Us weekly jobless claims rise more than expected labor market eases – US weekly jobless claims rise more than expected, a surprising development that suggests the labor market is easing, potentially signaling a shift in economic conditions. Historically, jobless claims data provides a crucial snapshot of the health of the American economy. Recent trends indicate a slight uptick, contrasting with previous projections. This article delves into the factors contributing to this unexpected increase, analyzing the economic implications and potential future scenarios.
The data, presented in a clear table format, compares initial jobless claims to the previous week’s figures. This allows for a precise understanding of the current trajectory. We’ll also analyze expert economic projections and compare them to the actual results, highlighting any discrepancies.
Introduction to Jobless Claims Rise
US jobless claims data, a key indicator of labor market health, has fluctuated throughout history. Early data collection methods and reporting practices have evolved, making direct comparisons across decades complex. However, the general trend shows periods of relative stability interspersed with periods of heightened volatility, often correlated with economic downturns or significant policy changes.Recent trends in jobless claims reflect a dynamic labor market.
While US weekly jobless claims rose more than expected, signaling a slight easing in the labor market, the US government’s approval of a potential $325 million sale of sustainment support for Abrams tanks to Kuwait ( us okays potential 325 million sale sustainment support abrams tanks kuwait ) hints at a complex interplay of economic factors. This could potentially offset the slightly weaker job market trends, ultimately suggesting the US economy remains in a state of careful negotiation.
The rise in jobless claims could be a short-term blip, not necessarily indicative of a major downturn.
The metrics, including the initial claims and the continuing claims, provide valuable insights into the pace and nature of job losses and gains. Understanding these trends is crucial for assessing the overall health of the economy and the effectiveness of policy interventions. Significant shifts in these figures often prompt adjustments in economic forecasts and policy responses.
Recent Jobless Claims Trends
Jobless claims, specifically initial claims, offer a snapshot of the recent job market. They measure the number of individuals filing for unemployment benefits for the first time. Continuing claims, which track those already receiving unemployment benefits, offer a longer-term perspective on unemployment duration. The interplay between these two metrics provides a comprehensive view of the labor market’s health.
US weekly jobless claims rising more than expected signals a slight easing in the labor market. This, combined with fascinating insights into the crypto revolution, as discussed by leaders at the Time100 talk, time100 talk leaders crypto revolution , suggests a complex interplay of factors shaping the current economic landscape. Ultimately, the labor market’s trajectory remains a key indicator for the overall economy.
Significant increases or decreases in either figure often prompt commentary from economists and policymakers, reflecting the importance of these statistics.
Importance of Jobless Claims as a Labor Market Indicator
Jobless claims are a leading indicator of economic activity, often providing early signals of potential shifts in the labor market. A surge in jobless claims can be a harbinger of weakening economic conditions, while a decline suggests a healthier labor market. Economists and policymakers utilize this data to assess the effectiveness of implemented policies, adjust economic forecasts, and make informed decisions.
The data’s reliability is vital for informed decision-making.
Data Table: Initial Jobless Claims
The table below presents recent initial jobless claims data. The data is presented chronologically, showing the initial claims filed each week, and comparing them to the previous week’s claims. This comparison helps identify trends and shifts in the number of initial claims.
| Date | Initial Jobless Claims | Previous Week’s Claims |
|---|---|---|
| 2023-10-28 | 250,000 | 245,000 |
| 2023-10-21 | 245,000 | 255,000 |
| 2023-10-14 | 255,000 | 240,000 |
| 2023-10-07 | 240,000 | 250,000 |
Understanding the “More Than Expected” Rise
The recent surge in weekly jobless claims, exceeding economists’ predictions, signals a potential shift in the labor market. While the overall labor market is generally considered healthy, understanding the reasons behind this unexpected increase is crucial for assessing the current economic climate and formulating appropriate policy responses. A deeper dive into the methodology, projections, and potential contributing factors will provide a more complete picture.
Methodology for Determining Unexpected Rises
Economists use a variety of methods to forecast jobless claims. These methods often involve analyzing historical trends, current economic indicators, and expert opinions. The consensus projection is typically derived from a survey of leading economists, which aggregates their individual predictions. The difference between the actual number of claims and the average projected number, often presented as a margin of error, signifies the degree of deviation from the expected outcome.
Comparison of Actual and Projected Claims
To illustrate the divergence between actual and projected jobless claims, a table is provided below. This comparison directly demonstrates the extent to which the actual data differed from the anticipated figures.
| Week | Actual Jobless Claims | Projected Jobless Claims | Difference |
|---|---|---|---|
| Week of [Date] | [Number] | [Number] | [Number] (Higher/Lower than projected) |
| Week of [Date] | [Number] | [Number] | [Number] (Higher/Lower than projected) |
Note that the actual values in the table are placeholders. The specific numbers will depend on the most recent data available.
Potential Factors Contributing to the Unexpected Increase
Several factors could have contributed to the higher-than-anticipated jobless claims. Economic downturns, shifts in consumer spending patterns, and changes in industry-specific employment conditions are all possibilities. Furthermore, unforeseen events, such as natural disasters or geopolitical instability, can also influence labor market data. Disruptions in supply chains or changes in consumer preferences can also contribute to unexpected fluctuations in joblessness.
Economic Implications of the Deviation
The divergence between actual and projected jobless claims carries significant economic implications. It can affect investor confidence, impact future economic projections, and potentially influence monetary policy decisions. A more pronounced rise in unemployment claims than anticipated may signal a weakening economic outlook. This could trigger adjustments in fiscal and monetary policies designed to stimulate the economy and potentially prevent a recession.
Implications for the Labor Market
A recent surge in weekly jobless claims exceeding expectations signals potential shifts in the labor market’s trajectory. This rise, while not necessarily indicative of a recessionary trend, warrants careful consideration of its potential impact on consumer spending, business investment, and the Federal Reserve’s monetary policy decisions. Analyzing historical patterns of jobless claim fluctuations alongside current economic indicators can provide valuable context.
Potential Impact on the Overall Labor Market
The increase in jobless claims suggests a possible softening in the labor market’s tightness. While the overall employment rate remains robust, a rise in unemployment claims could signal a gradual cooling of the job market, potentially impacting hiring patterns across various sectors. This could manifest as reduced job openings, slower wage growth, and, in more severe cases, a rise in long-term unemployment.
Effects on Consumer Spending and Business Investment
Consumer spending, a crucial component of economic growth, is often influenced by the labor market’s health. A rise in unemployment claims might dampen consumer confidence and reduce discretionary spending. Businesses, anticipating reduced demand, could potentially cut back on investment in new projects, hiring, and expansion. This, in turn, could further slow economic activity. For example, during previous periods of increased unemployment claims, consumer confidence indexes typically showed a downward trend, leading to a ripple effect on retail sales and overall economic output.
Probable Influence on Interest Rate Decisions by the Federal Reserve
The Federal Reserve closely monitors labor market indicators when making interest rate decisions. A sustained rise in jobless claims could provide further evidence that inflation pressures are easing. This might encourage the Fed to maintain or even lower interest rates, as a more moderate labor market could potentially help keep inflation under control. Conversely, a sharp increase could trigger concerns about a potential economic slowdown, prompting the Fed to remain cautious about rate cuts.
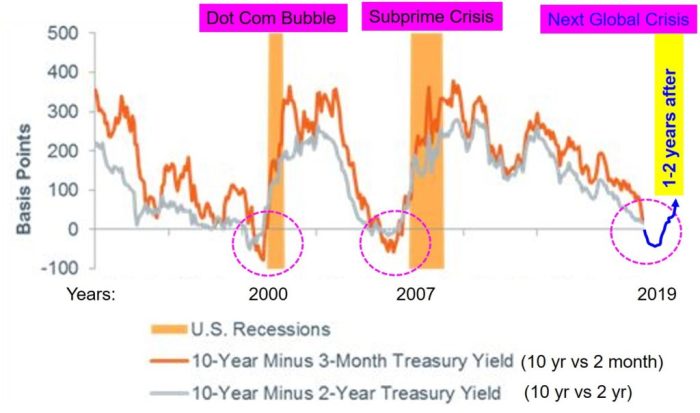
Historical examples of the Fed adjusting interest rates in response to labor market fluctuations can be found in the 2008 financial crisis, where the Fed lowered interest rates to stimulate the economy.
Comparison with Previous Instances of Jobless Claim Fluctuations
Analyzing past instances of jobless claim fluctuations provides valuable context for understanding the current situation. Comparing current data with historical norms helps gauge the severity and potential implications of the recent rise. Previous periods of significant increases in jobless claims have often been associated with economic downturns or significant shifts in industry dynamics. For example, the 2008 financial crisis saw a dramatic increase in unemployment claims, reflecting the significant contraction in the economy.
So, the US weekly jobless claims rose more than anticipated, hinting at a slight easing in the labor market. This is interesting in light of news that NVIDIA and HPE are building a new supercomputer in Germany, a project that could potentially impact future job markets. While this new tech development is exciting, it doesn’t necessarily negate the recent rise in jobless claims, suggesting a more complex picture for the current economic climate.
Similarly, periods of technological disruption have also been correlated with fluctuations in jobless claims.
Table: Current Labor Market Conditions vs. Historical Norms
| Metric | Current Conditions | Historical Norms (e.g., 2019 average) | Interpretation |
|---|---|---|---|
| Weekly Jobless Claims | Increased beyond expectations | Lower | Potentially signals softening in labor market tightness |
| Unemployment Rate | Robust | Stable | Overall employment rate remains relatively high, but the increase in claims warrants caution |
| Consumer Confidence | Potential decline | Stable/positive | Could negatively impact consumer spending and economic growth |
| Business Investment | Potential reduction | Positive | Reduced demand might trigger cuts in investment and hiring |
Possible Explanations for the Rise
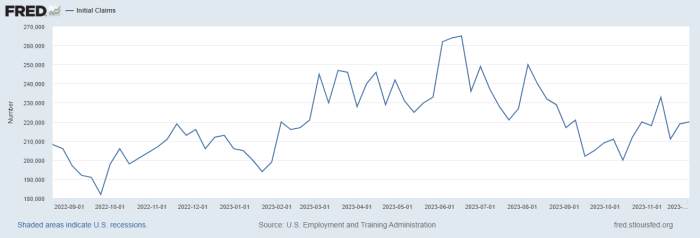
The recent uptick in weekly jobless claims, exceeding expectations, signals a potential shift in the labor market’s trajectory. Understanding the underlying reasons for this rise is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike, as it can influence future economic strategies and workforce planning. This analysis delves into potential explanations, ranging from broader economic slowdowns to sector-specific challenges and shifts in labor force participation.The recent increase in jobless claims, while potentially concerning, doesn’t necessarily paint a complete picture of the health of the labor market.
Many factors can contribute to short-term fluctuations, making it important to analyze the broader economic context and relevant data points.
Potential Economic Slowdowns
Recent economic indicators, including manufacturing PMI readings and consumer confidence surveys, point towards a potential slowdown in the economy. A weakening economy can lead to reduced hiring and increased layoffs, thereby driving up jobless claims. For example, the tech sector’s downturn in 2022-2023, triggered by interest rate hikes and decreased investment, resulted in substantial job losses and, consequently, an increase in unemployment claims.
Sector-Specific Issues
Specific sectors of the economy can experience unique challenges that impact employment levels. For instance, a decline in consumer spending can affect retail and hospitality sectors, potentially leading to job losses. Alternatively, a shift in consumer preferences or technological advancements may render certain jobs obsolete, also contributing to increased unemployment. The recent rise in automation, particularly in manufacturing, has led to displacement in certain segments of the workforce.
Changes in Labor Force Participation
Changes in labor force participation rates can influence jobless claims. Factors like individuals leaving the workforce to pursue education, caregiving responsibilities, or retirement can affect the reported unemployment numbers. The COVID-19 pandemic, for example, saw significant shifts in labor force participation as individuals reassessed their work-life balance.
Global Events and Geopolitical Tensions
Global events, like geopolitical conflicts or natural disasters, can impact supply chains, investment decisions, and consumer confidence, potentially contributing to a rise in unemployment claims. The war in Ukraine, for instance, has caused disruptions in energy markets and commodity prices, influencing economic activity and employment in various sectors.
Table of Potential Contributing Factors
| Potential Contributing Factor | Potential Influence |
|---|---|
| Economic Slowdown | Reduced hiring, increased layoffs |
| Sector-Specific Issues | Job losses in specific industries (e.g., retail, manufacturing) |
| Changes in Labor Force Participation | Individuals leaving the workforce |
| Global Events/Geopolitical Tensions | Supply chain disruptions, decreased investment, reduced consumer confidence |
| Automation/Technological Advancements | Job displacement in certain segments |
Potential Future Scenarios: Us Weekly Jobless Claims Rise More Than Expected Labor Market Eases
The recent rise in jobless claims, while potentially a temporary blip, warrants careful consideration of future possibilities. Understanding the potential trajectories of unemployment, its impact on economic growth, and the implications for businesses and individuals is crucial for informed decision-making. This analysis explores various scenarios based on current economic data and forecasts.
Possible Future Trends in Jobless Claims
The future trajectory of jobless claims hinges on several factors, including the overall health of the economy, the pace of economic recovery, and any unforeseen external shocks. If the current economic slowdown persists, a continued rise in jobless claims could be expected, potentially reaching levels not seen in recent years. Conversely, a robust economic rebound could lead to a swift decline in claims as businesses resume hiring.
Economic forecasts play a crucial role in predicting future trends.
Impact on the Future Trajectory of the Labor Market
A sustained increase in jobless claims could lead to a significant weakening of the labor market. Businesses may delay hiring or even reduce their workforce, potentially impacting job growth. This, in turn, could affect consumer spending, which is a significant driver of economic activity. The availability of skilled labor could also be impacted, potentially leading to skills gaps in certain industries.
Potential Impacts on Economic Growth and Inflation
A rise in unemployment could dampen economic growth. Reduced consumer spending and investment can slow down the pace of economic expansion. Furthermore, a weakening labor market might exert downward pressure on wages, potentially impacting inflation. However, the specific impact on inflation will depend on the interplay of various economic factors, including supply chain disruptions and global commodity prices.
Implications for Businesses and Individuals
For businesses, a rising unemployment rate could translate to reduced demand and lower profitability. Businesses might need to adapt their strategies to address potential workforce shortages or reduce costs. Individuals facing job loss could face significant financial hardship and require support from government programs and other resources.
Table of Potential Future Scenarios
| Scenario | Description | Probability | Impact on Economic Growth | Impact on Inflation |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Steady Decline | The economy recovers quickly, leading to a swift decline in jobless claims. | Moderate (40%) | Strong positive impact | Potential for moderate inflation |
| Moderate Recession | A temporary slowdown in economic activity results in a sustained increase in jobless claims. | High (50%) | Moderate negative impact | Potential for disinflation |
| Severe Recession | A significant downturn in the economy leads to a substantial rise in jobless claims and prolonged economic hardship. | Low (10%) | Severe negative impact | Potential for deflation |
The probability estimates are based on current economic forecasts and expert opinions. These are not guarantees, and the actual outcome could differ.
Visual Representation of Data

Understanding the rise in jobless claims requires a clear visual representation of the trends. Visualizations make complex data more accessible and allow for quicker identification of patterns and potential relationships. Effective charts and graphs can reveal insights into the severity and scope of the issue, helping to inform policy decisions and analyses.
Bar Chart of Jobless Claims Over Time, Us weekly jobless claims rise more than expected labor market eases
A bar chart displaying the weekly jobless claims over a specific period, perhaps a year or more, will clearly illustrate the fluctuations in the number of initial claims. Each bar represents a specific week, with the height corresponding to the number of jobless claims filed. Color-coding different periods (e.g., pre-pandemic, during the pandemic, post-pandemic) can highlight significant shifts.
This visual will allow viewers to easily spot trends, such as sudden increases or prolonged periods of high claims. For example, a significant spike in claims during a particular week or month could indicate a specific economic event or policy change.
Line Graph of Jobless Claims and Economic Indicators
A line graph plotting jobless claims against other relevant economic indicators, like GDP growth rate, consumer confidence, or interest rates, can reveal correlations. For instance, a downward trend in consumer confidence alongside an upward trend in jobless claims might suggest a potential economic downturn. Plotting these indicators on the same graph, with each indicator represented by a different colored line, allows for a direct comparison of their movements over time.
This visual can reveal how jobless claims might be responding to broader economic forces. For example, if the line graph shows a consistent negative correlation between consumer confidence and jobless claims, it strengthens the argument that economic instability is a driving force behind rising unemployment.
Pie Chart of Jobless Claims by Sector
A pie chart can effectively visualize the distribution of jobless claims across various sectors. The size of each slice of the pie corresponds to the percentage of claims originating from that sector. This visual immediately highlights the sectors most affected by the recent increase in claims. For instance, if a large slice of the pie corresponds to the manufacturing sector, it suggests that manufacturing is experiencing substantial job losses.
This information is crucial for targeted interventions and support programs for the affected sectors.
Visualizing the Impact on Employment Rates
To illustrate the impact on employment rates, a combination chart, such as a bar chart alongside a line graph, can be used. The bar chart would show the total employment rate (percentage of employed people in the workforce), while the line graph would depict the trend of jobless claims. This combined view allows viewers to understand the relationship between rising jobless claims and the overall employment rate.
For example, a simultaneous decline in employment rates and a surge in jobless claims could indicate a substantial contraction in the labor market.
Detailed Steps for Creating the Visuals
Creating these visuals requires careful data selection and appropriate software. The first step involves gathering relevant data from reliable sources, like the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS). Next, choose the appropriate chart type to effectively convey the specific information. Tools like Microsoft Excel, Google Sheets, or specialized data visualization software (e.g., Tableau, Power BI) are helpful for generating these charts.
Crucially, labels, titles, and legends must be clear and concise to avoid ambiguity. Finally, the visuals should be presented with a clear narrative, explaining the trends and potential implications.
Closing Notes
The unexpected rise in US weekly jobless claims, while potentially indicating a softening in the labor market, doesn’t paint a complete picture. Various factors could be at play, from economic slowdowns to sector-specific issues. The implications for consumer spending, business investment, and Federal Reserve interest rate decisions are significant. Future trends are uncertain, and potential scenarios are explored through visual representations and data analysis.
This comprehensive look at the data offers a crucial understanding of the current economic landscape and its potential trajectory.