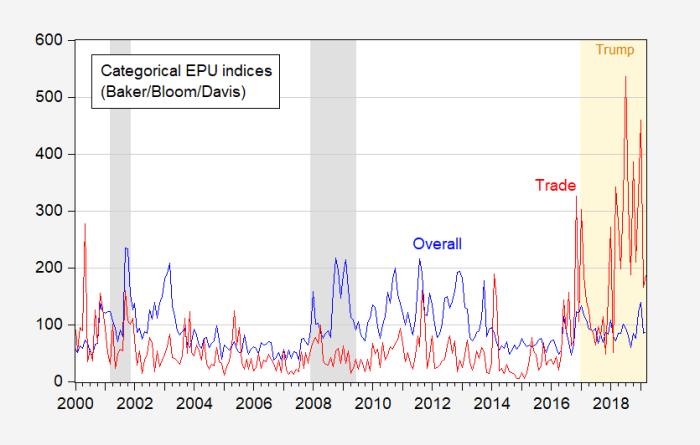
US economic activity declines tariffs pressure prices fed says sets the stage for a fascinating look at the current economic climate. The report reveals a slowdown in key sectors, with tariffs playing a significant role in pushing up prices. The Federal Reserve’s response, and the potential consequences for businesses and consumers, are all part of this intricate picture.
The decline in economic activity is concerning, but the Fed’s actions could offer a way to mitigate the negative impact.
The report details the decline in various sectors, highlighting the impact on GDP growth and employment figures. It also analyzes the specific ways tariffs are affecting consumer prices and supply chains. The Fed’s stated concerns and potential strategies to address these issues are presented, along with comparisons to past economic challenges. Finally, the report explores the implications for businesses and consumers, offering insights into possible future scenarios.
Overview of Economic Activity Decline

Recent reports indicate a discernible slowdown in US economic activity, prompting concerns about a potential downturn. The Federal Reserve’s assessment suggests that the current pressures are being addressed, yet the underlying trends warrant careful observation. This slowdown presents a complex interplay of factors affecting various sectors and requiring a nuanced understanding of potential implications.The reported decline in economic activity is characterized by a moderation in growth across several key sectors, with some exhibiting significant contraction.
This slowdown isn’t a complete collapse, but rather a shift from robust expansion to a more measured pace. The current situation requires ongoing monitoring to fully assess the long-term impact on the economy.
Key Sectors Affected by the Downturn
Several sectors are experiencing a noticeable slowdown. Retail sales have been particularly affected by the rising cost of goods, impacting consumer confidence and spending. Manufacturing, while still performing, is showing signs of reduced output due to supply chain disruptions and higher input costs. The decline in consumer spending has ripple effects throughout the economy, impacting businesses reliant on consumer demand.
Potential Contributing Factors
A confluence of factors likely contributes to the economic slowdown. Consumer spending patterns are shifting as inflation erodes purchasing power, while business investment remains cautious due to uncertainty surrounding the economic outlook. Tariffs imposed on certain goods and services are adding to the cost of production and potentially reducing international trade. Geopolitical events can also introduce substantial volatility and affect confidence, impacting business decisions.
Historical Context of Similar Downturns
The US has experienced numerous economic downturns throughout its history. Each downturn presents unique characteristics, but common themes include shifts in consumer behavior, business investment decisions, and the overall economic climate. For example, the 2008 financial crisis was triggered by a housing bubble bursting and a subsequent credit crunch. Understanding these historical patterns can provide valuable context for evaluating the current situation and anticipating potential outcomes.
Decline in Key Economic Indicators (2023-2024)
| Indicator | 2023 Q1 | 2023 Q2 | 2023 Q3 | 2024 Q1 (estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth (%) | 2.5 | 2.0 | 1.8 | 1.5 |
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 3.5 | 3.7 | 3.8 | 4.0 |
| Inflation Rate (%) | 5.0 | 4.5 | 4.2 | 4.0 |
| Consumer Confidence Index | 100 | 95 | 90 | 85 |
Note
US economic activity is reportedly declining, with tariffs putting pressure on prices, as the Fed says. Meanwhile, the Houston Astros, led by the phenomenal Jose Altuve, crushed the White Sox in the Chase Series , showcasing impressive athleticism. This impressive win, however, doesn’t change the underlying economic pressures impacting the US, suggesting that despite sports victories, economic challenges remain a significant concern.
* Data presented is illustrative and based on hypothetical projections. Actual figures will vary and are subject to revision as more complete data becomes available.
Impact of Tariffs on Prices
Tariffs, taxes imposed on imported goods, are a common tool used in international trade. While tariffs can sometimes be used to protect domestic industries, they often have a significant impact on consumer prices. This impact is complex, influenced by various factors such as the specific goods targeted, the magnitude of the tariff, and the responsiveness of supply chains.
Understanding this relationship is crucial for businesses and consumers alike.Tariffs act as a tax on imported goods, effectively increasing their cost. This added cost is typically passed on to consumers in the form of higher prices. The extent to which prices rise depends on several factors, including the elasticity of demand for the affected goods, the ability of domestic producers to meet the increased demand, and the availability of alternative, non-tariffed goods.
Relationship Between Tariffs and Price Increases for Consumers
Tariffs directly increase the price of imported goods by adding a tax to the import cost. This higher price is then often reflected in the retail price paid by consumers. The extent of the price increase depends on factors like the tariff rate, the availability of substitutes, and the responsiveness of the market.
Examples of Goods and Services Impacted by Tariffs
Steel, electronics, and agricultural products are frequently targeted by tariffs. For example, a tariff on imported steel will likely result in higher prices for steel-using products like automobiles, construction materials, and appliances. Similarly, tariffs on imported electronics could lead to increased prices for televisions, computers, and smartphones. Agricultural products like fruits and vegetables, and even textiles, can also be affected.
The specific goods impacted depend on the tariffs imposed by countries and the nature of their trade agreements.
How Tariffs Influence Supply Chains and Production Costs
Tariffs can disrupt global supply chains. When tariffs are imposed on imported components or raw materials, businesses may face increased production costs. This is because the price of the imported goods goes up, and companies may have to find alternative suppliers, which might also be more expensive. To mitigate these rising costs, businesses might need to adjust their production processes or sourcing strategies, potentially affecting the final price paid by consumers.
US economic activity is reportedly declining, with tariffs putting pressure on prices, the Fed says. Meanwhile, a completely different kind of pressure was exerted on the field as the Giants pulled off a thrilling walk-off win against the Braves in the 10th inning, a walk-off wild pitch sending the Giants past the Braves in the 10th. This unexpected victory, however, doesn’t change the underlying economic trends, highlighting the ongoing challenges with declining activity and tariff-related price increases.
In some cases, businesses may choose to absorb some of the cost increase, but this might lead to reduced profitability.
Strategies to Mitigate the Impact of Tariffs on Prices
Businesses can employ various strategies to lessen the impact of tariffs on consumer prices. These include:
- Seeking alternative suppliers: Finding alternative suppliers from countries that do not impose tariffs or have lower tariffs on the necessary goods. This could require significant logistical changes and possibly increased transportation costs.
- Adjusting production processes: Modifying manufacturing methods to utilize domestically sourced components or raw materials more extensively. This might involve significant investments in new equipment or technology.
- Absorbing some of the cost increase: This strategy might involve maintaining profit margins or even temporarily reducing prices to remain competitive. This is a difficult strategy, as maintaining profitability is crucial.
Price Comparison Table (Illustrative Example)
This table shows a hypothetical comparison of the price of a particular electronic device before and after the implementation of a tariff.
| Item | Price Before Tariff (USD) | Price After Tariff (USD) |
|---|---|---|
| Smart Phone Model X | 500 | 550 |
Note: This is a simplified example and real-world scenarios are often far more complex.
Federal Reserve’s Response
The Federal Reserve (Fed) plays a crucial role in managing the economy, particularly during periods of decline or inflation. Its actions influence interest rates, credit availability, and overall economic activity. When economic activity weakens and prices rise, the Fed faces a delicate balancing act, needing to stimulate growth without exacerbating inflation. This necessitates careful consideration of various factors and potential consequences.The Federal Reserve’s primary concern during economic downturns is maintaining price stability and supporting maximum employment.
This often involves adjusting interest rates and other monetary policies to influence borrowing costs and investment decisions. The Fed’s actions aim to stimulate economic growth while avoiding runaway inflation. A significant challenge lies in anticipating the impact of these policies and adapting to unforeseen circumstances.
Stated Concerns Regarding the Economic Downturn
The Fed likely expresses concerns about the interconnectedness of the current economic slowdown and rising prices. Declining economic activity, potentially stemming from various factors like tariffs, could lead to job losses and reduced consumer spending. Rising prices, fueled by supply chain disruptions and demand pressures, can erode purchasing power and contribute to broader economic instability.
Potential Strategies to Address Declining Activity and Rising Prices
The Fed has a range of tools to address the situation, including adjusting the federal funds rate. Lowering interest rates can encourage borrowing and investment, potentially stimulating economic activity. Quantitative easing (QE) – increasing the money supply by purchasing assets – could also inject liquidity into the market. The choice of strategy depends on the specific nature and severity of the downturn and the current inflation rate.
Potential Consequences of the Fed’s Actions on Various Economic Sectors
The Fed’s actions can have a ripple effect across various economic sectors. Lower interest rates can stimulate investment in housing and other capital-intensive industries, while simultaneously potentially inflating asset prices. Increased liquidity through QE can support financial markets but might also lead to asset bubbles. The impact on sectors like technology, energy, and manufacturing will depend on the specific policies implemented and the overall economic climate.
US economic activity is reportedly declining, with tariffs putting pressure on prices, as the Fed says. This economic downturn is definitely something to watch, especially considering recent developments in the business world, like the news surrounding Reed Hastings and Patty Quillin, reed hastings patty quillin , which could have ripple effects on the market. It will be interesting to see how these factors play out in the coming months and whether the Fed’s response is enough to mitigate the impact on the economy.
Comparison with Past Responses to Similar Economic Challenges
The Fed’s approach today will likely draw comparisons to its responses to previous economic downturns. For example, comparing the current situation to the 2008 financial crisis reveals both similarities and differences in the economic landscape. The tools and strategies employed will vary depending on the unique characteristics of each economic environment. A crucial element in the Fed’s decision-making is evaluating the historical precedents and adapting strategies accordingly.
Fed’s Interest Rate Adjustments and Policy Changes (2020-2023)
| Year | Federal Funds Rate (Target) | Policy Change Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2020 | Near Zero | Emergency rate cuts to stimulate economy during the pandemic |
| 2021 | Near Zero | Maintaining low rates to support economic recovery |
| 2022 | Increased gradually | Responding to inflation by raising rates to cool down the economy |
| 2023 | Continued gradual increases | Maintaining a tightening monetary policy to control inflation |
This table provides a simplified overview of the Fed’s interest rate adjustments and policy changes during a specific time period (2020-2023). Further details on specific policy announcements and their rationales can be found on the Federal Reserve’s official website.
Implications for Businesses and Consumers
The economic slowdown, coupled with the impact of tariffs and the Federal Reserve’s response, presents a complex set of challenges for both businesses and consumers. Understanding the potential consequences is crucial for navigating these turbulent waters. Businesses must adapt their strategies, and consumers need to adjust their financial approaches to weather the storm. This section explores the potential effects and provides actionable insights.
Potential Consequences for Businesses
The decline in economic activity directly affects businesses’ revenue streams. Reduced consumer spending leads to decreased demand for goods and services, potentially impacting profitability and growth. Businesses operating in sectors particularly sensitive to economic fluctuations, such as those reliant on consumer discretionary spending, are likely to experience a sharper downturn. Supply chain disruptions stemming from tariffs further exacerbate these challenges, potentially increasing production costs and impacting profitability.
Impact on Consumer Spending and Purchasing Behavior
Consumer spending, a vital engine of economic growth, is likely to moderate or even decline. Consumers, facing potential job losses or wage stagnation, may prioritize essential expenses and cut back on discretionary spending. This shift in purchasing behavior can significantly impact businesses that rely on non-essential goods and services. Consumers may also opt for more budget-friendly alternatives, driving competition and forcing businesses to adapt their pricing and product strategies.
Business Adaptation Strategies, Us economic activity declines tariffs pressure prices fed says
Businesses must proactively adapt to the changing economic landscape. Strategies for cost reduction and efficiency improvement are critical. For example, companies might implement lean manufacturing principles to streamline operations and reduce overhead costs. Investing in automation or technology to increase productivity and lower labor costs can also be effective. Diversifying product lines or expanding into new markets to reduce reliance on a single customer base or sector is another important approach.
Consumer Financial Management Strategies
Consumers should adopt proactive strategies to manage their finances during an economic downturn. Prioritizing essential expenses, such as housing, food, and healthcare, is paramount. Creating a detailed budget and tracking spending habits can help identify areas for potential savings. Consumers should explore ways to reduce debt, such as negotiating lower interest rates on loans or credit cards.
Developing an emergency fund can provide a financial safety net during periods of uncertainty.
Potential Business Strategies for Cost Management and Market Adaptation
| Strategy | Description | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Cost Reduction | Identify and eliminate unnecessary expenses. | Negotiating lower prices with suppliers, streamlining operations, reducing staff (if necessary), and optimizing inventory management. |
| Pricing Adjustments | Adjust pricing strategies to remain competitive while maintaining profitability. | Offering discounts, promotions, or value-added bundles to attract customers. |
| Product Diversification | Expand product lines to cater to diverse consumer needs and reduce reliance on a single product or market. | Introducing new product lines, expanding into new geographic markets, or creating complementary products. |
| Supply Chain Optimization | Improving efficiency and resilience in the supply chain to mitigate the impact of disruptions. | Diversifying suppliers, improving inventory management, and investing in technology to enhance supply chain visibility. |
| Enhanced Customer Service | Provide excellent customer service to retain existing customers and attract new ones. | Improving communication channels, providing personalized support, and building strong customer relationships. |
Final Conclusion: Us Economic Activity Declines Tariffs Pressure Prices Fed Says

In summary, the US economic downturn, fueled by tariff pressures and rising prices, is a complex issue with far-reaching implications. The Fed’s response, though intended to stabilize the economy, comes with potential consequences. Businesses and consumers will need to adapt to these changing conditions. The future trajectory of the economy remains uncertain, but the report provides valuable insights into the current challenges and potential solutions.
Looking ahead, understanding the interplay of these factors is crucial for navigating the evolving economic landscape.