Nato east flank backs ukraine membership poland romania lithuania say – NATO east flank backs Ukraine membership, Poland, Romania, and Lithuania say. This signifies a crucial shift in the geopolitical landscape of Eastern Europe, highlighting the growing support for Ukraine’s aspirations to join the alliance. The decision reflects a collective concern about regional security and Russia’s actions, underscoring the deepening strategic partnership between NATO member states and Ukraine. The nations’ statements signal a commitment to bolstering Ukraine’s defense capabilities and potentially deterring further aggression.
This support comes amidst a complex web of historical context, security concerns, and potential consequences. The historical evolution of NATO’s eastward expansion, the geopolitical significance of the region, and the evolving security landscape in Eastern Europe are all crucial factors to consider. Ukraine’s motivations for seeking NATO membership, along with the arguments for and against it, will be explored.
The positions of Poland, Romania, and Lithuania, their shared interests, and potential benefits and drawbacks of supporting Ukraine’s membership will also be examined. Furthermore, the potential impact on regional stability, security implications, and public perception will be analyzed.
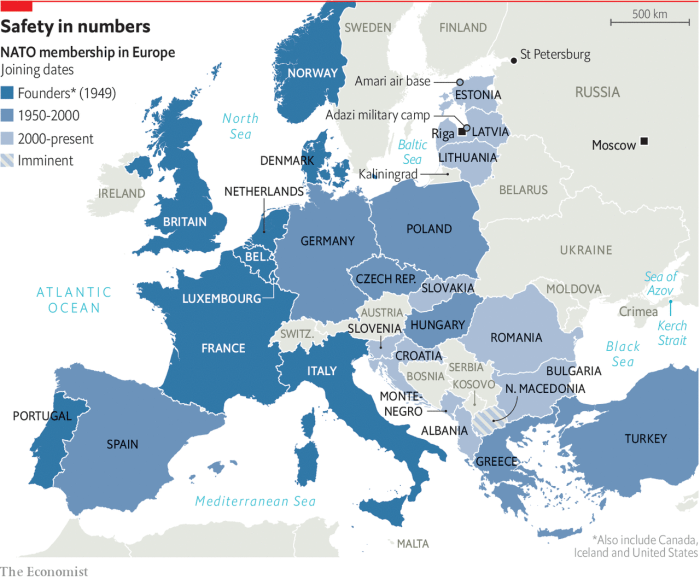
NATO’s Eastern Flank
NATO’s eastward expansion, a complex geopolitical phenomenon, has profoundly reshaped the security landscape of Eastern Europe. The post-Cold War era saw a fundamental shift in the balance of power, prompting NATO to adapt and solidify its presence in the region. This evolution is intricately linked to the evolving security concerns of the nations bordering Russia, driving the alliance’s strategic decisions.The Eastern Flank of NATO is not merely a geographical designation; it signifies a critical zone of strategic importance.
The region’s history is marked by shifting alliances and power struggles, making its current security situation a delicate balancing act. The ongoing conflict in Ukraine, in particular, has dramatically altered the security dynamics in the area, necessitating a deeper understanding of the challenges and opportunities facing the nations in this vital region.
Historical Overview of NATO’s Eastward Expansion
NATO’s eastward expansion has been a gradual process, driven by various factors, including the desire to stabilize the region following the collapse of the Soviet Union. The initial enlargement focused on former Warsaw Pact countries, reflecting a shift from Cold War confrontation to a collaborative security framework. The expansion continued in subsequent years, with new members joining the alliance, gradually pushing its presence closer to Russia’s borders.
This expansion has been a source of both support and concern for different countries, creating a complex security landscape.
Geopolitical Significance of the Region
The Eastern European region holds immense geopolitical significance due to its strategic location and rich history. It serves as a crucial transit point for energy resources and trade routes, making it a focal point for international interests. The region’s diverse ethnic and cultural composition also contributes to its complex political dynamics. Furthermore, its proximity to Russia underscores its importance in maintaining regional stability and preventing potential conflicts.
Evolving Security Landscape in Eastern Europe
The security landscape in Eastern Europe is constantly evolving, influenced by numerous factors. The rise of nationalism, economic disparities, and the lingering effects of past conflicts continue to shape the region’s dynamics. The situation in Ukraine has become a significant catalyst, highlighting the vulnerability of countries bordering Russia and prompting a reassessment of security postures across the region. The ongoing conflict, and its potential implications for regional stability, have created an environment of heightened tension and uncertainty.
Key Security Concerns of Nations in the Region
The nations in the Eastern Flank face a multitude of security concerns. These concerns stem from a range of issues, including the potential for Russian aggression, the impact of regional conflicts, and the need to integrate into the broader European security architecture. The economic dependence on certain countries also plays a role in shaping the security priorities of these nations.
Ultimately, the desire for stability and security within the region remains a paramount concern for each nation.
The NATO east flank’s backing of Ukraine’s membership, with Poland, Romania, and Lithuania leading the charge, is significant. It’s a clear show of support, but also raises questions about the long-term implications for the region. Interestingly, the ongoing debate about the potential impact on regional stability reminds me of the recent controversy surrounding Marty Makary, a Trump nominee for the FDA marty makary trump nominee fda , which further highlights the complexities of political appointments and their potential influence on policy.
Ultimately, the support for Ukraine’s membership by the eastern NATO flank is a critical step in the ongoing conflict and its resolution.
Geographic Locations and NATO Membership Dates
| Country | Geographic Location | NATO Membership Date |
|---|---|---|
| Poland | Central Eastern Europe | 1999 |
| Romania | Southeastern Europe | 2004 |
| Lithuania | Baltic region | 2004 |
| Ukraine | Eastern Europe | Not a member |
The table above provides a concise overview of the geographic locations of the four nations and their current status within NATO. The varying dates of NATO membership reflect the gradual integration of these countries into the alliance’s security framework. Ukraine’s absence from the list signifies its current status as a non-member, although its aspirations for NATO membership are notable.
Ukraine’s Membership Aspirations
Ukraine’s unwavering pursuit of NATO membership reflects a deep-seated desire for security and a commitment to aligning with democratic values. This aspiration, however, is met with complex political considerations and geopolitical implications. The country’s journey toward potential alliance membership is a crucial aspect of understanding the evolving security landscape in Europe.Ukraine’s motivations for seeking NATO membership are multifaceted.
The country’s historical experience with Russian aggression, coupled with the ongoing conflict in the Donbas region and the full-scale invasion of 2022, underscore the importance of collective security guarantees. Joining NATO would provide Ukraine with a robust framework for defense and deterrence, potentially reducing the likelihood of future attacks. Moreover, membership would solidify Ukraine’s integration into the Western democratic sphere, enhancing its political and economic ties with member states.
Motivations for Membership
Ukraine’s desire for NATO membership stems from a combination of security concerns, geopolitical aspirations, and a commitment to democratic values. The country seeks protection from potential future threats and a framework for collective defense. Membership would also enhance Ukraine’s integration into the Western political and economic systems, providing a significant boost to its long-term stability.
Arguments For and Against Membership
Arguments for Ukraine’s membership often center on bolstering the country’s security and promoting democratic values within the Euro-Atlantic community. Proponents emphasize that NATO membership would deter further Russian aggression and provide Ukraine with vital military and political support. Conversely, arguments against membership frequently raise concerns about escalating tensions with Russia, potential implications for regional stability, and the potential need for NATO to commit military resources to defend Ukraine.
Furthermore, the process of fulfilling NATO membership criteria can be lengthy and demanding.
Comparison with Other Countries Seeking Membership
Ukraine’s situation is unique in that it faces an ongoing armed conflict and direct threat from a neighboring state. While other countries have sought NATO membership, many have not faced such immediate and significant security challenges. The potential ramifications of admitting Ukraine, given the ongoing conflict, are different from previous cases. A crucial consideration is how NATO would address the specific security threats Ukraine faces, and the implications for other countries in the region.
Timeline of Ukraine’s Interactions with NATO
Ukraine’s relationship with NATO has evolved over several decades, marked by a series of statements and agreements. The country has actively pursued closer ties with NATO, seeking to align its defense and security policies with the alliance’s principles. A key development was the 2008 Bucharest Summit, where Ukraine was promised a clear path toward NATO membership. However, the full-scale invasion of 2022 has significantly altered the landscape of these interactions.
- 2008 Bucharest Summit: Ukraine was promised a clear path toward NATO membership, but the issue remained unresolved due to the geopolitical context of the time.
- 2014 Invasion of Crimea: The Russian invasion of Crimea and subsequent conflict in the Donbas region underscored Ukraine’s vulnerability and heightened its desire for NATO protection.
- 2022 Full-Scale Invasion: The full-scale invasion of Ukraine by Russia significantly intensified the pressure for NATO membership and underscored the need for collective security guarantees.
Security Concerns Expressed by Ukraine and Other Nations in the Region
The security concerns of Ukraine and other nations in the region are diverse and multifaceted. A detailed understanding of these concerns is essential for addressing the complexities of the situation.
NATO’s eastern flank backing Ukraine’s membership, with Poland, Romania, and Lithuania voicing support, is a significant development. This bolstering of Ukraine’s potential European integration is certainly a response to ongoing geopolitical tensions. Interestingly, Taiwan has indicted four suspected spies in a China-related case, the investigation reaching the presidential office. This highlights the escalating tensions and espionage activities across the globe, echoing the support for Ukraine’s NATO membership and demonstrating the intricate web of international relations.
So, the solidarity expressed by the eastern flank nations for Ukraine’s future in Europe continues to be a crucial element in the broader geopolitical landscape.
| Country | Specific Security Concerns |
|---|---|
| Ukraine | Ongoing Russian aggression, including the occupation of Crimea, conflict in the Donbas region, and the full-scale invasion of 2022. |
| Poland | Concerns about the potential for Russian aggression along its eastern border and the security of its neighboring states. |
| Romania | Concerns regarding the security of its southern border and potential destabilization in the Black Sea region. |
| Lithuania | Concerns about Russian influence and potential aggression in the Baltic region, and the security of its neighboring states. |
Poland, Romania, and Lithuania’s Positions
The Eastern Flank nations of Poland, Romania, and Lithuania play a crucial role in supporting Ukraine’s aspirations to join NATO. Their positions are vital in shaping the alliance’s response to the ongoing conflict and future security arrangements. These nations share a history of close cooperation and a deep understanding of the security threats posed by the current geopolitical landscape.
Their support for Ukraine’s NATO membership underscores their commitment to regional security and stability.These nations have a strong vested interest in bolstering Ukraine’s defenses and deterring further aggression. Their shared border with Russia and Belarus, coupled with their historical experiences with authoritarian regimes, highlight the importance of collective security mechanisms in the region.
Official Statements Regarding Ukraine’s NATO Membership
Poland, Romania, and Lithuania have consistently expressed their support for Ukraine’s aspirations to join NATO. These statements emphasize the need for a robust and unified response to the ongoing conflict and underscore the importance of expanding the alliance’s security perimeter. The official statements, while not identical in tone or specific phrasing, all express a shared commitment to Ukraine’s sovereignty and territorial integrity.
Their support is not just symbolic but also reflects a practical understanding of the need to strengthen the collective defense of the region.
Potential Benefits and Drawbacks for Supporting Ukraine’s Membership
Supporting Ukraine’s NATO membership offers several potential benefits to Poland, Romania, and Lithuania. It strengthens the collective defense posture of the alliance, thereby enhancing the security of the entire region. This support also solidifies partnerships with other NATO members, creating opportunities for economic cooperation and technological advancements.However, supporting Ukraine’s membership also presents potential drawbacks. These include the potential for escalation of the conflict and the need for increased defense spending and resource allocation.
Moreover, there’s the risk of straining relations with certain nations, or the possibility of increased Russian aggression against the supporting nations themselves. The potential risks and benefits are not evenly distributed, and each nation must carefully weigh the implications of its position.
Shared Security Interests Among the Three Nations
Poland, Romania, and Lithuania share significant security interests, primarily stemming from their shared borders with Russia and Belarus, and their proximity to potential conflict zones. Their geographic location makes them vulnerable to potential threats from their eastern neighbors. These security interests drive their collaboration within NATO and their joint support for Ukraine’s integration into the alliance. This collective approach strengthens their regional security posture and underscores their shared understanding of the importance of a united front.
Comparison of Approaches to NATO Membership and Ukraine Support
While Poland, Romania, and Lithuania share a common goal of supporting Ukraine’s NATO membership, their approaches may differ in specific strategies and the emphasis on certain aspects. Poland, with its extensive border with Belarus and Russia, has historically been more vocal in advocating for Ukraine’s membership. Romania, strategically located in the Black Sea region, emphasizes the importance of regional security and stability.
Lithuania, being a small Baltic nation with a direct border to Belarus, stresses the need for a rapid and decisive response to Russian aggression. These nuances reflect the unique circumstances and security priorities of each nation.
Military Alliances and Agreements
| Nation | NATO Membership | Bilateral Agreements with Other Nations | Specific Alliances |
|---|---|---|---|
| Poland | Yes | Numerous bilateral defense agreements with NATO members | NATO, Visegrad Group |
| Romania | Yes | Defense agreements with NATO members | NATO, Black Sea regional cooperation initiatives |
| Lithuania | Yes | Defense agreements with NATO members and Baltic neighbors | NATO, Baltic Council |
The table above illustrates the established military alliances and agreements among these nations and with NATO. These agreements and memberships demonstrate the importance of collective defense in the face of emerging security challenges. The complex web of alliances underscores the importance of coordinated action and shared responsibility in maintaining regional stability.
Impact on Regional Stability
Ukraine’s aspirations to join NATO, coupled with the current geopolitical landscape, present a complex challenge to regional stability. The potential for a significant shift in the balance of power in Eastern Europe, coupled with the existing tensions, raises concerns about the future. The actions of various actors in the region will be critical in determining the long-term implications.
Potential Responses from Other Actors
Several actors in the region, including Russia, Belarus, and other bordering nations, are likely to react to Ukraine’s potential NATO membership. These responses could range from diplomatic pressure to more assertive military posturing. The responses will be influenced by perceived threats to their security interests and their own geopolitical objectives.
- Russia, already involved in the conflict in Ukraine, may perceive NATO expansion as a direct threat to its security. This could lead to increased military activity along its borders and a further escalation of the conflict.
- Belarus, closely allied with Russia, may be drawn into a more direct role in the conflict. This could involve providing military support or taking a more confrontational stance.
- Other bordering nations, including Poland and the Baltic states, may experience increased security concerns, leading to heightened military preparedness and potentially strengthening their alliances.
Long-Term Implications for International Relations
The potential consequences of Ukraine’s NATO membership extend beyond the immediate region. It could reshape the international security architecture, potentially leading to new alliances and realignments. Existing international agreements and treaties may need to be re-evaluated to address the new geopolitical realities.
- The expansion of NATO could solidify existing alliances and lead to a more structured security arrangement in Europe. However, it could also fracture existing alliances and increase the risk of conflict.
- The conflict’s impact on international relations will likely involve shifts in economic and political partnerships. Countries may re-evaluate their trade and diplomatic relationships, potentially forming new blocs based on shared security interests.
- The precedent set by Ukraine’s case may encourage other nations to pursue similar membership aspirations, creating a ripple effect across the globe and influencing international relations in new and unpredictable ways.
Potential for Conflict Escalation or De-escalation
The inclusion of Ukraine in NATO presents a significant risk of conflict escalation. However, it is also possible for the situation to de-escalate through diplomatic engagement and strategic adjustments. The outcome will depend on the actions of all parties involved, including Ukraine, NATO, Russia, and other actors in the region.
- Escalation is possible if Russia views Ukraine’s NATO membership as a direct threat to its security interests and responds with a more aggressive military posture. Examples of this include the invasion of Ukraine in 2022.
- De-escalation could occur through negotiations and diplomatic initiatives aimed at mitigating security concerns. Examples such as the Minsk agreements (though unsuccessful in the Ukrainian conflict) show the potential for diplomatic solutions.
- The path taken will depend heavily on the willingness of all parties to engage in constructive dialogue and find common ground.
Potential Scenarios and Probable Consequences
A table outlining potential scenarios and their probable consequences illustrates the complex nature of this situation. The scenarios are hypothetical, but they are based on known historical patterns and current geopolitical dynamics.
| Scenario | Probable Consequences |
|---|---|
| NATO Membership Approved; Russia Responds with Limited Military Actions | Increased tension, potential for localized conflict, diplomatic efforts to de-escalate |
| NATO Membership Approved; Russia Responds with Aggressive Military Actions | Significant escalation of conflict, potential for regional war, significant shifts in international relations |
| NATO Membership Rejected; Ukraine Maintains its Aspirations | Continued tensions, potential for future conflicts, protracted diplomatic standoff |
Security Implications and Challenges
The escalating security situation in Eastern Europe, driven by Russia’s actions, presents profound challenges for NATO’s collective defense strategy and the stability of the region. Ukraine’s aspirations for NATO membership, coupled with the growing resolve of Eastern European members like Poland, Romania, and Lithuania, has heightened tensions and necessitated a careful consideration of potential responses. Understanding the security implications and the potential challenges in implementing NATO’s support for Ukraine is crucial for navigating this complex geopolitical landscape.
Security Challenges Posed by Russia’s Actions
Russia’s military actions in the region have created a volatile security environment. The invasion of Ukraine, coupled with the ongoing military buildup and rhetoric, has fostered an atmosphere of uncertainty and fear among neighboring nations. The potential for further escalation, including the use of chemical or biological weapons, adds another layer of complexity to the existing threats. These actions have destabilized the region, prompting concerns about the future of European security.
Implications for NATO’s Collective Defense Strategy
NATO’s collective defense strategy, enshrined in Article 5, is under unprecedented strain. The invasion of Ukraine, and the potential for further Russian aggression, forces a reassessment of the alliance’s posture and its response capabilities. The need to strengthen deterrence, bolstering the Eastern Flank, and enhancing the alliance’s rapid response mechanisms becomes paramount. The security of member states directly bordering Russia, and those with a history of conflict, now depends on NATO’s ability to effectively deter future aggression.
Possible Responses to Russian Concerns
Addressing Russian concerns is a complex diplomatic endeavor. Open dialogue, focused on security guarantees and reducing regional tensions, is essential. However, any response must be firm, demonstrating NATO’s unwavering commitment to the territorial integrity and sovereignty of its members. Negotiations aimed at de-escalation and establishing a framework for future cooperation are critical. The aim is not just to contain Russian aggression, but to find pathways toward a more stable and predictable security architecture.
Potential Challenges in Implementing NATO’s Support for Ukraine
Providing support to Ukraine faces numerous practical and political hurdles. The logistical challenges of supplying weapons, training personnel, and coordinating military aid are significant. Political disagreements among member states on the level and type of support can hinder effectiveness. Maintaining public support for a prolonged commitment to Ukraine’s defense is crucial, particularly as the conflict continues.
NATO’s eastern flank is firmly backing Ukraine’s membership, with Poland, Romania, and Lithuania vocal in their support. Meanwhile, oil prices are continuing their upward trend this week, with China and the US reportedly resuming trade talks, potentially impacting global markets. This geopolitical tension, combined with fluctuating energy costs, underscores the interconnectedness of global events and their potential effect on Ukraine’s future.
It’s a complex situation with many moving parts.
Security Threats, NATO Responses, and Potential Outcomes
| Security Threat | NATO Response | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Russian military aggression against a NATO member state | Invoking Article 5, deploying troops and military assets, enhancing defensive capabilities, and imposing sanctions | Deterrence of further aggression, potential escalation, or a negotiated resolution |
| Russian cyberattacks targeting critical infrastructure | Strengthening cybersecurity defenses, sharing intelligence, and coordinating response mechanisms | Reduced effectiveness of cyberattacks, enhanced resilience of infrastructure, potential for escalation |
| Russian disinformation campaigns aimed at undermining NATO unity | Counter-disinformation efforts, strengthening media literacy, and promoting transparency | Reduced effectiveness of disinformation campaigns, strengthened public trust, potential for further escalation |
| Russian support for proxy conflicts | Providing humanitarian aid, training, and military support to affected countries | Deterrence of proxy conflicts, regional stability, and potential for escalation |
Public Perception and Diplomacy
Public opinion plays a crucial role in shaping political decisions regarding Ukraine’s NATO membership aspirations. Understanding the nuanced perspectives in Poland, Romania, Lithuania, and Ukraine is essential for navigating the complexities of this issue. The diplomatic efforts to address concerns, as well as the potential impact on political decisions, must be carefully considered. International organizations play a vital mediating role in fostering dialogue and solutions.Public sentiment varies across these nations, reflecting diverse historical experiences, security concerns, and geopolitical considerations.
The strength of support for Ukraine’s aspirations, as well as the willingness to potentially engage in conflict, varies significantly. Diplomatic efforts to address these varying viewpoints are essential to ensure a unified and effective response to the evolving security landscape.
Public Opinion in Key Countries, Nato east flank backs ukraine membership poland romania lithuania say
Public opinion in Poland, Romania, Lithuania, and Ukraine regarding NATO membership is multifaceted. While strong support for Ukraine’s aspirations exists in some segments of the population, concerns about potential security implications, economic costs, and the political ramifications of NATO expansion are also present. This complex interplay of opinions necessitates careful consideration and open dialogue. The degree of support and the reasons behind it vary significantly among these nations.
Diplomatic Efforts to Address Concerns
Various diplomatic channels are utilized to address concerns from different parties. These efforts include bilateral talks, multilateral summits, and engagement with international organizations. The effectiveness of these strategies depends on their ability to address the specific concerns of each country, acknowledge their differing perspectives, and foster a shared understanding of the situation.
Role of International Organizations
International organizations, such as the United Nations and the OSCE, play a crucial role in mediating the situation. Their presence provides a platform for dialogue, facilitating communication between nations and helping to build consensus. Their role extends beyond mere observation; they contribute actively to finding solutions and mediating disputes.
Potential Impact on Political Decisions
Public opinion significantly influences political decisions related to NATO expansion and Ukraine’s membership. Governments are compelled to consider public sentiment when formulating policies. The political landscape in each country dictates the degree of influence public opinion holds. This is especially true in countries with strong democratic traditions, where public opinion is a major factor in shaping political choices.
Table of Diplomatic Efforts
| Country/Organization | Diplomatic Effort | Focus |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Bilateral meetings with key European nations | Building consensus and coordinating responses |
| NATO | Summit meetings and consultations | Addressing security concerns and strengthening alliances |
| European Union | Joint statements and initiatives | Promoting stability and coordinating aid packages |
| Ukraine | Direct outreach to allies | Advocating for membership and highlighting security concerns |
Final Summary: Nato East Flank Backs Ukraine Membership Poland Romania Lithuania Say
In conclusion, the NATO east flank’s backing of Ukraine’s membership application underscores a significant escalation in the East European security crisis. The decision, driven by shared security concerns and a desire to deter further Russian aggression, carries significant implications for regional stability and international relations. While the path forward is fraught with potential challenges, the commitment of the NATO nations to Ukraine’s security signifies a firm stance against further Russian expansionism.







