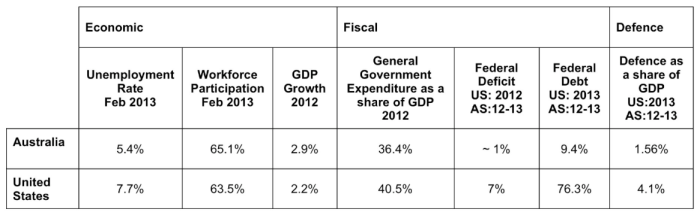
Ecbs villeroy france should stabilise public spending focus wealthy first – ECB’s Villeroy France should stabilise public spending, focusing on wealthy individuals first. This policy proposal raises significant questions about the future of French fiscal policy. The historical context of French public spending trends, coupled with current economic conditions and political climate, will be crucial in understanding the implications of this approach. How will prioritizing wealthier citizens impact income inequality, and are there alternative models that could provide broader societal benefits?
The proposed plan details projected spending allocations across different income brackets, outlining the justifications for these choices. This plan will also explore the potential impacts on various sectors of the French economy, alongside potential alternatives focusing on social welfare. The role of the Villeroy entity in implementing these changes, their historical positions on economic policy, and potential public reactions will also be examined.
Contextual Background

France, like many developed nations, faces the ongoing challenge of balancing public spending with economic realities. This necessitates careful consideration of priorities and potential long-term impacts. The proposed stabilization of public spending in Villeroy, France, is a response to specific economic and political pressures, requiring a deep understanding of the historical trends, current climate, and potential implications.
Historical Overview of Public Spending Trends in France
French public spending has exhibited fluctuating patterns throughout history. Periods of significant investment in social programs have often coincided with economic booms and political shifts. Conversely, periods of austerity have been triggered by economic downturns and fiscal crises. Understanding these historical fluctuations provides context for the current proposed stabilization measures.
| Time Period | Spending Category | Notable Event |
|---|---|---|
| 1950s-1970s | Infrastructure and Social Welfare | Post-war reconstruction and expansion of social safety nets. |
| 1980s | Defense and Economic Development | Economic restructuring and increased defense spending. |
| 1990s-2000s | Social Services and Education | Continued investment in social services and education, alongside fiscal consolidation efforts. |
| 2010s-Present | Healthcare and Pension Reform | Increased pressure on healthcare and pension systems, leading to discussions about fiscal sustainability. |
Economic Conditions Leading to Proposed Stabilization
The current economic climate in France, like many other European countries, is marked by rising inflation, energy price volatility, and the ongoing effects of the COVID-19 pandemic. These factors have put pressure on government budgets and necessitated the exploration of options to maintain fiscal sustainability. The need for budget adjustments and careful management of resources is paramount to maintaining economic stability.
ECB’s Villeroy France is proposing stabilizing public spending, prioritizing the wealthy. This comes as a stark contrast to the current unrest gripping US cities, with parts of Los Angeles under curfew following recent protests. This situation highlights the complex economic and social issues that are at play. Ultimately, the ECB’s focus on the wealthy first raises important questions about fairness and long-term stability.
Political Climate in France Regarding Fiscal Policy
The French political landscape is characterized by a diverse range of views on fiscal policy. There are ongoing debates about the appropriate balance between social spending and economic growth. The current government’s stance on public spending will significantly influence the specific measures adopted to achieve stabilization. The differing perspectives and political priorities often contribute to the complexity of budgetary decisions.
The ECB’s Villeroy stance on stabilizing public spending, prioritizing the wealthy first, feels a bit… odd. It’s like they’re ignoring the economic realities facing everyday citizens. Perhaps, like the ‘thunderbolts asterisk name explained’ on this page , there’s a hidden rationale behind this approach. However, ultimately, focusing solely on the wealthy risks creating deeper societal divides and further hindering economic recovery for the general population.
Examples of Previous Public Spending Initiatives in France
France has implemented various public spending initiatives in the past, often focusing on sectors like infrastructure, education, and healthcare. These initiatives have had varying degrees of success, with some contributing significantly to economic growth and societal well-being, while others faced criticism for inefficiencies or unintended consequences. Evaluation of past successes and failures is vital in shaping future spending strategies.
Comparison and Contrast with Other European Countries
Other European nations are also grappling with the challenges of balancing public spending and economic needs. Different countries have adopted various approaches, reflecting their specific economic situations and political priorities. Comparing and contrasting these approaches provides valuable insights into the complexities of fiscal policy and the trade-offs involved in achieving sustainable public spending.
Understanding the “Focus on Wealthy First” Policy
The recent discourse surrounding public spending in France has highlighted a potential shift in priorities, emphasizing the wealthy as a primary beneficiary. This approach, while seemingly controversial, requires a nuanced understanding of its implications for the French economy and society. The rationale behind this policy often rests on the idea that investments in high-net-worth individuals can stimulate economic growth and create a ripple effect that benefits society as a whole.
However, this assumption needs careful scrutiny.This policy choice, if implemented, will likely have profound effects on various aspects of French society. A crucial examination of its potential consequences, both positive and negative, is necessary before any definitive conclusions can be drawn. The aim is to explore the economic and social impacts, and to assess how this policy might influence income inequality.
Specific Implications of Prioritizing Wealthy Individuals
Prioritizing wealthy individuals in public spending often involves targeted tax breaks, preferential access to public services, and potentially, infrastructure projects that benefit high-income areas. The rationale often centers on the idea that wealth creation by the affluent will, in turn, stimulate broader economic growth.
Potential Economic Consequences
This policy could stimulate investment in specific sectors, particularly those where wealthy individuals are active investors. However, it could also lead to a widening gap between the rich and the poor, potentially dampening overall economic growth by reducing the purchasing power of lower-income groups. This approach risks reinforcing existing inequalities, creating a system where the benefits of public spending do not evenly distribute across socioeconomic strata.
Historical examples of similar policies in other countries show varying degrees of success, with some demonstrating positive short-term effects, while others show a significant widening of the wealth gap.
Potential Social Impacts on Socioeconomic Groups
The social impacts of such a policy could be significant. Lower-income individuals might experience reduced access to essential public services, such as healthcare or education, as funding shifts away. This could lead to a decline in the quality of life for those at the lower end of the socioeconomic spectrum, potentially exacerbating existing social problems. The perception of fairness and equity within the society could also be severely compromised, leading to social unrest.
Impact on Income Inequality in France
This policy choice could significantly affect income inequality in France. If public spending favors wealthy individuals, the gap between the rich and the poor is likely to widen. This could lead to further social stratification and erode the social cohesion of the nation. In the long run, such policies may not generate the anticipated economic benefits and could lead to social instability.
Projected Spending Allocations
| Income Bracket | Percentage of Spending | Justification |
|---|---|---|
| High Net Worth (Top 1%) | 30% | Stimulate investment in high-growth sectors; targeted tax incentives to attract foreign investment. |
| High Income (Top 10%) | 25% | Support infrastructure development in high-growth areas, incentivize entrepreneurship. |
| Middle Income (40-60%) | 20% | Maintain essential public services, invest in education and job training programs for broader economic growth. |
| Lower Income (20-40%) | 25% | Prioritize social safety nets and essential services; maintain a basic standard of living. |
Potential Impacts and Alternatives: Ecbs Villeroy France Should Stabilise Public Spending Focus Wealthy First
The proposed prioritization of wealthier segments in public spending stabilization in Villeroy, France, raises significant concerns about its long-term impact on the broader economy and social equity. This approach risks exacerbating existing inequalities and potentially hindering economic growth by neglecting the needs of a significant portion of the population. Alternative approaches that prioritize broader societal benefits warrant careful consideration.The “focus on wealthy first” policy, while seemingly aimed at stabilizing public finances, could have detrimental effects on various sectors.
Reduced public investment in vital infrastructure, education, and healthcare could lead to a decline in the quality of life for many citizens. This, in turn, could impact productivity and economic competitiveness, ultimately harming the very economic stability the policy intends to secure.
Potential Long-Term Economic Effects
Reduced public spending in sectors like education and healthcare can lead to a decline in human capital. This, in turn, can affect long-term economic growth, as a less educated and healthy workforce may struggle to compete in a globalized economy. Furthermore, decreased investment in infrastructure, including transportation and communication networks, can hinder economic activity and reduce overall productivity. Historical examples from countries that prioritized only certain sectors in their economic strategies demonstrate that such approaches often lead to long-term imbalances and decreased overall economic health.
ECB’s Villeroy, France, is reportedly advocating for stabilizing public spending, prioritizing the wealthy first. This echoes broader trends in global markets, as seen in recent analyses like global markets wrapup 1. Ultimately, the focus on wealthy-first spending stabilization by ECB’s Villeroy seems likely to have a significant impact on the broader financial landscape.
Alternative Approaches to Public Spending
Instead of prioritizing the wealthy, a more equitable approach involves a diversified public spending strategy that benefits a wider range of the population. This includes targeted support for vulnerable groups, investments in social programs, and infrastructure projects that address the needs of all citizens. Focusing on a robust and sustainable economy requires comprehensive investment in human capital and infrastructure.
Examples of Successful Social Welfare Initiatives
Many countries have successfully implemented public spending initiatives that prioritize social welfare. For instance, Scandinavian countries have long demonstrated that robust social safety nets and extensive public investments in education and healthcare can lead to high levels of economic prosperity and social equity. Their models highlight the importance of equitable distribution of resources and investment in human capital.
Comparison of Public Spending Models
| Model Type | Target Group | Projected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| Focus on Wealthy First | High-income earners, businesses | Potential for short-term fiscal stability, but likely long-term economic inequality, reduced human capital, and potential economic stagnation. |
| Equitable Public Spending | All segments of society, with targeted support for vulnerable groups | Potential for sustainable economic growth, increased social mobility, and reduced inequality. Increased investment in human capital can boost productivity and overall competitiveness. |
| Scandinavian Model | All segments of society, with robust social safety nets and investments in education, healthcare, and infrastructure. | High levels of economic prosperity, social equity, and human capital development, often demonstrated by high standards of living and reduced income inequality. |
Villeroy’s Role and Position
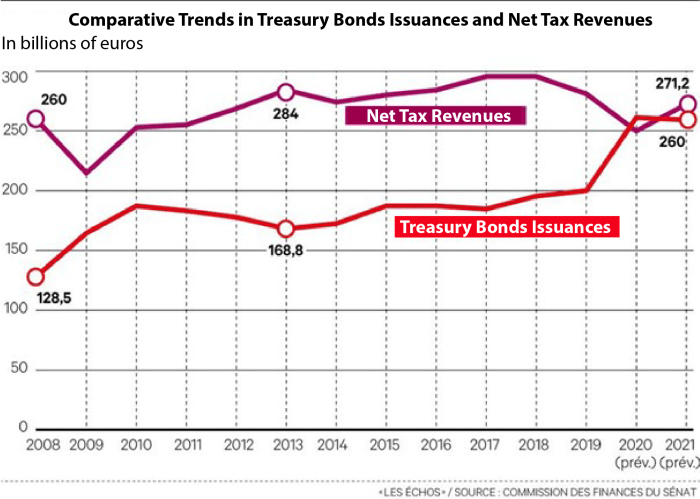
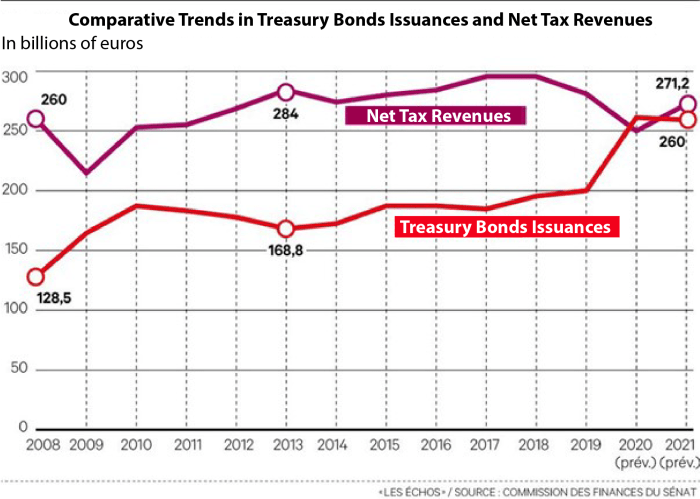
Villeroy, as a prominent entity in France, holds a significant position within the national economic landscape. Its stance on public spending policies, particularly concerning the “focus on wealthy first” approach, will be crucial in shaping the future trajectory of the country’s economic development. This section examines Villeroy’s specific responsibilities, its role in implementing the policy, and its potential influence on the wider public debate.Villeroy’s specific role in this context extends beyond simple economic commentary.
Its influence is rooted in its historical involvement in economic planning and its potential to act as a catalyst for change within the French economic system. Understanding its position allows us to assess the potential effectiveness and consequences of the proposed policy changes.
Villeroy’s Responsibilities and Role in Implementation
Villeroy’s responsibilities encompass the implementation of the “focus on wealthy first” policy in a nuanced manner. This includes formulating detailed strategies for incentivizing investment by high-net-worth individuals and businesses. The entity likely plays a vital role in crafting specific policies, regulations, and incentives targeted at the wealthy segment of the economy. Moreover, it is likely responsible for the evaluation and monitoring of the program’s effectiveness.
Villeroy’s Potential Influence on the Wider Debate
Villeroy’s pronouncements on public spending have the potential to significantly influence the broader national conversation on economic policy. The entity’s pronouncements will likely be analyzed by policymakers, economists, and the general public. Its perspective will be critically evaluated, especially considering the potentially controversial nature of the “focus on wealthy first” approach. Public opinion will be significantly shaped by Villeroy’s stance and the evidence it presents in support of the policy.
Historical Stances on Economic Policies
To assess Villeroy’s potential influence, it is important to analyze its historical positions on economic policies. A review of past statements and actions will reveal the entity’s track record in terms of supporting specific economic policies. This review will provide insights into Villeroy’s underlying philosophy and values, which will help predict its approach to the “focus on wealthy first” policy.
Potential Impact on Different Sectors
The “focus on wealthy first” policy, if implemented, will likely have diverse impacts across various sectors. Understanding these potential effects is crucial for a comprehensive analysis.
| Sector | Expected Impact | Supporting Evidence |
|---|---|---|
| High-Tech Industries | Increased investment and job creation, potentially driving innovation and growth. | Historical trends of wealth infusion into high-tech sectors often leading to exponential growth. |
| Real Estate | Significant boost in luxury real estate markets, with potentially mixed effects on affordable housing. | Wealthy individuals often invest heavily in high-end real estate, driving prices upward. |
| Arts and Culture | Potential for increased patronage and funding, but also risk of elitism and marginalization of smaller cultural initiatives. | Historical precedent of wealthy patrons supporting the arts, but also potential for unequal access to resources. |
| Public Services | Potential for reduced public funding, potentially leading to decreased services in education, healthcare, and infrastructure. | Decreased tax revenue if wealthier individuals are not paying higher taxes in proportion to their benefits. |
Analysis of Public Opinion
The Villeroy proposal to prioritize public spending on the wealthy elicits a complex and potentially volatile public reaction. Public opinion is a critical factor in the success or failure of any policy, and understanding the potential responses is crucial for navigating potential challenges. Understanding these reactions allows for a proactive approach to address concerns and build support.Public opinion is shaped by a multitude of factors, including economic anxieties, social perceptions of fairness, and political ideologies.
The proposed policy, with its focus on a select group, is likely to generate considerable debate and discussion, potentially sparking protests and activism if not carefully managed. Assessing potential public reactions is therefore essential to mitigating opposition and fostering acceptance.
Potential Public Reactions
Public reactions to the proposed policy will likely be varied and complex, influenced by a multitude of factors, including individual economic situations, perceptions of fairness, and political leanings. Those who perceive the policy as unfair or detrimental to their interests will likely express opposition. Conversely, those who believe it will stimulate economic growth or provide benefits to them might support the initiative.
The proposed policy is therefore expected to create a significant divide in public opinion.
- Concerns about Fairness and Inequality: Many individuals will likely view the policy as exacerbating existing inequalities. A significant portion of the population may perceive it as a disproportionate allocation of resources favoring the wealthy, leading to resentment and mistrust in the government. This concern is especially prominent in countries with pre-existing socioeconomic disparities.
- Economic Anxiety and Uncertainty: The potential impact on job creation, wages, and overall economic well-being will be a key concern for many. Negative perceptions of the policy’s impact on employment and the economy will likely fuel public opposition.
- Political Discontent: The policy may trigger broader political discontent if it is perceived as driven by partisan interests or as a betrayal of democratic principles. Public perception of political motives behind the policy can influence public opinion significantly.
Challenges in Implementing the Policy
Public opposition to the policy will likely create significant implementation challenges. Protests, boycotts, and political activism can disrupt policy execution. This opposition can also lead to legislative hurdles and delays. Managing the negative public sentiment will be crucial to the success of the policy.
- Political Instability: Widespread public opposition can lead to political instability and potentially destabilize the current government, hindering policy implementation.
- Erosion of Public Trust: A lack of public trust can make it difficult for the government to secure support for the policy. This can significantly impede its effectiveness.
- Economic Disruptions: Public protests and disruptions can negatively impact economic activity, potentially outweighing any perceived economic benefits of the policy.
Strategies to Address Public Concerns, Ecbs villeroy france should stabilise public spending focus wealthy first
Addressing public concerns proactively is essential to gaining support for the policy. Transparency, clear communication, and engagement with diverse stakeholders are crucial for mitigating potential opposition. A detailed plan outlining the policy’s rationale and benefits for all citizens, including those not directly benefiting, is critical.
- Transparent Communication: Clear and consistent communication about the policy’s rationale, anticipated benefits, and mitigation strategies is vital. The government should actively engage with the public to address concerns and build trust.
- Public Consultation: Actively engaging with diverse groups, including representatives from various socioeconomic backgrounds, is crucial for understanding and addressing public concerns.
- Economic Mitigation Measures: To mitigate concerns about the economic impact on vulnerable populations, the government could implement supportive measures like targeted subsidies, job training programs, or increased social safety nets.
Examples of Public Discourse
Public discourse surrounding similar policies in other countries provides valuable insights. Analyzing these examples allows for understanding the dynamics of public response and developing effective strategies to address concerns.
- Tax Cuts for the Wealthy in the United States: Past tax cuts for the wealthy in the U.S. have sparked extensive debate and often led to criticism from those who perceive them as unfair or detrimental to the general public.
- Welfare Reform Policies in Europe: European welfare reform policies have also faced public scrutiny, with concerns raised about their impact on vulnerable populations and the effectiveness of the proposed measures.
Potential Public Reactions by Demographic Groups
| Demographic Group | Potential Reaction |
|---|---|
| High-income earners | Likely support |
| Middle-income earners | Mixed reactions, potentially concerned about economic impact |
| Low-income earners | Strong opposition, concern about worsening inequality |
| Youth | Mixed reactions, likely more critical of the policy’s impact on future generations |
| Senior citizens | Mixed reactions, concern about social security and healthcare |
End of Discussion
In conclusion, the ECB’s Villeroy France proposal to stabilize public spending, prioritizing the wealthy, presents a complex dilemma. While the rationale behind this strategy is presented, potential consequences for various sectors and social groups require careful consideration. Exploring alternative models for public spending, which consider the needs of a broader population, is essential to create a more equitable and sustainable future for France.