View analysts react us china trade agreement, delving into the complex interplay of perspectives surrounding this crucial economic pact. This analysis unpacks the agreement’s key provisions, objectives, and historical context, offering a comprehensive view of the potential benefits and drawbacks for both the US and China.
From the nuanced viewpoints of various analysts, we explore potential positive and negative impacts on specific industries. The agreement’s global economic implications, long-term consequences, and areas of disagreement among experts are also thoroughly examined.
Overview of the US-China Trade Agreement

The US-China trade relationship has been a complex and often contentious issue for decades. Recent trade agreements have aimed to address imbalances and ensure fair competition. This overview details the key provisions, objectives, and historical context of these agreements, as well as varying perspectives on their significance.
Summary of the US-China Trade Agreement
The US-China trade agreements, while not a single, unified accord, encompass a series of negotiations and agreements spanning several years. These agreements primarily focused on reducing trade imbalances, ensuring fair competition, and protecting intellectual property rights. Their scope extends beyond tariffs and includes issues such as technology transfer and market access.
Key Provisions and Objectives
| Provision | Objective | Perspective |
|---|---|---|
| Reduced tariffs on certain goods | To lessen trade barriers and promote greater market access for US companies. | Supporters highlight increased market opportunities; critics express concerns about potential job losses in the US. |
| Intellectual property protection | To safeguard US companies’ intellectual property from theft or infringement by Chinese companies. | Advocates emphasize the need for a level playing field; detractors suggest this could hinder Chinese innovation. |
| Technology transfer provisions | To ensure fair competition and prevent unfair advantages for Chinese companies. | Supporters believe this will reduce the risk of forced technology transfer; opponents contend it is too vague and difficult to enforce. |
| Market access commitments | To improve access for US businesses to the Chinese market. | Proponents see increased opportunities for US businesses; critics point to China’s continued protectionist practices. |
Historical Context
The history of US-China trade relations has been marked by periods of both cooperation and conflict. Early trade agreements were focused on establishing basic economic ties. Subsequent agreements arose from concerns about trade imbalances and intellectual property theft. The rise of China as a global economic power has further complicated the relationship.
Different Perspectives on the Agreement’s Significance
The US-China trade agreements are viewed differently depending on the stakeholder. For instance, US businesses hoping to enter the Chinese market see the agreement as an opportunity for growth. On the other hand, Chinese businesses may view these agreements as an attempt to curb their expansion. The US government’s perspective often considers national security and economic competitiveness.
Analyst Reactions: Positive Aspects: View Analysts React Us China Trade Agreement
The US-China trade agreement, while complex, has garnered varying analyst reactions. Some analysts highlight potential benefits for both economies, pointing to specific sectors that stand to gain. Understanding these positive aspects is crucial to assessing the overall impact of the agreement.Analysts generally acknowledge the potential for increased trade and economic growth stemming from the agreement. This optimism is often tied to the agreement’s provisions related to market access, intellectual property protection, and dispute resolution.
Analysts are buzzing about the US-China trade agreement, dissecting its potential impacts on global markets. While the specifics remain to be seen, many are trying to gauge the long-term effects. Interestingly, the debates surrounding this agreement are reminiscent of the ongoing free speech discussions at Columbia University. Free speech on campus at Columbia University has become a hot topic, highlighting the importance of open dialogue in a democratic society, similar to the complex negotiations involved in the US-China trade deal.
The agreement’s potential ramifications are definitely something to keep an eye on as the implications for global trade unfold.
The specifics of these provisions, as well as the potential benefits for both nations, are important considerations in evaluating the agreement’s overall merit.
Positive Aspects Highlighted by Analysts, View analysts react us china trade agreement
Analysts frequently emphasize the potential for expanded trade volumes as a key positive outcome of the agreement. This increased trade, in theory, would stimulate economic activity in both countries. For example, increased exports of US agricultural products to China could bolster farm incomes and create jobs in the US. Similarly, increased access to the Chinese market for US companies could lead to higher profits and employment opportunities.
Potential Benefits to the US and China
The agreement’s potential benefits are not limited to trade volumes. Analysts also highlight the potential for reduced trade friction and improved relations between the two nations. This improved climate could facilitate further cooperation on global issues, such as climate change and pandemics. Such cooperation is crucial for addressing global challenges effectively. The US and China stand to benefit from the improved diplomatic relations as well as the economic opportunities.
Specific Industry Sectors Benefiting from the Agreement
Several industry sectors are expected to benefit significantly from the agreement, as viewed by analysts. For example, the agricultural sector in the US is expected to see increased demand for its products in China. Similarly, the technology sector in both countries could benefit from enhanced market access. Other sectors, such as manufacturing and energy, might also experience positive impacts, contingent on the agreement’s successful implementation.
Analyst Perspectives on Positive Impacts
Analyst perspectives on the positive impacts vary somewhat. Some analysts are cautiously optimistic, emphasizing the potential for significant gains but also acknowledging the risks involved in complex international agreements. Other analysts express more profound optimism, suggesting that the agreement could lead to substantial economic growth in both countries. The nuanced views highlight the complexity of the agreement and the various factors influencing its potential impact.
Comparison of Analyst Viewpoints
| Analyst | Perspective | Industry Sector |
|---|---|---|
| Analyst A | Cautiously optimistic, highlighting potential gains but acknowledging risks | Agricultural, Technology |
| Analyst B | Profoundly optimistic, suggesting substantial economic growth | Manufacturing, Energy |
| Analyst C | Neutral, emphasizing the need for careful monitoring of implementation | All sectors |
Analyst Reactions: Negative Aspects
The US-China trade agreement, while lauded by some, has drawn significant criticism from various analysts. These concerns highlight potential pitfalls and risks for both economies, demanding careful consideration of the long-term implications. A deeper dive into the negative aspects provides a more nuanced understanding of the agreement’s potential drawbacks.Analysts have identified several key negative aspects of the trade deal.
These concerns often center on the potential for the agreement to exacerbate existing economic imbalances, stifle innovation, and ultimately hinder economic growth in the long run. The specific concerns and the predicted outcomes vary depending on the analyst’s perspective and the specific sectors they focus on.
Potential Downsides for the US
Concerns regarding the agreement’s impact on the US economy are varied. Some analysts highlight the potential for job losses in specific sectors, as US companies may struggle to compete with lower-cost Chinese imports. Further, concerns exist about the agreement’s impact on intellectual property protection, which could disadvantage American businesses in the long term.
- Job displacement: Certain sectors within the US manufacturing and agricultural industries are expected to face increased competition from Chinese imports, potentially leading to job losses. This is particularly true for industries with labor-intensive processes where China’s lower labor costs offer a significant advantage.
- Intellectual property theft: Analysts express concern that the agreement might not adequately address concerns regarding intellectual property theft from US companies operating in China. This could create a disincentive for US innovation and investment in the long term, as the potential rewards may not be adequately protected.
- Unbalanced trade: The agreement might not effectively address the existing trade imbalance between the two countries. This could perpetuate the reliance of US consumers on Chinese products, without a corresponding increase in American exports to China.
Potential Downsides for China
The agreement also presents potential challenges for the Chinese economy. Concerns revolve around the agreement’s impact on China’s domestic industries, as well as its potential for generating internal political pressures.
- Domestic industry pressure: The agreement might put pressure on Chinese domestic industries that are not competitive with foreign products. This could lead to job losses and potentially social unrest, as domestic companies struggle to maintain market share.
- Dependence on export markets: Concerns exist about the potential for China to become overly reliant on export markets for economic growth. This could leave the Chinese economy vulnerable to external shocks or changes in global demand.
- Reduced economic flexibility: Some analysts worry that the agreement might reduce China’s economic flexibility to adapt to future global economic changes. This could hinder China’s ability to respond to unexpected challenges or pursue alternative growth strategies.
Potential Risks and Challenges
The agreement’s implementation faces numerous risks, including the potential for unforeseen consequences, difficulties in enforcement, and a lack of transparency.
- Enforcement difficulties: Analysts express concern over the challenges in effectively enforcing the agreement’s provisions. This could lead to a situation where certain provisions are not adhered to by either side.
- Unforeseen consequences: The long-term consequences of the agreement are not entirely clear. Analysts highlight the possibility of unforeseen negative impacts on specific sectors or the global economy as a whole.
- Lack of transparency: Some analysts argue that the agreement’s specifics lack transparency, potentially hindering public understanding and creating opportunities for future disputes.
Analyst Perspectives on Negative Impacts
Different analysts hold varying perspectives on the negative impacts of the agreement. Some focus on the potential for job losses, while others emphasize the risks to intellectual property. The varying viewpoints highlight the complexity of the situation and the potential for different interpretations of the agreement’s implications.
| Analyst | Perspective | Potential Risks |
|---|---|---|
| Analyst A | Focus on job losses in US manufacturing | Increased competition from Chinese imports, potential for US job losses in affected sectors |
| Analyst B | Concerns about intellectual property theft | Weakened protection for US intellectual property, potential disincentive for innovation |
| Analyst C | Focus on potential trade imbalance | Increased reliance on Chinese imports, limited growth in US exports to China |
Impact on Specific Industries
The US-China trade agreement’s ripple effects are felt most acutely within specific sectors. Industries reliant on Chinese imports or exports, and those directly competing with Chinese producers, face significant adjustments. Understanding these sector-specific impacts is crucial for evaluating the overall economic ramifications of the agreement. Analysts’ predictions paint a complex picture, ranging from cautious optimism to outright concern.
Agricultural Sector
The agricultural sector has historically been a focal point of US-China trade tensions. The agreement’s impact on this sector hinges on the reduction of tariffs and the resumption of trade flows. Analysts predict that increased exports of US agricultural products to China could boost farm incomes in specific regions, such as the Midwest. Conversely, some sectors within the agricultural industry, like soybeans, may experience temporary setbacks if Chinese buyers shift to other suppliers.
- Increased US agricultural exports to China are anticipated to boost farm incomes, but this is contingent upon sustained trade agreements and a lack of new trade disputes.
- Specific regions, particularly the Midwest, could see a significant positive impact if the agreement leads to higher demand for US agricultural products.
- Some agricultural products, like soybeans, may face short-term challenges as Chinese buyers explore alternative sources if the agreement doesn’t fully address their needs.
Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector faces a multifaceted impact. Some US manufacturers rely on Chinese components for their products. A smoother trade relationship could lead to reduced costs and increased production. However, analysts are concerned about potential job displacement in certain manufacturing sectors if Chinese goods become more competitive in the US market.
- US manufacturers utilizing Chinese components could potentially experience lower production costs and increased output if trade flows are stabilized and tariffs are lowered.
- However, analysts anticipate possible job displacement in sectors directly competing with cheaper Chinese imports.
- Data from past trade disputes reveals fluctuating trade volumes and potential shifts in supply chains, making it difficult to accurately predict the immediate impact on manufacturing jobs.
Technology Sector
The technology sector is another key area impacted by the agreement. Analysts highlight the importance of intellectual property protection and fair competition. The agreement’s provisions on technology transfer and market access are crucial for US tech companies seeking to penetrate the Chinese market.
- The agreement’s provisions regarding intellectual property protection and fair competition are essential for the success of US tech companies operating in China.
- Analysts believe the agreement could foster greater access for US technology companies to the Chinese market, but the level of success depends on the actual implementation and adherence to the agreed-upon terms.
- Potential for increased competition from Chinese tech companies is also expected in the US market, although the extent of this impact is subject to further analysis.
Table: Impact on Industries
| Industry | Analyst Prediction | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Increased exports, potentially higher farm incomes in some regions | Potential for temporary setbacks in specific sectors if China shifts to alternative suppliers. |
| Manufacturing | Reduced costs, increased output in some sectors; potential job displacement in others. | Shift in supply chains, impacting employment in specific manufacturing areas. |
| Technology | Improved market access for US companies, potential for increased competition. | Continued need for intellectual property protection and fair competition policies. |
Global Economic Implications
The US-China trade agreement, a complex interplay of tariffs, quotas, and concessions, has far-reaching implications for the global economy. Understanding these effects requires examining potential ripple effects across various countries and regions, as well as how it might alter international trade relationships. Experts predict a mix of positive and negative outcomes, with the ultimate impact depending on various factors, including the agreement’s implementation and subsequent reactions from other nations.The agreement’s influence extends beyond the direct participants.
The intricate web of global supply chains means that adjustments in US-China trade can trigger cascading effects throughout the international economy. Changes in import/export patterns, shifts in investment flows, and altered production strategies can have considerable consequences for nations reliant on these trade relationships. The anticipated impact on specific industries, like technology and manufacturing, will be critical to monitor.
A nuanced perspective encompassing different viewpoints is necessary for a comprehensive understanding of the global implications.
Potential Ripple Effects Across Countries and Regions
The trade agreement’s potential to impact different countries and regions varies. For instance, countries heavily reliant on trade with either the US or China could experience significant adjustments in their economies. Those countries that act as intermediaries in the global supply chain, facilitating trade between the US and China, may see changes in their import/export volumes and revenue streams.
The agreement’s impact on emerging economies is a critical consideration, as these nations often rely on global trade for growth and development. Developing countries that export goods to both the US and China face a delicate balancing act.
Potential Effects on International Trade Relationships
The agreement’s impact on international trade relationships will be multifaceted. The agreement may encourage other countries to forge their own trade deals, potentially leading to a more fragmented global trading system. This could involve the formation of new alliances or the strengthening of existing ones. It might also lead to a re-evaluation of existing trade policies and agreements, prompting adjustments and renegotiations.
Countries might seek to diversify their trade partners, reducing their reliance on specific economies.
Comparative Analysis of the Global Impact
Analyzing the global impact requires considering different perspectives. Economists, policymakers, and industry representatives will have varying opinions regarding the agreement’s overall effect. Some may emphasize the potential for increased stability and reduced trade tensions, while others might highlight the risks of unintended consequences or regional disparities. This analysis necessitates a careful evaluation of the short-term and long-term consequences, acknowledging the potential for both positive and negative outcomes for different stakeholders.
Analysts are buzzing about the US-China trade agreement, weighing the potential impacts on global markets. Meanwhile, the tennis world is abuzz with the upcoming French Open quarter-finals, where Aryna Sabalenka is aiming for revenge against Zheng Qinwen. This match is shaping up to be a compelling showdown, and it’s hard to ignore the parallel to the complex negotiations between the two countries.
Ultimately, the US-China trade agreement’s success will hinge on the willingness of both sides to compromise, just as Sabalenka needs to find a way to overcome Zheng’s strong game in sabalenka eyes revenge against zheng french open quarter finals. The outcome of the agreement will undoubtedly affect the global economy, much like a major tennis match can affect the entire sport.
Summary of Global Impact
| Region | Predicted Effect | Related Industries |
|---|---|---|
| North America | Potential for increased stability in trade relations, but potential for regional job displacement in some sectors. | Manufacturing, technology, agriculture |
| East Asia | Significant adjustments in export patterns and production strategies, potentially affecting manufacturing and technology sectors. | Electronics, textiles, automobiles |
| Europe | Potential for increased competition in global markets, leading to adjustments in some sectors. | Automotive, pharmaceuticals, technology |
| Developing Countries | Varying impacts depending on the country’s specific trade relationships with the US and China, impacting agriculture, textiles, and manufacturing. | Agriculture, textiles, manufacturing |
Long-Term Implications
The US-China trade agreement, while potentially offering short-term economic benefits, carries significant long-term implications for both nations and the global economy. Analysts are carefully assessing the potential ripple effects across various sectors and geopolitical landscapes. This analysis delves into the predicted future scenarios, the likelihood of future negotiations, and the impact on the evolving relationship between the two superpowers.The agreement’s long-term success hinges on sustained adherence to its terms and a proactive approach to resolving emerging disputes.
The complex interplay of economic interests, political ideologies, and technological advancements will shape the future trajectory of this relationship. The potential for unforeseen events and shifts in global power dynamics cannot be ignored.
Potential Future Scenarios
Several scenarios are emerging regarding the future trajectory of the US-China relationship and the trade agreement. These are not mutually exclusive and are likely to intertwine in various ways.
- Scenario 1: Continued Cooperation and Gradual De-escalation: Both countries might find common ground on certain issues, leading to a more stable and predictable relationship. This scenario involves continued dialogue and compromise, with future agreements addressing new challenges. A prime example is the evolving relationship between the US and Japan, where cooperation on security issues is balanced by economic competition.
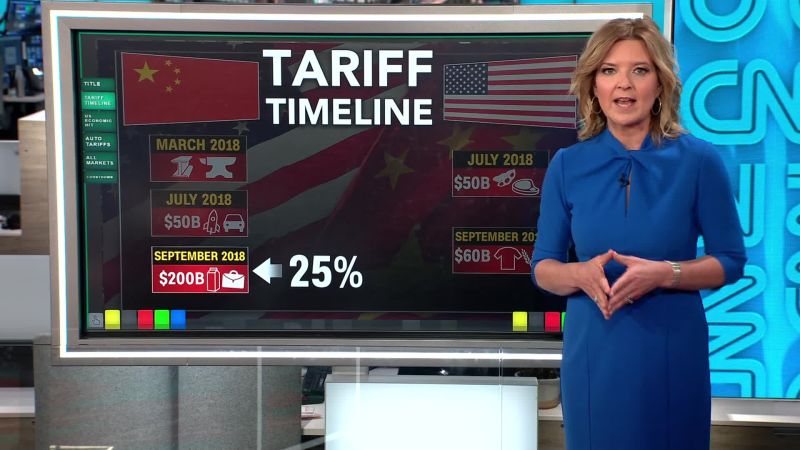
- Scenario 2: Escalation of Tensions and Trade Disputes: Disagreements on key issues like intellectual property or technology transfer could escalate tensions, leading to further trade restrictions and sanctions. Historical precedents, such as the 2018 trade war, demonstrate the potential for such scenarios.
- Scenario 3: Emergence of New Trade Agreements: Both countries may look to forge new trade alliances with other nations, potentially leading to shifts in global trade dynamics. The Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) is an example of such a scenario, with countries focusing on alternative trade partnerships.
Potential for Future Negotiations and Agreements
The trade agreement is not a static document; it is likely to be revisited and renegotiated as global economic and political landscapes evolve. Analysts predict that future negotiations will likely address emerging issues such as technology transfer, environmental standards, and labor practices.
- Future negotiations could focus on specific sectors, like technology or renewable energy, where both nations have substantial interests.
- The inclusion of new participants in future negotiations, such as other major economies, is also possible, leading to a broader framework for global trade agreements.
Impact on Future US-China Relations
The trade agreement will significantly influence the future relationship between the US and China. It is anticipated that the agreement will either foster closer cooperation or deepen existing mistrust, based on the effectiveness of its implementation.
- The agreement’s success or failure will likely affect broader bilateral relations, influencing areas like security and diplomacy.
- This will affect international cooperation on global issues, like climate change and pandemics, potentially either improving or straining existing partnerships.
Potential Long-Term Implications Table
| Time Frame | Predicted Effect | Related Actors |
|---|---|---|
| 1-5 years | Increased trade volumes in specific sectors, potential for disputes on intellectual property or technology transfer | US businesses, Chinese companies, trade organizations |
| 5-10 years | Shift in global supply chains, potential for new trade alliances, significant impact on specific industries | Global businesses, governments, international organizations |
| 10+ years | Reshaping of global economic order, alteration in international power dynamics, impact on geopolitical alliances | All nations, global institutions |
Analyst Differences and Disagreements
Analyzing the US-China trade agreement reveals a fascinating spectrum of opinions among experts. While some hail it as a crucial step towards stabilizing global trade, others express skepticism, highlighting potential pitfalls and long-term implications. This divergence in viewpoints underscores the complexity of the agreement and the inherent challenges in predicting its ultimate impact. The reasons for these differences stem from various factors, including differing methodologies, potential biases, and varying interpretations of the available data.
Areas of Disagreement
Analyst opinions diverge on several crucial aspects of the agreement. These disagreements often center on the efficacy of specific provisions, the long-term sustainability of the deal, and the potential ripple effects on global markets. Different schools of thought exist regarding the extent to which the agreement will address underlying trade imbalances, promote fair competition, and foster a more stable economic relationship between the two superpowers.
Reasons Behind Differing Opinions
Analysts’ perspectives are shaped by a multitude of factors. Some analysts might favor a more interventionist approach to trade, advocating for stronger protections for domestic industries. Others may lean towards a more laissez-faire approach, emphasizing the benefits of free trade and market forces. The specific economic models employed also play a critical role in shaping analysts’ interpretations. Some analysts might focus on short-term gains, while others consider long-term implications.
Their methodologies, the data they utilize, and their pre-existing biases can influence their conclusions.
Methodologies Used by Analysts
Different analysts employ various methodologies to analyze the trade agreement. Some might use econometric models to predict the impact on specific industries, while others rely on qualitative assessments based on interviews and industry reports. Quantitative methods are frequently used, yet the models and data sets can vary. The choice of methodology can significantly impact the conclusions reached.
Analysts are buzzing about the US-China trade agreement, and it’s interesting to see how it’s impacting various sectors. For example, BESI, a company specializing in advanced solutions, has just boosted its forecast, expecting higher demand for its products, which could be a positive sign for the future of the industry. BESI lifts its forecast expects higher demand its advanced solutions.
This suggests a potentially strong market response to the agreement, although it’s still early days to definitively say how the deal will ultimately affect the broader trade landscape.
Potential Biases in Analyst Reports
Analyst reports can be susceptible to various biases. Analysts may have preconceived notions about the likely outcomes of the agreement, which could skew their interpretation of the data. Their affiliations with specific institutions or industries could also influence their analysis. It’s crucial to recognize these potential biases and critically evaluate the methodologies employed to assess the validity of the conclusions.
Table of Analyst Disagreements
| Analyst | Disagreement Point | Reasoning |
|---|---|---|
| Analyst A (Pro-agreement) | Long-term sustainability of reduced tariffs | Believes the agreement will lead to sustained growth and cooperation. |
| Analyst B (Skeptical) | Impact on developing countries | Concerns about potential trade diversion and negative effects on less developed economies. |
| Analyst C (Focus on specific industry) | Impact on the agricultural sector | Foresees negative consequences for domestic agricultural producers due to increased imports. |
| Analyst D (Global perspective) | Potential for geopolitical implications | Highlights the agreement’s influence on the broader geopolitical landscape. |
| Analyst E (Data-driven) | Accuracy of GDP forecasts | Points out limitations of the models used to predict future GDP growth. |
Illustrative Examples of Analyst Reports
Diving into the specifics of analyst reports on the US-China trade agreement reveals a fascinating array of approaches and methodologies. These reports, often meticulously crafted, provide valuable insights into the potential impacts of the agreement, but also showcase the inherent complexities of predicting the future. Understanding these diverse perspectives is crucial for forming a well-rounded opinion on the agreement’s ultimate effect.Analyst reports often employ a mix of quantitative and qualitative analysis, ranging from detailed economic models to expert opinions.
This variety in approaches allows readers to evaluate the agreement’s potential outcomes from different lenses, helping to assess the reliability of the predictions. The choice of methodology is often dictated by the specific focus of the analyst and the questions they seek to answer.
Analyst Perspectives and Approaches
Different analysts bring unique perspectives and approaches to their analysis. Some prioritize macroeconomic factors, while others focus on the microeconomic impact on specific industries. This diverse range of viewpoints is vital for a comprehensive understanding of the agreement’s ramifications.
Examples of Analyst Report Excerpts
| Analyst | Report Excerpt | Methodology |
|---|---|---|
| Global Macroeconomic Research Group | “Our model projects a 1.5% GDP growth increase in the US within the next 2 years. This surge is largely attributed to increased export opportunities in the agricultural sector and a resultant surge in domestic investment.” | Employs a dynamic stochastic general equilibrium (DSGE) model, integrating factors such as trade flows, capital investment, and consumer spending. Data sources include government statistics, trade organization reports, and industry surveys. |
| International Trade and Finance Consulting Firm |
|
Focuses on industry-specific analysis, utilizing case studies, interviews with industry leaders, and quantitative analysis of historical trade data. |
| Independent Economist | “The agreement’s long-term implications for global supply chains are uncertain. The agreement may lead to greater regionalization, with companies seeking to reduce reliance on single, distant suppliers. This shift may create new opportunities in emerging markets but also present challenges for existing supply chains.” | Utilizes qualitative research, including interviews with experts and reviews of academic literature, combined with historical data on global trade patterns. The analyst highlights potential future trends and risks. |
Data Visualization in Analyst Reports
Data visualizations, such as bar graphs, line charts, and scatter plots, play a crucial role in communicating complex information in analyst reports. These visuals often highlight key trends and relationships, making it easier for readers to grasp the core arguments and findings. For instance, a bar graph could illustrate the expected change in export volumes for various sectors, or a line graph could depict the projected trajectory of GDP growth over a given period.
A scatter plot might illustrate the correlation between the value of trade and economic growth rates in different regions. The choice of visualization depends on the specific data being presented and the message the analyst wants to convey.
Ending Remarks

In conclusion, the US-China trade agreement presents a multifaceted challenge, laden with both opportunities and potential pitfalls. Analyst reactions reveal a spectrum of opinions, highlighting the complex interplay of economic, political, and social factors. The long-term implications are still unfolding, and this analysis serves as a starting point for further exploration and understanding.