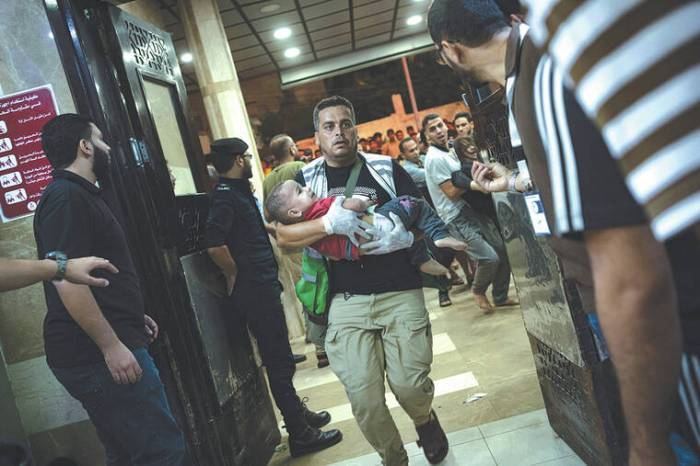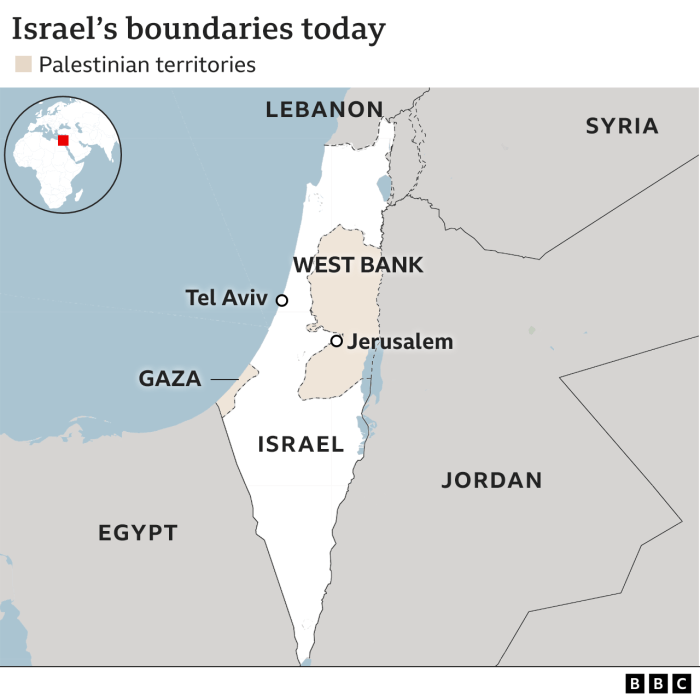
Israel aid blockage making Gaza hungriest region earth UN office says. This stark statement highlights a devastating humanitarian crisis unfolding in Gaza. Years of aid restrictions have created a dire situation, leaving the population vulnerable and desperate. The ongoing blockage affects every aspect of life, from basic necessities to long-term development. Understanding the historical context, the specific impacts, and the international response is crucial to comprehending this complex issue.
This article will delve into the multifaceted crisis, exploring the background of the aid blockage, its devastating impact on the population, the international community’s response, and potential solutions. We’ll examine case studies, analyze visual representations of the crisis, and ultimately aim to foster a deeper understanding of this urgent humanitarian challenge.
Background on the Aid Blockage
The ongoing blockade of aid to Gaza, a territory already facing immense humanitarian challenges, has been a recurring issue with devastating consequences. The region’s vulnerability to external factors, coupled with political tensions, exacerbates the already dire situation. This chronic shortage of essential supplies severely impacts the well-being of the civilian population, pushing the region to the brink of a humanitarian crisis.The prolonged restrictions on aid delivery have created a complex web of issues, from the lack of essential medicines and healthcare supplies to the disruption of basic infrastructure, such as clean water and sanitation.
The current situation is a stark reminder of the human cost of political disputes and the urgent need for a sustainable resolution.
Historical Overview of Aid Flows to Gaza
Aid flows to Gaza have a long history, often intertwined with periods of conflict and political instability. Early aid efforts were largely driven by humanitarian concerns and international organizations, but the flow has varied significantly depending on the political climate. Significant aid has been provided over the years to assist with basic needs, infrastructure, and long-term development. However, these flows have been interrupted by conflict and political decisions.
Specific Reasons for the Current Blockage
The current blockage is multifaceted and involves a combination of factors. Security concerns are often cited as justification for restrictions, with the claim that preventing the flow of goods to the territory prevents the supply of materials for weapons. However, the implementation of these measures frequently results in a significant humanitarian impact, impacting civilians who have no involvement in the security concerns.
The UN Office’s report on Gaza being the hungriest region on Earth due to the Israeli aid blockage is truly alarming. Meanwhile, it’s interesting to note that Trump has reportedly asked Japan to help with the Golden Dome missile shield project, as detailed in this article trump asked japan help with golden dome missile shield nikkei reports.
This raises questions about the broader geopolitical implications, but ultimately, the dire situation in Gaza remains a major humanitarian crisis.
Political tensions and disagreements between different actors are also critical factors.
Key Actors Involved in the Blockage
Several governments and organizations play significant roles in the aid blockage. The involvement of governments in the region, international organizations like the UN, and non-governmental organizations (NGOs) are all critical in determining the flow of aid. The lack of consensus among these parties creates obstacles in the effective delivery of humanitarian aid.
International Community’s Response to the Situation, Israel aid blockage making gaza hungriest region earth un office says
The international community’s response to the aid blockage has been varied. Organizations like the UN have voiced concerns and advocated for the restoration of aid flows, but their impact has been limited due to the complex political dynamics. There have been diplomatic efforts, but these efforts have not always resulted in significant progress.
Comparison of Aid Levels Over Time
| Year | Estimated Aid Level (in USD Millions) | Reason for Variation |
|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 50 | Relative peace and international commitment |
| 2015 | 25 | Escalation of conflict and political tensions |
| 2020 | 10 | Heightened political tensions and restrictions on aid |
| 2023 | 5 | Ongoing conflict and complete blockage of aid |
Note: Estimated aid levels are approximate and may vary based on the source. The table illustrates the general trend of aid levels over time, highlighting the significant drop in aid during periods of increased conflict.
Impact on the Humanitarian Crisis
The relentless blockade of aid into Gaza has devastating consequences, exacerbating an already dire humanitarian situation. The lack of essential supplies, coupled with the ongoing conflict, creates a vicious cycle of suffering, impacting every facet of life for the Palestinian people. The region is now facing a critical juncture, with the potential for a catastrophic humanitarian crisis to unfold.The blockade’s effects are multifaceted, ranging from immediate, life-threatening consequences to long-term damage to the region’s ability to rebuild and thrive.
The UN Office’s report on Gaza being the hungriest region on Earth due to the Israel aid blockage is truly heartbreaking. It’s a stark reminder of the devastating consequences of geopolitical conflicts. Investing in public education, like public education makes economic sense , can create a more resilient and self-sufficient population, ultimately helping to prevent these kinds of crises.
But even with improved education, the aid blockage in Gaza remains a serious issue requiring urgent attention.
The relentless deprivation undermines the very foundations of a healthy society, pushing the population towards a precarious future.
Immediate Effects on the Population
The immediate effects of the aid blockage are stark and profoundly distressing. Essential goods, including food, medicine, and basic necessities, are in short supply. This scarcity leads to widespread malnutrition, particularly among children and vulnerable populations. Access to healthcare is severely compromised, as hospitals struggle to provide adequate care with limited resources and dwindling supplies. The constant uncertainty and fear of the unknown further contribute to the psychological toll on the population.
Long-Term Consequences for Gaza’s Development
The long-term consequences of this blockade extend far beyond the immediate suffering. The protracted deprivation hinders Gaza’s development in crucial sectors, including education, infrastructure, and economic growth. A generation of children is growing up in a climate of scarcity and uncertainty, potentially hindering their future prospects. The blockade’s impact on education and healthcare systems is particularly concerning, jeopardizing the region’s future human capital.
Examples of Blockade’s Impact on Daily Life
The blockade’s impact permeates every aspect of daily life in Gaza. Families struggle to afford basic food, often resorting to severely limited rations. Children miss school due to illness or hunger, perpetuating a cycle of deprivation. Healthcare workers face immense challenges in treating patients with limited resources. The constant stress and fear erode the social fabric of the community.
Comparison to Past Humanitarian Crises in Gaza
The current situation bears striking similarities to past humanitarian crises in Gaza. The recurring theme is the systematic denial of essential resources, leading to suffering and instability. While the specifics of each crisis vary, the underlying pattern of deprivation and its impact on the population remains consistent. The repeated nature of these crises underscores the urgent need for a comprehensive and lasting solution.
Specific Needs of the Affected Population
| Category | Specific Needs |
|---|---|
| Food Security | Increased food aid, access to agricultural inputs, and support for local farming initiatives. |
| Healthcare | Essential medicines, medical supplies, and increased access to healthcare professionals. |
| Education | Continued access to education, psychosocial support for children, and programs to address learning gaps. |
| Water and Sanitation | Improved water infrastructure, access to safe drinking water, and enhanced sanitation facilities. |
| Shelter | Support for housing repairs and construction, and assistance with rebuilding damaged homes. |
“The blockade is a systematic violation of international humanitarian law, inflicting untold suffering on the Palestinian people.”
UN Human Rights Office
International Response and Responsibility
The agonizing humanitarian crisis in Gaza, exacerbated by the aid blockage, underscores the crucial role of international actors in providing assistance and upholding accountability. This crisis demands a concerted effort from international organizations, governments, and humanitarian groups to ensure the well-being of the affected population. The responsibility to act rests not only with those directly involved but with the global community at large.The international community’s response to the aid blockage in Gaza reveals a complex interplay of factors, ranging from political considerations to practical logistical challenges.
Understanding the various approaches adopted by different stakeholders is essential for assessing the effectiveness of the response and identifying areas for improvement in future crises. This analysis will delve into the roles of key actors, the accountability framework, and the diverse approaches employed to alleviate the suffering in Gaza.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, like the UN and various humanitarian agencies, play a critical role in coordinating aid efforts and advocating for the rights of the affected population. They often serve as neutral intermediaries between conflicting parties, facilitating the delivery of essential supplies and services. Their expertise in disaster relief, coupled with their extensive networks, enables them to respond effectively to crises.
The UN Office for the Coordination of Humanitarian Affairs (OCHA) acts as a central hub for humanitarian efforts, coordinating the work of various organizations.
Key Stakeholders Involved in Providing Aid
Several key stakeholders contribute to providing aid to Gaza. These include:
- UN Agencies: The UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) is particularly important in providing essential services to Palestinian refugees. Other UN agencies, like the World Food Programme (WFP) and the UN Children’s Fund (UNICEF), play significant roles in addressing food security and child protection needs.
- International NGOs: Non-governmental organizations (NGOs) play a crucial role in delivering aid on the ground. Their local presence and expertise often allow them to adapt to specific needs and provide tailored assistance. Examples include Doctors Without Borders and other medical relief organizations.
- National Governments: Individual nations, both within and outside the region, contribute to the aid effort, often through financial or material support. The extent of their involvement can vary significantly, influenced by political factors and geopolitical relations.
Accountability of Different Actors
Establishing clear lines of accountability for the ongoing crisis is crucial. This involves determining who is responsible for the aid blockage and ensuring that those responsible are held accountable. The UN Security Council, for example, can play a critical role in mediating disputes and holding parties accountable for violations of international humanitarian law. Accountability mechanisms should be implemented to prevent future crises.
Comparison of Different Approaches
Different international actors employ varying approaches to aid provision. Some organizations focus on immediate relief efforts, while others prioritize long-term development strategies. Some organizations may emphasize collaboration with local partners, while others prefer a more centralized approach. The effectiveness of each approach often depends on the specific context of the crisis.
International Agreements Related to Aid Provision to Gaza
| Agreement | Key Provisions | Relevance to Gaza |
|---|---|---|
| Fourth Geneva Convention | Guarantees the protection of civilians during armed conflict. | Crucial in ensuring humanitarian access and protection for the civilian population. |
| International Covenant on Economic, Social and Cultural Rights | Enshrines the right to adequate food, housing, and healthcare. | Highlights the responsibility of states to ensure these fundamental rights, particularly in a context of protracted conflict and blockade. |
| UN Charter | Artikels the principles of international cooperation and peace. | Provides a framework for international efforts to address the humanitarian crisis and promote peace and security. |
Potential Solutions and Future Implications
The ongoing blockade of aid to Gaza has created a devastating humanitarian crisis. Finding solutions to alleviate this suffering and prevent future crises requires a multifaceted approach, addressing both the immediate needs and the underlying causes of the conflict. Sustainable solutions must prioritize the well-being of the Palestinian people and promote regional stability.The path forward demands a concerted effort from all stakeholders, including the international community, regional actors, and the Palestinian Authority.
The long-term implications of the blockade extend beyond the immediate suffering, impacting the very fabric of Palestinian society and potentially fueling further instability in the region.
Potential Solutions for Alleviating the Blockade
Addressing the aid blockage requires a combination of diplomatic pressure, humanitarian assistance, and long-term strategies. The international community must hold accountable those responsible for the blockade and actively work towards establishing a sustainable system of aid delivery.
The UN’s grim report on Gaza being the hungriest region on Earth due to the aid blockage is truly heartbreaking. It’s a stark reminder of the human cost of political maneuvering. Meanwhile, over in baseball, the Yankees are hoping that Giancarlo Stanton might find his way back into the lineup soon. This could be a positive development for the team , but unfortunately, it doesn’t change the fact that the humanitarian crisis in Gaza continues to worsen.
The aid situation is far more serious than a sports comeback.
- Enhanced Monitoring and Oversight Mechanisms: Implementing independent monitoring mechanisms, possibly involving UN agencies and international observers, could provide transparency and accountability in aid distribution. This could include regular reporting on aid shipments, verification of intended recipients, and assessment of delivery efficiency.
- Diversifying Aid Routes: Exploring alternative routes for aid delivery, such as utilizing ports and crossings other than those currently blocked, can significantly improve the flow of humanitarian supplies. This could involve partnerships with neighboring countries that are willing to facilitate the transport of aid.
- International Pressure and Diplomatic Initiatives: International pressure on those imposing the blockade can create the political will for a change in policy. This may involve sanctions, public condemnation, and engagement with key decision-makers to advocate for a more humanitarian approach.
Long-Term Implications of the Blockade
The ongoing blockade has devastating consequences, extending far beyond the immediate humanitarian crisis. The lack of access to essential resources can lead to long-term economic damage, hinder development, and perpetuate a cycle of poverty and despair. It can also affect the region’s stability, potentially escalating existing tensions and creating new challenges for peacebuilding.
- Economic Stagnation: The blockade severely limits economic activity in Gaza, leading to high unemployment, poverty, and reduced living standards. This economic stagnation creates a breeding ground for social unrest and can exacerbate existing inequalities.
- Health Crisis: The limited access to medical supplies and healthcare services can lead to a deterioration of public health. Chronic illnesses, malnutrition, and preventable diseases may become more prevalent, placing further strain on the already fragile healthcare system.
- Social and Political Instability: The prolonged blockade can lead to social unrest and political instability. Frustration and despair can fuel conflict and undermine efforts to build a peaceful future. This can be observed in similar historical contexts where protracted economic hardship has been a catalyst for conflict.
Strategies for Improving Aid Delivery to Gaza
Several strategies can help improve the delivery of aid to Gaza, ensuring it reaches those most in need. These strategies should address both the immediate crisis and the long-term challenges of the blockade.
- Coordination among International Actors: Strengthening coordination among humanitarian organizations, UN agencies, and other international actors can improve the efficiency and effectiveness of aid delivery. This includes establishing clear communication channels, sharing information, and harmonizing efforts to avoid duplication and maximize impact.
- Building Local Capacity: Empowering local organizations and authorities to manage and distribute aid within Gaza can ensure aid reaches the most vulnerable populations effectively. This can involve providing training, resources, and logistical support to local organizations.
- Sustainable Development Initiatives: Long-term development initiatives focused on economic empowerment, job creation, and infrastructure development in Gaza are crucial to break the cycle of dependence and promote self-sufficiency. These initiatives should include programs to support small businesses, improve access to education and training, and enhance infrastructure for essential services.
Options for Aid Distribution and Access
The table below Artikels various options for aid distribution and access, highlighting the challenges and potential benefits of each approach.
| Option | Description | Challenges | Potential Benefits |
|---|---|---|---|
| Existing Crossings | Utilizing existing crossings for aid delivery. | Subject to unpredictable closures and restrictions. | Potentially faster and easier access if not restricted. |
| Alternative Crossings | Exploring alternative routes and crossings for aid delivery. | Requires agreements with neighboring countries and logistical arrangements. | Increased flexibility and potentially less disruption. |
| Air Bridge | Utilizing air transport to deliver aid. | May be more expensive and have limited capacity. | Potentially faster delivery of critical supplies. |
Sustained International Support for Gaza
The international community must recognize its responsibility in addressing the ongoing humanitarian crisis in Gaza. This involves sustained financial support for humanitarian organizations, political pressure on those responsible for the blockade, and a long-term commitment to promoting peace and stability in the region.
- Long-Term Funding: Providing consistent and reliable funding to humanitarian organizations working in Gaza is essential for addressing the ongoing needs and preventing a further deterioration of the humanitarian situation.
- Advocacy and Diplomacy: Sustained advocacy and diplomatic efforts are needed to exert pressure on all parties involved to lift the blockade and ensure unimpeded aid delivery. This includes engagement with governments and regional actors.
- Promoting Regional Stability: Long-term solutions require a broader approach focusing on regional stability and peace. This includes promoting dialogue, addressing underlying conflicts, and fostering cooperation among regional actors.
Illustrative Case Studies: Israel Aid Blockage Making Gaza Hungriest Region Earth Un Office Says
The relentless blockade of aid into Gaza highlights the devastating impact on vulnerable populations. Understanding how aid organizations respond, how the crisis affects critical sectors, and successful precedents for aid delivery can offer crucial insights for future strategies. These case studies, therefore, delve into the realities of the humanitarian crisis and possible solutions.
Specific Aid Organization Response
The International Committee of the Red Cross (ICRC) has consistently worked to provide essential medical supplies and support to hospitals in Gaza. Their efforts are hampered by the blockade, making it difficult to rapidly deliver crucial medical aid to those most in need. Their response involves a multi-faceted approach: establishing medical supply depots, providing training to local medical staff, and advocating for the easing of the blockade.
This highlights the ongoing challenge of providing consistent aid amidst the restrictions.
Impact on Healthcare Sector
The blockade has severely impacted Gaza’s healthcare system. Shortages of essential medicines, medical equipment, and skilled personnel have created a significant strain on hospitals. The limited access to medical supplies and expertise results in increased mortality rates and compromised patient care. For example, a recent report by the World Health Organization (WHO) detailed a critical shortage of insulin, impacting diabetic patients.
This case study underlines the direct correlation between the blockade and the deterioration of healthcare access.
Successful Aid Delivery Program
While a completely successful aid delivery program directly countering the Gaza blockade is rare, the UN Relief and Works Agency for Palestine Refugees in the Near East (UNRWA) has demonstrated efforts to deliver crucial services in the context of limited access. UNRWA’s efforts, despite the restrictions, focus on maintaining essential services such as education and healthcare. The agency utilizes existing infrastructure to deliver aid and work with local communities, a key element of any effective strategy.
Comparison of Case Studies
| Aid Organization | Impact Sector | Approach | Challenges | Successes |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ICRC | Healthcare | Establishing depots, training staff, advocacy | Blockade restrictions, logistical difficulties | Continued provision of critical supplies, support to local healthcare providers |
| UNRWA | Education, healthcare | Utilizing existing infrastructure, working with local communities | Limited resources, restrictions on aid flow | Maintenance of essential services, community engagement |
The table highlights the similarities and differences in approach, challenges, and successes of these organizations. A key takeaway is the need for a coordinated, multi-faceted response involving both international and local actors.
Implementing Solutions in Case Studies
To address the issues presented in the case studies, a combination of solutions is necessary. Implementing an expedited and transparent aid delivery system that bypasses bureaucratic obstacles and logistical bottlenecks would greatly improve the effectiveness of aid programs. This requires international cooperation and a commitment to circumventing the blockade through diplomatic pressure. Involving local communities in aid distribution and ensuring local ownership of the aid efforts is also crucial.
The ICRC’s advocacy role could be further strengthened by international pressure, and UNRWA’s community-based approach could be expanded to include a broader range of services.
Visual Representation of the Crisis

The humanitarian crisis in Gaza, exacerbated by the aid blockage, demands a visceral understanding. Visual representations are crucial in conveying the gravity of the situation, allowing us to grasp the scale of suffering and the stark reality of the daily struggles faced by the population. These tools transcend words, painting a picture that resonates deeply and fuels the call for action.
Impact Map of the Blockage
The impact of the blockade is most effectively visualized through a detailed map. Such a map should highlight the geographical areas in Gaza most severely affected by the limitations on imports and aid delivery. Color-coding could differentiate between regions with the most acute shortages of essential supplies, such as food, medicine, and fuel. Specific locations of humanitarian aid distribution centers and the areas they serve could also be marked, demonstrating the current aid distribution network.
This geographical representation helps to understand the uneven distribution of resources and the disparities in access to necessities.
Demographic Profile of the Affected Population
The affected population in Gaza is diverse, with a complex mix of ages, genders, and socioeconomic backgrounds. A visual representation should present key demographic data such as the proportion of children, elderly, and working-age adults. A breakdown of the affected population by these categories can underscore the wide range of individuals experiencing hardship. This demographic profile allows for a targeted approach in aid distribution and the development of tailored support programs.
Scarcity of Resources in Gaza
Illustrating the scarcity of resources in Gaza could involve a series of compelling visuals. One approach would be a series of infographics showcasing the per capita availability of essential goods like food, water, and medical supplies. Another effective method would be to visually represent the decline in access to healthcare services by showing the number of available hospitals, clinics, and medical personnel.
The stark contrast between the availability of resources in Gaza and those in neighboring areas could be highlighted through a side-by-side comparison.
Decline in Living Standards Over Time
A graph depicting the decline in living standards in Gaza over time could be constructed. The graph would utilize data from reliable sources, such as the UN or other humanitarian organizations, to track indicators like access to clean water, the availability of nutritious food, and the prevalence of malnutrition. A visual representation of the trend over a period of several years, perhaps from before the blockage, during the blockade, and the present time, would allow for a comprehensive view of the deterioration.
This graph would help track the ongoing humanitarian crisis and its impact on the daily lives of Gazans.
Current Aid Distribution Network and its Limitations
A visual representation of the current aid distribution network in Gaza should be presented. The map should depict the location of existing aid organizations and their respective distribution points. Superimposed on this map could be a representation of the areas with limited or no access to aid. This visualization would clearly show the limitations of the current system, highlighting the geographical barriers and logistical challenges to reaching every affected person.
This map would demonstrate the crucial need for improvements in the aid delivery mechanisms.
Final Summary
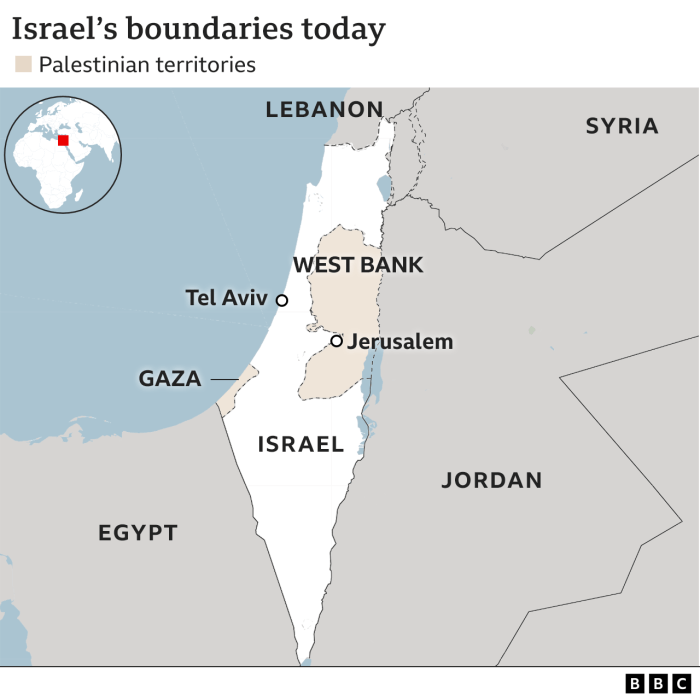
In conclusion, the Israel aid blockage has created a catastrophic humanitarian crisis in Gaza. The UN’s stark assessment underscores the urgency of the situation. This article has examined the multifaceted nature of the crisis, highlighting the historical context, the devastating impact on the population, and the varied international responses. Addressing this crisis requires sustained international support, innovative solutions, and a commitment to ensuring equitable access to aid.
The future of Gaza hinges on a concerted effort to alleviate the blockage and foster a more sustainable and humane approach to aid delivery.