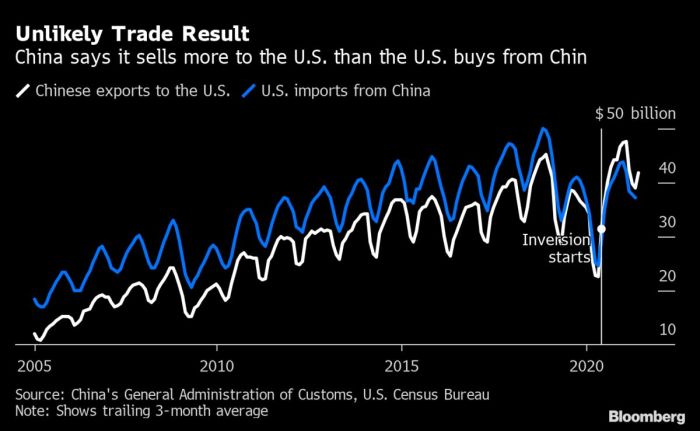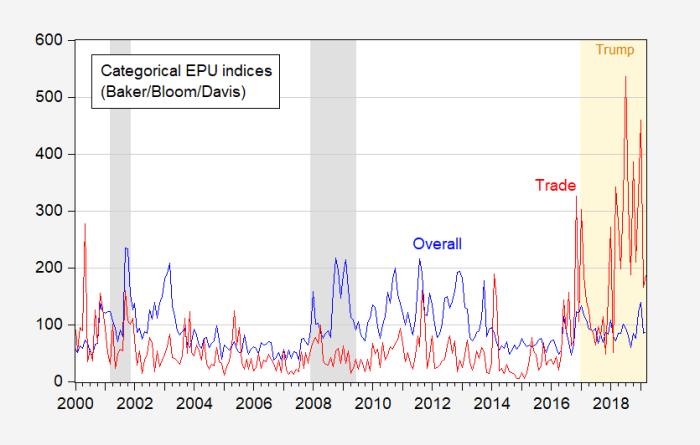
Economic uncertainty tariffs recession – Economic uncertainty, tariffs, and recession are intertwined forces shaping global economies. This exploration delves into the multifaceted impacts of tariffs on domestic industries, examining their ripple effects on supply chains and consumer prices. We’ll also analyze recessionary pressures, highlighting key indicators and the role of economic uncertainty in triggering or exacerbating downturns. The interplay between tariffs and recessionary trends, along with their global implications, will be thoroughly investigated.
Policy responses to economic uncertainty and illustrative scenarios will provide a comprehensive view of this complex issue.
The impact of tariffs extends far beyond individual industries, affecting global trade and investment flows. We’ll examine the potential for retaliatory tariffs and analyze the economic performance of countries with varying tariff policies. This analysis considers short-term and long-term consequences, providing insights into how tariffs can exacerbate existing vulnerabilities and contribute to economic uncertainty during a recession. Understanding the cascading effects of these factors is crucial for developing effective policy responses.
Economic Impacts of Tariffs
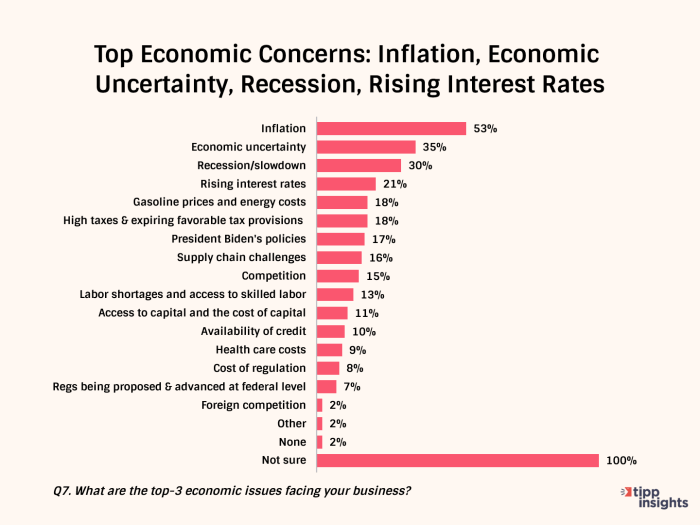
Tariffs, taxes imposed on imported goods, can have significant and multifaceted effects on a nation’s economy. While proponents argue for protectionist benefits, tariffs often lead to unintended consequences that can impact various sectors and consumers. Understanding these complexities is crucial for evaluating the overall economic impact of these policies.
Tariff Impact on Domestic Industries
Tariffs directly affect domestic industries by altering the cost of imported inputs and finished goods. Higher tariffs increase the price of imported materials, components, or finished products, which can raise production costs for domestic companies that rely on these imports. This can lead to reduced competitiveness in the global market, as domestic prices rise, making exports less attractive to foreign buyers.
Industries heavily reliant on imported components or raw materials are most vulnerable.
Examples of Industries Negatively Impacted by Tariffs
The automotive industry is a prime example of an industry vulnerable to tariff-related price increases. Tariffs on imported steel, aluminum, and other components raise production costs for car manufacturers, potentially leading to higher prices for consumers. Similarly, the electronics industry, which relies heavily on imported semiconductors and other specialized components, can face similar challenges. The textile industry, depending on imported fibers and fabrics, experiences a similar impact, leading to reduced competitiveness and potentially lower employment in these sectors.
Ripple Effects on Supply Chains and Consumer Prices
Tariffs can trigger a ripple effect throughout the supply chain. Higher costs for imported inputs can lead to higher prices for intermediate goods, impacting manufacturers and distributors. Ultimately, these increased costs are often passed on to consumers through higher prices for final goods. This phenomenon is especially evident in industries with complex supply chains, where the impact of tariffs can be amplified throughout the system.
For example, a tariff on a crucial component for manufacturing a product can increase the cost of that product for the consumer.
Short-Term and Long-Term Economic Consequences of Tariffs
The short-term consequences of tariffs can include a reduction in imports, potentially leading to a temporary decrease in consumer choice and variety of goods available. In the long run, tariffs can result in reduced economic growth and innovation. Industries that become less competitive due to increased costs may struggle to adapt and innovate, ultimately hindering their long-term growth and competitiveness.
Economic uncertainty, tariffs, and recession fears are definitely weighing heavy on global markets right now. The ongoing debate about Israeli expansion and settlements in the West Bank, as detailed in this article on Israel expansion settlements west bank , further complicates the picture. These factors all seem to be intertwined, creating a volatile situation that could trigger a significant downturn in the global economy.
Table: Industry Impacts of Tariffs
| Industry | Tariff Impact | Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Automotive | Increased costs of imported steel, aluminum, and components | Higher car prices, reduced competitiveness, potential job losses |
| Electronics | Increased costs of imported semiconductors and components | Higher prices for electronics, reduced competitiveness, potential job losses |
| Textiles | Increased costs of imported fibers and fabrics | Higher prices for clothing and textiles, reduced competitiveness, potential job losses |
| Pharmaceuticals | Increased costs of imported active pharmaceutical ingredients (APIs) | Higher drug prices, potential impact on accessibility |
Recessionary Pressures and Economic Uncertainty: Economic Uncertainty Tariffs Recession
Economic downturns, often characterized by recessionary pressures, are a persistent feature of modern economies. Understanding the indicators that signal an impending recession, the role of economic uncertainty, and its impact on investment, consumer confidence, and spending are crucial for mitigating potential negative consequences. A comprehensive grasp of these factors allows for proactive measures to navigate turbulent economic periods.
Key Indicators of an Impending Recession
Several economic indicators often precede a recession. These signals provide valuable insights into the potential for a downturn. Monitoring these indicators helps anticipate and prepare for possible economic contractions.
- Decreasing consumer confidence:
- High unemployment rates:
- Decreasing industrial production:
- Falling housing prices:
Consumer confidence, a crucial driver of economic activity, often declines before a recession. Reduced confidence leads to decreased spending, impacting businesses and overall economic growth. For example, a significant drop in consumer confidence during the 2008 financial crisis foreshadowed the subsequent recession.
A persistent increase in unemployment rates is a strong signal of a potential recession. As job losses mount, consumer spending typically decreases, which further impacts economic activity. Historical data demonstrates that high unemployment rates are consistently associated with periods of economic contraction.
Reduced manufacturing output and industrial production frequently precedes a recession. This decline often indicates a weakening of the overall economy and can be a precursor to widespread job losses. Manufacturing activity is a significant component of many economies, and its decline often mirrors the overall economic health.
Declining housing prices often signal a weakening economy. This is especially true when coupled with rising mortgage delinquencies. The 2008 housing market crash serves as a stark example of how a downturn in the housing sector can trigger a broader economic recession.
The Role of Economic Uncertainty
Economic uncertainty plays a critical role in triggering or exacerbating a recession. When investors and consumers are unsure about the future economic outlook, they tend to be more cautious. This hesitancy can lead to decreased investment and spending, which in turn can create a downward spiral in economic activity.
Impact on Investment Decisions
Uncertainty about the future often leads to a decline in investment. Companies may postpone or cancel expansion plans, reducing capital expenditure. Investors, anticipating potential losses, may reduce their portfolio allocation to riskier assets. This hesitation, in turn, reduces job creation and further hampers economic growth. For instance, during periods of high political uncertainty, companies may be hesitant to invest in new projects.
Impact on Consumer Confidence and Spending
Economic uncertainty directly affects consumer confidence. When consumers are uncertain about the future, they are less likely to spend. This reduced spending directly impacts businesses, leading to reduced profits and potentially impacting employment. Examples of periods of heightened economic uncertainty include the 2008 financial crisis, the COVID-19 pandemic, and the 2022 energy crisis. These events demonstrated how economic uncertainty can significantly impact consumer spending and confidence.
Contrasting Recessionary Scenarios
| Scenario | Sector | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| Moderate Recession | Retail | Reduced sales and lower profits. |
| Manufacturing | Decreased production and layoffs. | |
| Technology | Reduced investment in new products and slower innovation. | |
| Severe Recession | Housing | Significant drop in housing prices and increased foreclosures. |
| Financial Services | Reduced lending and increased defaults. | |
| Energy | Reduced demand and lower prices. |
Global Economic Implications
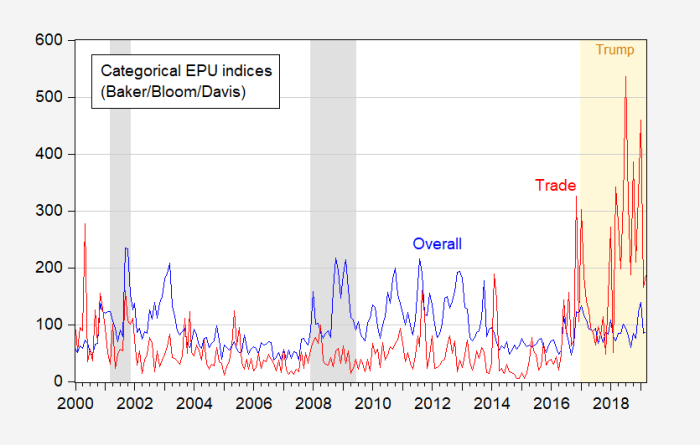
The imposition of tariffs by major economies has profound ripple effects throughout the global economic landscape. These actions, intended to protect domestic industries, often trigger retaliatory measures and disrupt established trade patterns, leading to unforeseen consequences for participating nations and the international community. The global interconnectedness of economies means that a disturbance in one area can quickly spread, impacting supply chains, investment decisions, and overall economic stability.The intricate web of international trade and investment is susceptible to disruption when tariffs are introduced.
The imposition of tariffs by one nation can prompt retaliatory measures from others, creating a cycle of escalating trade restrictions. This can result in higher prices for consumers, reduced availability of goods and services, and a contraction in international trade volumes. Understanding the global ramifications of tariffs is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike to navigate the complexities of the modern global economy.
Economic uncertainty, tariffs, and the looming recession are definitely weighing on my mind lately. It’s easy to get caught up in the anxieties of a potentially shaky economy, but sometimes, a good laugh can help put things in perspective. Have you checked out this fascinating essay on embracing cringe dating experiences? embrace cringe dating essay might offer a fresh take on navigating the complexities of modern dating, which in a way, mirrors the complexities of the current economic climate.
Perhaps a bit of self-deprecating humor is just what we all need in these turbulent economic times.
Global Ramifications of Tariffs
Tariffs, implemented by major economies, often provoke retaliatory measures from trading partners. This reciprocal imposition of tariffs can create a trade war, characterized by escalating restrictions on imports and exports. The consequences extend beyond the direct participants, impacting global supply chains and potentially triggering a domino effect on other economies. This can be seen in reduced trade volumes, impacting global economic growth.
Potential for Retaliatory Tariffs and Their Consequences
Retaliatory tariffs are a common response to trade restrictions. When one country imposes tariffs on another’s goods, the targeted country may respond in kind, often with tariffs of similar magnitude. This escalation can result in a trade war, where the initial dispute expands to encompass multiple countries, creating uncertainty in the global market. The economic consequences of such a scenario can include a decline in global trade, increased prices for consumers, and potential job losses in import-export sectors.
Examples of historical trade disputes and their outcomes illustrate the complex and often unpredictable nature of these events.
Impact of Tariffs on International Trade and Investment Flows
Tariffs directly impact international trade flows by increasing the cost of imported goods. Higher prices can reduce demand for imported products, leading to a decrease in trade volumes. Moreover, tariffs can deter foreign investment as businesses face higher costs and increased uncertainty in operating across borders. This can manifest in reduced foreign direct investment (FDI) as companies reconsider their investment strategies in light of increased trade barriers.
Examples of International Trade Disputes Involving Tariffs and Their Outcomes
Numerous international trade disputes have involved tariffs, each with unique circumstances and outcomes. The 2018 trade war between the United States and China, for example, saw both countries imposing tariffs on each other’s goods. The result was a significant disruption to global supply chains, increased prices for consumers, and uncertainty in the global economy. Other instances, such as the European Union’s disputes with other trading partners, showcase the complex and often protracted nature of international trade disagreements.
Comparison of Economic Performance of Countries with and without Significant Tariff Policies
| Country | Tariff Policy | Economic Performance |
|---|---|---|
| United States (pre-2018) | Relatively low tariffs | Strong economic growth |
| China (pre-2018) | Relatively low tariffs | Rapid economic growth |
| United States (2018-present) | Increased tariffs | Mixed economic performance (some sectors benefited, others suffered) |
| China (2018-present) | Increased tariffs | Slower economic growth, particularly in export-oriented sectors |
| European Union (pre-2018) | Moderate tariffs | Steady economic growth |
Note: This table provides a simplified overview. Economic performance is influenced by numerous factors beyond tariffs, including macroeconomic conditions, domestic policies, and global events.
Policy Responses to Economic Uncertainty
Navigating economic uncertainty requires a multifaceted approach. Governments employ various tools, from fiscal and monetary policies to regulatory adjustments, to try and stabilize the economy and mitigate the negative impacts of downturns. This section examines the different strategies implemented and their effectiveness in the face of economic challenges.Economic downturns, whether triggered by tariffs, recessions, or global events, often necessitate swift and decisive policy responses.
Governments have a crucial role in cushioning the blow to individuals and businesses, preventing a deeper spiral into economic hardship. The effectiveness of these policies, however, is often debated and depends on various factors, including the specific nature of the crisis and the timely implementation of the measures.
Government Policies to Mitigate Economic Uncertainty
Governments employ a range of policies to counteract economic uncertainty. These include adjustments to fiscal policy, such as changes in government spending and taxation, and adjustments to monetary policy, including interest rate adjustments and quantitative easing. Additionally, regulatory changes can play a role in shaping market behavior and investor confidence.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustments: Changes in government spending and taxation can influence aggregate demand. Increased government spending on infrastructure projects or social programs can stimulate economic activity during a downturn. Tax cuts can increase disposable income for households, encouraging spending. However, the effectiveness of fiscal policy depends on the specific economic conditions and the government’s ability to execute these policies efficiently.
For example, the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, aimed at stimulating the economy during the Great Recession, sparked debate about its overall impact.
- Monetary Policy Interventions: Central banks use interest rates and quantitative easing to manage money supply and credit conditions. Lowering interest rates makes borrowing cheaper, encouraging investment and consumption. Quantitative easing involves injecting liquidity into the market by purchasing government securities, which can lower long-term interest rates and increase the money supply. The effectiveness of these policies can be influenced by the responsiveness of the economy to these interventions and the overall confidence in the economy.
Economic uncertainty, tariffs, and recession worries are definitely a heavy lift, but it’s important to remember that young Africans are tackling significant health challenges head-on. A compelling essay, “young africans protect health essay ndidi okonkwo nwuneli charlize theron” young africans protect health essay ndidi okonkwo nwuneli charlize theron , highlights the vital role individuals play in their communities.
These issues, while seemingly unrelated, both point to the importance of resilient communities and the need for proactive strategies, regardless of the economic climate.
- Regulatory Adjustments: Regulations can play a crucial role in maintaining market stability and confidence. For example, stricter regulations on financial institutions can prevent excessive risk-taking that could lead to a financial crisis. However, regulations can sometimes stifle economic growth if not carefully designed and implemented.
Effectiveness of Fiscal and Monetary Policies
The effectiveness of fiscal and monetary policies in countering recessionary pressures is a complex issue. While these policies can stimulate demand and potentially prevent a deeper recession, their impact can vary depending on the circumstances. Factors such as the depth of the recession, the credibility of the government, and the overall state of the global economy influence the outcome.
- Fiscal policy effectiveness often hinges on the government’s ability to spend efficiently and quickly. Uncoordinated or poorly targeted spending can lead to inefficiencies and reduced impact. Conversely, timely and targeted spending on critical infrastructure can provide a significant boost to the economy.
- Monetary policy’s impact can be hampered by factors such as low inflation or weak economic growth. If the economy is not responding to monetary stimulus, the central bank’s efforts might not yield the desired results. The effectiveness of interest rate cuts, for example, depends on the responsiveness of businesses and consumers to the lower borrowing costs.
Examples of Successful and Unsuccessful Policy Responses
Various historical examples demonstrate the diverse outcomes of policy responses to economic uncertainty. Some policies have proved effective in mitigating the severity of recessions, while others have had limited impact or even exacerbated the situation. The effectiveness of these policies is dependent on the specifics of the economic crisis and the political environment.
Challenges in Implementing Effective Policies, Economic uncertainty tariffs recession
Implementing effective policies in times of economic uncertainty presents various challenges. Coordination between different government agencies, securing public support for policies, and dealing with unforeseen circumstances can create obstacles. Political gridlock, differing perspectives on economic management, and the time lag between policy implementation and observed effects are further challenges.
Different viewpoints on policies to mitigate economic uncertainty
“Some economists advocate for aggressive fiscal stimulus, while others emphasize the importance of maintaining fiscal discipline. Similarly, there are differing opinions on the efficacy of various monetary policy tools, and whether interest rate cuts alone are sufficient to stimulate economic growth.”
Illustrative Scenarios of Economic Uncertainty
Navigating economic uncertainty is a constant challenge for policymakers and businesses alike. Understanding how different factors, such as tariffs and recessions, interact to create complex scenarios is crucial for developing effective strategies. These scenarios, while not guarantees, can illuminate potential paths and highlight vulnerabilities.
Tariffs Triggering a Recession
A significant increase in tariffs on imported goods can trigger a recession by increasing production costs for domestic companies. Higher input costs lead to reduced profitability and decreased investment. Consumers, facing higher prices for essential goods, cut back on spending, leading to a decrease in demand and a contraction in economic activity. This scenario can be further exacerbated by retaliatory tariffs imposed by other countries, creating a domino effect throughout the global economy.
For example, the 2018-2019 trade war between the United States and China demonstrated the potential for significant economic fallout.
Economic Uncertainty Leading to Reduced Investment
When economic uncertainty prevails, businesses tend to postpone major investments. The unpredictability of future economic conditions makes it difficult to assess the long-term viability of projects. This hesitancy leads to a decrease in capital expenditure, impacting job creation and economic growth. Businesses may also opt to hold onto existing cash reserves, further reducing investment in new ventures.
For example, the 2008 financial crisis saw a sharp decline in investment as businesses sought to preserve liquidity.
Negative Impact on Consumer Confidence
Economic uncertainty and tariffs can severely dampen consumer confidence. Uncertainty about future job security, rising prices, and potential economic downturns can lead consumers to curtail spending. Reduced consumer confidence translates into decreased demand, impacting businesses across various sectors. For example, during periods of high political uncertainty, consumers often postpone large purchases, impacting the overall economy.
Impact of Tariffs and Uncertainty on Employment
Tariffs and economic uncertainty can lead to job losses across various sectors. Higher production costs due to tariffs can make domestic companies less competitive, potentially leading to reduced output and layoffs. The uncertainty itself can discourage investment, hindering job creation and economic expansion. A significant example is the impact of the global financial crisis on employment across the globe.
Visual Representation of the Scenarios
Imagine a graph depicting the decline in consumer confidence due to rising tariffs and economic uncertainty. The x-axis would represent time, and the y-axis would represent consumer confidence levels. The graph would show a clear downward trend as tariffs increase and economic uncertainty escalates. Another visual representation could be a flowchart illustrating the cascading effect of tariffs, reduced investment, decreased consumer spending, and ultimately, a recession.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, economic uncertainty, tariffs, and recession are deeply interconnected phenomena with significant global ramifications. This analysis has highlighted the complex interplay of these factors, from the direct impact of tariffs on industries to the broader effects on consumer confidence and investment decisions. The discussion has also explored various policy responses and illustrative scenarios to better understand the challenges and complexities involved.
Navigating these turbulent economic waters requires a nuanced understanding of the interconnectedness of global economies and the potential consequences of various policy choices.