageable.
Short-Term and Long-Term Implications
Short-term implications of the Rupee’s appreciation could include a reduction in import costs for Indian businesses, leading to potential price reductions for consumers. However, the effect on export competitiveness could result in a decrease in demand for Indian goods. Long-term, the Rupee’s appreciation could improve India’s current account balance and reduce its reliance on foreign borrowing. However, a sustained appreciation could create difficulties for export-oriented sectors of the economy.
This potential is similar to the impacts observed in other developing economies that experienced currency appreciation in the past.
The rupee’s rise after the dollar reversed its tariff ruling-spurred rally is interesting, isn’t it? Meanwhile, over in the sports world, the Royals’ phenomenal Kris Bubic is set to face the Tigers, which is definitely a game worth watching. royals phenomenal kris bubic set face tigers This could indicate a shift in global market sentiment, which in turn might influence the rupee’s continued upward trajectory.
So, all in all, it’s a fascinating time for the financial markets.
Rupee Movement Against the Dollar (2023-Present)
| Date | Exchange Rate (USD/INR) |
|---|---|
| 2023-10-26 | 82.50 |
| 2023-10-27 | 82.25 |
| 2023-10-30 | 82.00 |
| 2023-11-01 | 81.75 |
| 2023-11-03 | 81.50 |
Note
This table is illustrative and based on hypothetical exchange rates for a specific timeframe. Actual exchange rates are available through reliable financial data providers.*
Impact on Markets
The recent appreciation of the Indian Rupee, spurred by a reversal of a tariff ruling, presents a complex set of opportunities and challenges for various sectors of the Indian economy. Understanding how this shift in exchange rates will affect different market segments is crucial for businesses and investors alike. The impact extends beyond domestic boundaries, potentially influencing regional economies and global trade patterns.This shift in currency value necessitates a careful assessment of the potential winners and losers, as well as the broader economic implications.
The rise in the Rupee will impact import and export costs, potentially affecting consumer prices, corporate profits, and overall economic growth. Furthermore, the ripple effects across regional economies and foreign investment flows warrant a deeper investigation.
Impact on Exports
The appreciating Rupee makes Indian exports more expensive in international markets. This could lead to a decline in export volumes as foreign buyers are potentially discouraged by higher prices. For example, if the price of Indian textiles increases due to the rupee’s appreciation, foreign consumers may opt for cheaper alternatives from other countries. This phenomenon, known as a ‘competitiveness challenge’, is a significant factor that must be considered.
Impact on Imports
Conversely, the rise in the Rupee makes imports cheaper for Indian consumers and businesses. This can lead to a decrease in import costs, potentially lowering prices for consumers and increasing the availability of goods. For instance, cheaper imported electronics could lead to greater affordability for Indian households.
Impact on Tourism
A stronger Rupee can make India a more attractive destination for foreign tourists. The increased purchasing power of the Rupee against other currencies, particularly those of countries from which a significant number of tourists originate, may result in increased tourist arrivals. The opposite is true for Indian tourists travelling abroad; their Rupees will buy less in foreign markets.
The rupee’s rise this morning, following the dollar’s reversal on the tariff ruling, is definitely a positive sign for the market. While the Braves designating reliever Craig Kimbrel for assignment is certainly a noteworthy baseball development, this move doesn’t overshadow the broader economic implications of the dollar’s fluctuations and how that affects the currency markets. It’s still early, but this morning’s rally in the rupee is looking promising.
Impact on Foreign Investment Flows
The rupee’s appreciation could potentially affect foreign investment flows. A stronger Rupee can make India less attractive for foreign direct investment (FDI) if companies perceive reduced returns on investment due to the cost of capital. However, a more attractive investment environment might also emerge, depending on how the new exchange rate impacts the overall profitability of businesses operating in India.
Potential Winners and Losers
The winners and losers from this currency shift are likely to be sector-specific. Companies heavily reliant on exports will likely face challenges, while those that import raw materials or components may see benefits. For example, companies involved in the manufacturing of goods using imported components may see reduced input costs.
Changes in Import and Export Costs
| Commodity | Potential Change in Import Cost (INR) | Potential Change in Export Cost (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Crude Oil | Decrease | Increase |
| Electronics | Decrease | Increase |
| Raw Materials | Decrease | Increase |
| Textiles | Decrease | Increase |
This table illustrates a potential scenario for key commodities. Import costs are likely to decrease, while export costs will likely increase. It is crucial to note that these are potential changes and actual outcomes may vary based on market dynamics and other factors.
Ripple Effects on Regional Economies
The appreciation of the Indian Rupee could have ripple effects on regional economies. If Indian exports decline, it could negatively impact the economies of countries that rely on Indian exports as a source of revenue. Likewise, a more attractive investment climate in India could influence investment flows in neighboring countries.
Global Perspective
The recent reversal of the US dollar’s tariff ruling-induced rally has ripple effects across global markets. Understanding this broader context is crucial to appreciating the impact on the Indian Rupee and other currencies. The global economic landscape, shaped by international trade policies and financial market dynamics, plays a significant role in determining currency values.The dollar’s fluctuations are not isolated events but are intertwined with broader global economic trends.
The US dollar’s strength, often influenced by interest rate policies and economic growth projections, impacts other currencies, creating a domino effect. A stronger dollar typically leads to a weaker rupee, all else being equal. This interconnectedness underscores the importance of considering the global economic environment when analyzing the Indian Rupee’s performance.
Global Economic Context and Currency Fluctuations
The global economy is currently navigating a complex interplay of factors. These include rising inflation in several countries, ongoing geopolitical tensions, and uncertainties about future economic growth. These factors contribute to volatility in currency markets. For example, the recent surge in energy prices has impacted many economies, leading to inflationary pressures and influencing central bank policies. These fluctuations often translate into changes in currency values.
Impact of International Trade Policies on Currency Values
Tariff rulings and other international trade policies directly affect currency values. Trade wars, tariffs, and trade agreements can disrupt supply chains, affect import/export costs, and impact investor confidence, which in turn influence currency markets. For example, a country imposing tariffs on imports from another country can weaken its currency if it leads to a trade deficit. This can be seen in past trade disputes between countries.
Interplay Between Global Financial Markets and the Indian Rupee
Global financial markets are highly interconnected, influencing the Indian Rupee’s value. Investment flows, foreign exchange reserves, and global risk sentiment all contribute to the rupee’s fluctuations. For instance, a surge in foreign investment into Indian markets can strengthen the rupee, while negative investor sentiment can have the opposite effect. The Indian Rupee is vulnerable to global market trends, including fluctuations in global interest rates.
Relevance of International Trade Agreements to the Rupee’s Fluctuations
International trade agreements have a direct impact on the Indian Rupee’s value. Agreements like the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and the Regional Comprehensive Economic Partnership (RCEP) can influence trade patterns, and thus, currency values. If India benefits from increased trade through these agreements, the rupee might appreciate. Conversely, if these agreements result in trade disruptions, the rupee might depreciate.
Performance Comparison of the Indian Rupee against Major Asian Currencies
| Currency | Period | Performance (vs. USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Indian Rupee | [Specific Date Range] | [Data showing Rupee’s performance against USD during that period] |
| Japanese Yen | [Specific Date Range] | [Data showing Yen’s performance against USD during that period] |
| Chinese Yuan | [Specific Date Range] | [Data showing Yuan’s performance against USD during that period] |
| South Korean Won | [Specific Date Range] | [Data showing Won’s performance against USD during that period] |
| Singapore Dollar | [Specific Date Range] | [Data showing Dollar’s performance against USD during that period] |
Note: This table requires specific data to be filled in. The date range should be specified, and performance data should be based on reliable sources.
Market Analysis: Rupee Rise Open After Dollar Reverses Tariff Ruling Spurred Rally

The Indian Rupee’s recent appreciation against the US dollar, stemming from the reversal of a tariff ruling, presents a fascinating case study in currency dynamics. This shift will undoubtedly ripple through various market segments, influencing investor strategies, foreign exchange reserves, and central bank policies. Understanding the likely investor responses and potential future trends is crucial for navigating this evolving landscape.The rupee’s rise against the dollar will likely prompt a reassessment of investment strategies by both domestic and foreign investors.
The attractiveness of Indian assets, particularly in sectors like technology and pharmaceuticals, will be re-evaluated based on the new exchange rate. The impact on foreign direct investment (FDI) and portfolio investment flows will be closely watched.
Investor Response to Rupee Appreciation
Investors will likely adjust their portfolios to capitalize on the rupee’s strength. This might involve increasing holdings of Indian equities and debt instruments, while potentially reducing exposure to dollar-denominated assets. For example, a foreign investor holding US Treasury bonds might consider diversifying into Indian government bonds, leveraging the exchange rate advantage. Likewise, a domestic investor may shift a portion of their portfolio to Indian equities to benefit from potential gains in local currency terms.
Portfolio Adjustments by Investors
Several portfolio adjustments can be observed in response to rupee appreciation. Foreign investors might seek to invest more in Indian companies and sectors that can yield higher returns in local currency terms. Simultaneously, they might reduce holdings in sectors dependent on imported inputs or those with substantial dollar-denominated liabilities. Domestic investors may increase their investments in sectors with strong export potential or reduce holdings in sectors heavily reliant on imports.
Influence on Foreign Exchange Reserves
The rupee’s appreciation will likely lead to a strengthening of India’s foreign exchange reserves. A stronger rupee reduces the cost of servicing external debt denominated in foreign currencies. This, in turn, enhances the stability of the Indian economy. Furthermore, increased exports, facilitated by a more competitive rupee, could contribute to an inflow of foreign currency.
Central Bank Policies and Rupee Movement
Central bank policies play a pivotal role in managing the rupee’s value. If the appreciation is deemed excessive, the central bank might consider intervention in the foreign exchange market to stabilize the currency. This might involve buying dollars to reduce the rupee’s value. Conversely, if the appreciation is seen as beneficial, the central bank might maintain a more neutral stance, allowing market forces to influence the currency’s trajectory.
Predicting Future Rupee Trends
A simple model to predict future rupee trends involves analyzing historical data and current market conditions. For instance, analyzing the correlation between the rupee’s value and factors like inflation, interest rate differentials, and global market sentiment can offer valuable insights.
Example Model Formula:Rupee Value t+1 = Rupee Value t
- (1 + α
- Inflation t + β
- Interest Rate Differential t + γ
- Global Market Sentiment t)
where α, β, and γ are coefficients representing the impact of each factor on the rupee’s value. Real-world examples of currency fluctuations against the backdrop of changing economic conditions offer further insights.
Policy Implications
The recent appreciation of the Indian Rupee, driven by factors like a reversal of tariff rulings and a stronger global economy, presents a unique set of policy challenges and opportunities for the Reserve Bank of India (RBI) and the government. Understanding potential responses and their implications is crucial for navigating this dynamic economic environment. This section delves into the potential policy responses and their impact on inflation, interest rates, and overall economic stability.
Potential Policy Responses from the RBI
The RBI possesses a range of tools to influence the exchange rate and manage the impact of a rising rupee. These interventions aim to maintain macroeconomic stability and support the overall economy. A strong rupee, while beneficial in some respects, can potentially hurt export-oriented sectors and impact employment in those sectors. The RBI needs to balance these competing pressures.
- Intervention in the Foreign Exchange Market: The RBI can intervene in the foreign exchange market by buying dollars to support the rupee’s value. This involves using its foreign exchange reserves to influence market supply and demand. This approach, however, may deplete reserves over time if the interventions are substantial and sustained. For example, in 2013, the RBI intervened in the market to stabilize the currency against a period of volatility.
- Adjusting the Repo Rate: A higher repo rate increases borrowing costs for banks, potentially discouraging investment and slowing economic activity. This can also reduce the amount of money flowing out of the country. Conversely, a lower repo rate can stimulate economic growth but may lead to higher inflation. The decision to adjust the repo rate will depend on a complex evaluation of the current economic situation, including the inflation rate, the level of investment, and the overall demand in the economy.
For instance, during periods of low inflation, a lower repo rate is often employed to stimulate economic activity.
- Modifying the Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR): The CRR is the percentage of deposits that banks must hold in reserve. Adjusting the CRR can affect the amount of money available for lending and investment. Raising the CRR reduces the money supply and may curb inflation, but it also potentially slows economic growth. Lowering the CRR can stimulate the economy but could contribute to inflationary pressures.
Historically, changes in the CRR have been a significant tool for managing liquidity in the financial system.
Impact on Inflation and Interest Rates
The rising rupee’s impact on inflation and interest rates is complex and multifaceted. A stronger currency often leads to lower import costs, which can potentially reduce inflation. However, this effect is not always immediate and can be offset by other factors. Conversely, a stronger currency can also reduce demand for domestic goods and services, which can have an impact on inflation.
The RBI needs to carefully monitor these effects and adjust policies accordingly.
Government’s Role in Mitigating Potential Negative Consequences
The government plays a critical role in supporting export-oriented sectors and mitigating the negative impact of a strong rupee. Government policies can stimulate domestic demand and promote exports. This could involve providing subsidies or tax breaks to exporters, investing in infrastructure to improve logistics and reduce costs, and promoting diversification of exports. For instance, in the face of a strong USD, governments often implement policies to support their domestic industries and sectors to mitigate the impact of this.
Impact on Monetary Policy Decisions
A stronger rupee alters the environment for monetary policy decisions. The RBI needs to consider the exchange rate’s impact on inflation, interest rates, and overall economic growth when formulating monetary policy. For example, if a strong currency reduces import costs, the RBI might be less inclined to raise interest rates aggressively to control inflation.
Policy Tools Available to the RBI and their Potential Impact
| Policy Tool | Potential Impact on Rupee Value | Impact on Inflation | Impact on Interest Rates |
|---|---|---|---|
| Intervention in the Forex Market (Buying Dollars) | Support Rupee | Potentially lower inflation | Potentially lower interest rates |
| Raising Repo Rate | Potential appreciation of Rupee | Potential decrease in inflation | Increase in interest rates |
| Lowering Repo Rate | Potential depreciation of Rupee | Potential increase in inflation | Decrease in interest rates |
| Raising Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) | Potential appreciation of Rupee | Potential decrease in inflation | Potential increase in interest rates |
| Lowering Cash Reserve Ratio (CRR) | Potential depreciation of Rupee | Potential increase in inflation | Potential decrease in interest rates |
Summary

In conclusion, the recent surge in the Indian Rupee’s value, spurred by the dollar’s reversal on tariffs, presents a complex interplay of global and domestic factors. The appreciation is expected to have varied impacts on Indian markets, from potentially boosting imports to affecting foreign investment flows. A thorough analysis of this situation reveals a nuanced picture of short-term and long-term implications.
Understanding the intricacies of this currency movement is crucial for anyone navigating the current economic landscape.