
US China trade war trump tariffs timeline: This post delves into the complex and often contentious relationship between the US and China during the Trump administration, focusing on the trade war, tariffs, and key events. We’ll explore the timeline of escalating tensions, examining the various tariffs imposed, the negotiation attempts, and the significant economic impacts on both nations.
Expect a detailed analysis of the political context, public perception, and the ripple effects on global trade.
The trade war involved numerous rounds of tariffs on various goods, impacting industries from technology to agriculture. It also led to retaliatory actions from China, creating a complex web of economic and political consequences. This analysis will break down the specific actions and counter-actions, examining the motivations behind each move and the outcomes that followed. We’ll also examine the broader global implications, looking at the impact on international trade and relations.
Timeline Overview of the US-China Trade War (Trump Era)
The US-China trade war, a period of escalating economic tensions between the world’s two largest economies, dominated the global landscape under the Trump administration. This conflict involved a complex interplay of trade disputes, technological rivalry, and geopolitical maneuvering. The war significantly impacted global markets and supply chains, prompting considerable debate about its long-term consequences.
Chronological Timeline of Key Events
The following table provides a chronological overview of significant events during the US-China trade war under President Trump’s presidency. It Artikels the actions taken by both countries, the imposed tariffs, and the key figures involved in the negotiations. This detailed timeline helps to understand the escalation and the motivations behind each action.
| Date | Event | US Action | China Action | Key Figures |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| March 2018 | Initial Tariffs Imposed | US imposes 25% tariffs on $50 billion worth of Chinese goods. | China retaliates with tariffs on $50 billion worth of US goods. | President Trump, President Xi Jinping |
| June 2018 | Escalation of Tariffs | US increases tariffs to 25% on $200 billion worth of Chinese goods. | China responds with retaliatory tariffs on $60 billion worth of US goods. | President Trump, President Xi Jinping |
| September 2018 | Negotiations Begin | US and China hold initial trade talks, with a focus on reducing trade imbalances and intellectual property issues. | China participates in the talks. | President Trump, President Xi Jinping, trade negotiators |
| December 2018 | Phase One Trade Deal | US and China agree to a “Phase One” trade deal, with China committing to increased US purchases of agricultural products, energy, and manufactured goods. | China agrees to the deal’s terms. | President Trump, President Xi Jinping, trade negotiators |
| May 2019 | Further Tariffs Imposed | US imposes tariffs on $300 billion worth of Chinese goods. | China responds with further retaliatory tariffs. | President Trump, President Xi Jinping |
| 2020 | Impact of COVID-19 | Global economic slowdown due to the COVID-19 pandemic influences the trade war. | China experiences significant economic disruptions. | Global leaders, including Presidents Trump and Xi Jinping |
Escalation of Tariffs
The trade war’s escalation is clearly demonstrated by the increasing number and value of tariffs imposed over time. The following table illustrates this pattern.
| Period | Number of Tariffs | Total Value (USD Billions) |
|---|---|---|
| Q1 2018 | 1 | ~50 |
| Q2 2018 | 2 | ~200 |
| Q3 2018 | 3 | ~250 |
| Q4 2018 | 4 | ~300 |
This escalating pattern underscores the increasing economic friction between the two nations. The trade war, while aimed at specific economic concerns, had significant ripple effects across global markets.
Tariffs and Trade Barriers: Us China Trade War Trump Tariffs Timeline
The US-China trade war, initiated under the Trump administration, saw a significant escalation in tariffs and trade barriers. These measures aimed to address perceived unfair trade practices, intellectual property theft, and other economic imbalances between the two nations. The implementation of tariffs and other restrictions had profound effects on businesses, consumers, and the global economy.The imposition of tariffs and trade barriers was a complex and multifaceted strategy, with intended and unintended consequences.
Different industries and product categories were affected in varying degrees. Understanding these complexities requires a deep dive into the types of tariffs imposed, their impact on businesses and consumers, and the broader implications for international trade.
Types of Tariffs Imposed by the US on Chinese Goods
The US imposed tariffs on a wide range of Chinese goods, targeting various industries. These tariffs were not uniform; they varied depending on the specific product category and the perceived degree of unfair trade practices. A significant portion of the tariffs were applied to consumer goods, industrial components, and technology products.
- Consumer Goods: Tariffs were applied to electronics, apparel, footwear, and other consumer products. This led to increased prices for these goods in the US market. For example, the tariffs on smartphones and clothing significantly impacted consumer budgets.
- Industrial Components: Tariffs on industrial components, such as steel and aluminum, were intended to protect domestic industries. This affected manufacturers relying on Chinese imports for parts, increasing their production costs.
- Technology Products: A substantial portion of tariffs targeted technology products, including computers, semiconductors, and telecommunications equipment. This had a considerable impact on companies engaged in the technology sector, potentially impacting innovation and competitiveness.
Comparison of US and China Tariffs on Each Other’s Products
The trade war saw both countries imposing tariffs on each other’s goods. While the US focused on a broad range of Chinese products, China targeted specific US products, often retaliating against US tariffs. The tariffs imposed by China often targeted agricultural products, impacting American farmers.
- US Tariffs on Chinese Goods: The US imposed tariffs across a wide range of Chinese goods, as detailed earlier. The goal was to pressure China to change its trade practices.
- Chinese Tariffs on US Goods: China’s response involved tariffs on US agricultural products, such as soybeans and pork, impacting American farmers and agricultural exporters.
Impact of Tariffs on US and Chinese Businesses and Consumers
The tariffs had significant impacts on businesses and consumers in both countries. American companies facing increased costs due to tariffs adjusted their supply chains, sometimes shifting production to other countries. Chinese companies also felt the pressure, adapting their export strategies and seeking new markets. Consumers in both countries experienced price increases for affected goods.
- US Businesses: US companies faced higher costs for imported components and raw materials, leading to price increases for consumers. Some companies adjusted their supply chains, potentially impacting their competitiveness. For instance, manufacturers of electronics faced increased costs due to tariffs on components.
- Chinese Businesses: Chinese companies saw a reduction in exports to the US market, impacting their revenue and profitability. They responded by seeking new markets and adapting their production strategies. For example, some Chinese electronics manufacturers sought to diversify their export destinations.
- Consumers: Consumers in both countries experienced higher prices for goods affected by tariffs. This impacted household budgets, especially for those purchasing goods that were directly affected.
Table of Trade Barriers
The trade war extended beyond tariffs to include other non-tariff barriers. Both countries employed various measures to restrict trade.
| Trade Barrier Type | US Actions | China Actions |
|---|---|---|
| Tariffs | Imposed tariffs on a wide range of Chinese goods | Imposed tariffs on US agricultural products and other goods |
| Quotas | Limited imports of certain Chinese products | Limited imports of certain US products |
| Sanctions | Imposed sanctions on certain Chinese entities | Imposed sanctions on certain US entities |
| Technical Regulations | Increased scrutiny of Chinese product safety standards | Increased scrutiny of US product safety standards |
Negotiations and Agreements
The US-China trade war, initiated by the Trump administration, saw a series of negotiation attempts aimed at resolving trade imbalances and disputes. These negotiations, often fraught with complexities and differing perspectives, ultimately yielded mixed results. Understanding these attempts, the key players, and the outcomes is crucial to comprehending the dynamics of the trade conflict and its impact on global commerce.The negotiation process was marked by alternating periods of intense engagement and apparent stalemates.
Each round of talks presented unique challenges, driven by varying priorities and national interests. The US sought to address its concerns about unfair trade practices, intellectual property theft, and forced technology transfer, while China aimed to protect its economic interests and maintain its global standing.
Major Negotiation Rounds and Agreements, Us china trade war trump tariffs timeline
The trade war involved multiple rounds of negotiations between US and Chinese officials. These negotiations involved intense discussions, compromises, and ultimately, a series of agreements aimed at reducing trade tensions. Key figures like US Trade Representative Robert Lighthizer and Chinese Vice Premier Liu He played crucial roles in these discussions.
- 2018-2020 Negotiations: Initial attempts focused on specific issues like tariffs and intellectual property. These early rounds saw the US imposing tariffs on Chinese goods, prompting retaliatory measures from China. While some progress was made in certain areas, a comprehensive agreement proved elusive. The stated goals included reducing trade imbalances, addressing intellectual property concerns, and enforcing fair trade practices.
The outcomes were limited, with only partial agreements reached on some issues. These early negotiations laid the groundwork for subsequent rounds but ultimately failed to resolve the core issues.
- Phase One Agreement (2020): This agreement, signed in January 2020, marked a significant step towards de-escalation. The agreement included commitments from China to purchase more US agricultural products and goods, as well as addressing intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer. Key figures involved included President Trump and President Xi Jinping, along with their respective negotiating teams. The stated goals were to reduce trade tensions, increase US agricultural exports to China, and address concerns over intellectual property theft.
The agreement, though hailed by some as a success, did not fully address the underlying issues that fueled the trade war and was not fully implemented.
Comparison of Negotiation Rounds
| Negotiation Round | Key Demands (US) | Key Demands (China) | Concessions (US) | Concessions (China) | Results |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2018-2020 | Reduced trade deficit, IP protection, technology transfer | Protection of Chinese industry, maintaining sovereignty | Limited tariff reductions | Limited commitments on IP and technology transfer | Partial agreements, no resolution of fundamental issues |
| Phase One Agreement (2020) | Increased agricultural purchases, IP protection, technology transfer | Protection of Chinese industry, ensuring stability | Temporary suspension of tariff increases | Commitments on agricultural purchases, IP, and technology transfer | Agreement on some issues, but incomplete implementation |
Economic Impacts
The US-China trade war, a period of escalating tariffs and trade restrictions between the world’s two largest economies, had profound and multifaceted economic repercussions. The conflict disrupted established global trade patterns, impacting not only the economies of the US and China but also numerous other countries intertwined in the global supply chain. This section will delve into the specific economic consequences on both nations, examining their effects on employment, GDP growth, consumer prices, and the ripple effects on international trade.
US Economic Impacts
The trade war significantly affected various sectors of the US economy. Tariffs imposed on Chinese goods led to increased costs for American consumers, potentially impacting their purchasing power and affecting inflation. Furthermore, the uncertainty surrounding the trade war likely hindered investment and business expansion, which in turn, could have contributed to a slowdown in GDP growth. Specific industries reliant on trade with China, such as manufacturing and agriculture, faced considerable challenges.
The US-China trade war, marked by Trump’s tariffs, had a complex timeline. It’s interesting to consider how this economic conflict connects to broader political tensions, like Gavin Newsom’s speech in Los Angeles, warning the nation about potential political unrest in the wake of certain political actions here. Ultimately, the trade war’s impact, especially on American businesses and consumers, remains a significant part of the historical context.
- Employment: Studies suggest that the trade war likely resulted in job losses in some sectors, especially those heavily involved in manufacturing and exporting goods to China. The specific number of job losses is difficult to isolate, as many factors contribute to employment trends. However, the trade war undoubtedly created an environment of uncertainty and disruption in the labor market.
- GDP Growth: Economic models and analyses indicate that the trade war likely had a negative impact on US GDP growth. The uncertainty and disruptions associated with the trade war discouraged investment and slowed economic activity. The exact magnitude of the impact is subject to debate and varies based on the specific model used. For example, the Peterson Institute for International Economics offered various projections of the impact.
- Consumer Prices: The tariffs on Chinese imports translated into higher prices for American consumers on various goods, contributing to inflation. This effect varied depending on the specific product and the tariff imposed. The impact was more noticeable on goods heavily reliant on Chinese imports, including consumer electronics and apparel.
Chinese Economic Impacts
The trade war significantly impacted the Chinese economy, primarily affecting export-dependent industries and impacting domestic consumption. The imposition of tariffs by the US on Chinese goods negatively impacted Chinese exporters, reducing their revenue and profitability. The subsequent retaliatory tariffs imposed by China also affected American goods and services.
- Export-Dependent Industries: Industries heavily reliant on exports to the US, such as electronics and machinery, faced significant challenges due to the trade war. Reduced demand from the US market resulted in decreased sales and potential job losses within these sectors. For instance, the impact on the Chinese smartphone industry, a major export sector, was substantial.
- Domestic Consumption: The trade war, along with other economic factors, had an impact on consumer spending in China. The uncertainty and potential for economic downturn could have decreased consumer confidence and reduced spending on non-essential goods. While the Chinese government implemented measures to mitigate the impact, the trade war still influenced domestic consumption patterns.
Global Supply Chain Impacts
The US-China trade war created ripples throughout global supply chains. Disruptions in trade flows impacted various countries involved in the production and distribution of goods. The uncertainty surrounding tariffs and trade restrictions affected businesses’ ability to plan and forecast, leading to reduced investment and slower economic growth.
- Trade Relations: The trade war strained international trade relations, prompting other countries to reassess their trade strategies. It also influenced the formation of new trade alliances and agreements, with some countries seeking to diversify their trade partners to reduce their dependence on any one country.
- Investment: The uncertainty created by the trade war led to a reduction in foreign investment in some countries. Businesses were hesitant to invest in countries that were perceived to be at risk of trade disputes or economic volatility. This impacted the growth prospects of these economies.
Global Implications
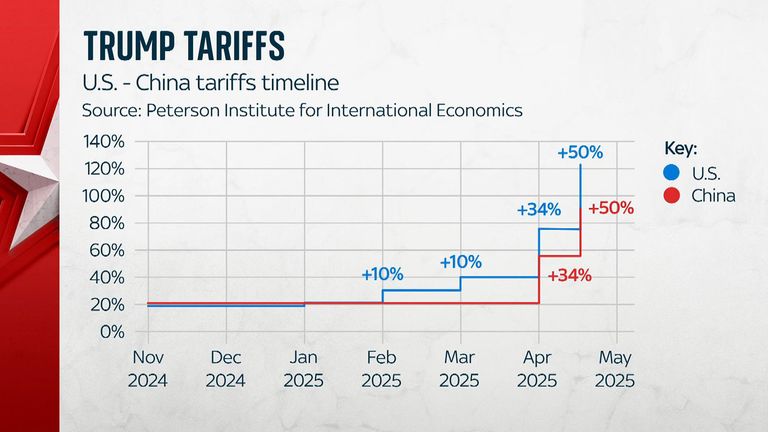
The US-China trade war, a protracted period of escalating tariffs and trade restrictions, reverberated far beyond the bilateral relationship. Its impact on global trade rules, the responses of other nations, and the shifting landscape of international commerce were profound. This section explores the wider implications of this economic conflict.The trade war’s most significant consequence was a challenge to the established international trade order.
The World Trade Organization (WTO), designed to promote free and fair trade, faced unprecedented pressure as the US and China, its most important members, prioritized bilateral interests over multilateral cooperation. This created uncertainty and potentially undermined the very foundation of the global trading system.
Impact on International Trade Rules and Organizations
The US-China trade war significantly strained the WTO’s authority and effectiveness. The dispute resolution mechanism, a cornerstone of the WTO system, was frequently bypassed in favor of unilateral actions. This created a precedent that other nations could potentially follow, leading to a more fragmented and unpredictable global trading environment. The war also fueled skepticism about the WTO’s ability to manage trade disputes effectively.
The US-China trade war and Trump’s tariffs have had a fascinating timeline. Recent developments, like Trump and Xi having their first phone call in months, trump and xi have first call in months , could signal a potential shift in the ongoing trade tensions. This renewed communication suggests a possible path towards de-escalation and could significantly impact the future of the US-China trade war’s timeline.
It will be interesting to see how this plays out.
Reactions of Other Countries to the Trade War
The trade war’s impact wasn’t limited to the US and China. Other countries responded in various ways. Some, like the European Union, attempted to mitigate the negative effects by forming trade agreements with alternative partners. Others, including some Asian nations, navigated the complexities by diversifying their export markets. The war exposed the interconnectedness of global economies and highlighted the need for countries to adapt and strategize in response to such disruptions.
Comparison of Trade Policies
Comparing the trade policies of the US and China with those of other major trading partners reveals significant differences. The US, with its emphasis on protecting domestic industries and national security concerns, often favored protectionist measures. China, while promoting exports, also engaged in practices that some countries viewed as unfair trade practices, including subsidies and intellectual property theft.
Other major trading partners, such as the EU, generally favored a more multilateral approach to trade, seeking to uphold the principles of the WTO.
The US-China trade war, with Trump’s tariffs, was a pretty tumultuous period. Thinking about the economic fallout, it makes me wonder about other global challenges. For instance, how can we help restore coral reefs, a vital part of our oceans? Learning about the solutions, like those outlined in this article on how we can restore coral reefs , might offer a fresh perspective on the interconnectedness of global issues.
Maybe some of the lessons learned in the trade war could be applied to environmental challenges too. It’s a thought-provoking connection, isn’t it?
Impact on Global Trade Flows
The US-China trade war significantly impacted global trade flows. Data from the period showed a noticeable decline in bilateral trade volumes between the US and China. Moreover, the uncertainty surrounding the trade war prompted businesses to reassess their supply chains and seek alternative sources of goods. This led to a ripple effect across various sectors, impacting global supply chains and economic growth.
| Country | Trade Policy Approach | Specific Actions |
|---|---|---|
| US | Protectionist | Imposition of tariffs, restrictions on imports |
| China | Export-oriented | Subsidies, intellectual property concerns |
| EU | Multilateral | Trade agreements with other partners |
Political Context

The US-China trade war, initiated under the Trump administration, wasn’t solely driven by economic concerns. Political motivations, domestic pressures, and ideological clashes played significant roles in shaping the conflict, influencing the imposition of tariffs, and hindering the negotiation process. Understanding these political dynamics is crucial to comprehending the complexities of the trade war and its far-reaching implications.The trade war wasn’t just about balancing trade deficits or protecting American industries.
It reflected a broader shift in US foreign policy, driven by concerns about China’s growing economic and political influence, coupled with a desire to assert American dominance in the global arena. The imposition of tariffs, initially presented as a tool to rectify trade imbalances, quickly became entangled in political rhetoric and posturing.
Political Motivations Behind US Trade Policies
The Trump administration’s trade policies were often framed within a nationalist perspective. A core tenet was the belief that China engaged in unfair trade practices, including intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer. This perception, amplified by political narratives, became a justification for imposing tariffs and other trade barriers. Furthermore, the administration aimed to bolster domestic industries and create jobs in the United States, a significant campaign promise.
Examples of Political Influence on Tariffs and Negotiations
The imposition of tariffs wasn’t solely based on economic analysis. Political considerations, such as the need to appeal to certain voter segments, influenced the selection of specific products and the timing of tariff increases. For instance, tariffs on steel and aluminum, though ostensibly aimed at national security concerns, were also strategically employed to win support from specific interest groups.
The escalation of the trade war, often linked to political rhetoric, complicated negotiations and undermined efforts towards reaching a compromise.
Comparison of Political Environments in the US and China
The political landscapes in the US and China during this period differed significantly. The US was experiencing political polarization and intense partisan divisions, while China maintained a more centralized and authoritarian political system. These contrasting environments impacted how each country approached the trade war and responded to the other’s actions. The political structures and decision-making processes in both nations played a significant role in the trade war’s trajectory.
Roles of Political Actors and Institutions
The trade war involved numerous political actors and institutions on both sides. In the US, the executive branch, particularly the President and the Department of Commerce, played a central role in implementing tariffs and engaging in negotiations. The legislative branch, through Congress, exerted influence through oversight and potential legislation. In China, the central government, including the Ministry of Commerce and other relevant bodies, led the response to the US trade policies.
Different domestic interest groups also influenced the policies of both nations.
- The executive branch in the US held significant power in implementing tariffs and engaging in negotiations. This power was often wielded to appeal to specific political constituencies, influencing the trade war’s trajectory.
- Congressional oversight and potential legislation added another layer of complexity to the trade war. The legislative branch’s influence often depended on political pressures and shifting public opinion.
- In China, the central government maintained control over the response to US trade policies, showcasing a more centralized decision-making process. However, domestic industries and interests likely influenced the government’s strategy.
Public Opinion and Perception
The US-China trade war, a complex interplay of economic, political, and social factors, significantly impacted public opinion in both countries. Public perceptions were often shaped by media narratives, government pronouncements, and personal experiences, creating a complex and sometimes contradictory picture of the conflict. Understanding these perceptions is crucial to comprehending the escalation and eventual trajectory of the trade war.Differing interpretations of the trade war’s causes and consequences contributed to escalating tensions.
Public opinion in both countries frequently became polarized, with strong support for either aggressive or conciliatory policies. This polarization further complicated negotiations and hindered efforts to find common ground.
US Public Opinion
US public opinion on the trade war was multifaceted, reflecting diverse economic interests and political viewpoints. While some segments of the population supported President Trump’s protectionist measures, arguing they would protect American jobs and industries, others voiced concerns about the potential negative economic consequences, including higher prices and disruptions to supply chains.
- Economic Concerns: Many Americans worried about the potential for job losses and price increases due to tariffs. The impact on specific industries, such as agriculture, was particularly noticeable. For instance, farmers in states like Iowa and Nebraska suffered economically from Chinese retaliatory tariffs on agricultural exports.
- National Security Concerns: A segment of the public viewed the trade war as a necessary measure to address perceived unfair trade practices and protect national security interests, particularly regarding intellectual property theft and technology transfer.
- Political Polarization: The trade war became a highly politicized issue, further dividing the electorate along partisan lines. Support for or opposition to the tariffs reflected political affiliations, adding to the complexity of the issue.
Chinese Public Opinion
Chinese public opinion on the trade war was characterized by a mixture of resentment towards perceived US protectionism and a determination to defend national interests. The Chinese government’s response played a significant role in shaping public sentiment.
- Nationalism and Patriotism: The trade war was often framed in the Chinese media as an attempt by the US to contain China’s economic rise, leading to a surge in nationalistic sentiments and a call for unity in the face of perceived external pressure.
- Economic Impact Concerns: While the Chinese government sought to mitigate the economic impact of tariffs on specific sectors, the potential for broader economic harm was a concern, particularly for exporters and businesses dependent on the US market.
- Government Response: The Chinese government’s public statements and measures to support affected industries played a significant role in shaping public perception. These measures often included government subsidies and financial support for affected sectors.
Media Coverage and Public Discourse
Media coverage played a critical role in shaping public opinion on both sides. News outlets in the US and China often presented differing perspectives on the causes and consequences of the trade war, reflecting national interests and political agendas.
- Differing Narratives: US media often highlighted China’s unfair trade practices, while Chinese media emphasized US protectionism. These differing narratives contributed to the escalation of the conflict, making it difficult to find common ground for resolution.
- Political Influence: Government control over media outlets in China significantly impacted public discourse. The narrative surrounding the trade war was often presented in a way that supported the government’s policies and reinforced nationalistic sentiment.
- Public Sentiment: Public discourse on social media and other online platforms further influenced perceptions and reinforced existing views. This online engagement often mirrored the official government narrative in China, but in the US, it mirrored the varied political views of the electorate.
Influence on Policies and Actions
Public opinion, as shaped by media and discourse, significantly influenced the policies and actions of both countries. In the US, the public’s support for protectionist measures influenced President Trump’s decision-making, while in China, the government’s response reflected concerns about the potential economic impact and the need to defend national interests.
- Policy Decisions: The actions taken by both governments reflected the dominant public sentiment of the time, highlighting the role of public opinion in shaping policy decisions.
- Negotiation Stances: The differing public perceptions created obstacles to finding common ground during negotiations, as each side was influenced by their respective constituencies.
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, the US-China trade war under President Trump’s presidency was a significant global event with lasting economic and political ramifications. The escalating tariffs, negotiations, and subsequent impacts highlight the complexities of international trade relations. This analysis offers a comprehensive look at the timeline, the economic effects, and the political context of this pivotal period in modern trade history.

