
Cicada brood XIV emerging what to know? This massive insect invasion is upon us! Get ready for a buzzing summer as these periodical cicadas emerge from the ground. We’ll explore their lifecycle, potential impacts on humans and the environment, and practical tips for navigating this natural phenomenon. From their emergence patterns to their fascinating behavior, this guide will equip you with the knowledge to understand and appreciate these remarkable creatures.
Expect to learn about their typical emergence patterns, timing, and duration. We’ll also dive into the ecological impacts of their arrival, how they interact with human activities, and even some misconceptions surrounding them. Plus, find out how to predict their emergence, what to do when they arrive, and how to manage any potential issues they may cause.
Introduction to Brood XIV Cicadas
Brood XIV cicadas, a fascinating species of periodical cicadas, are renowned for their unique life cycle and synchronized emergence. These insects, characterized by their robust bodies and distinctive calls, play a significant role in the ecological balance of their habitats. Their emergence patterns are predictable, allowing researchers and enthusiasts to anticipate their appearances and study their behavior.Brood XIV cicadas, unlike other cicada species, have a remarkable life cycle that involves an extended subterranean existence before surfacing to complete their life cycle.
This underground period, lasting 17 years, is critical for their survival and adaptation. The emergence of Brood XIV cicadas is a truly impressive display of nature’s synchronicity, impacting various ecosystems in the regions where they appear.
Brood XIV Lifecycle and Distribution
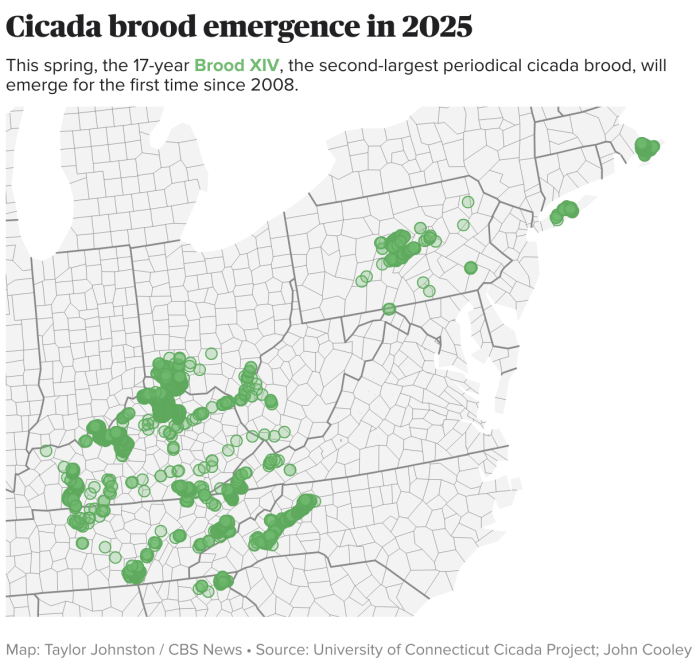
Brood XIV cicadas are a type of periodical cicada, meaning they emerge in a synchronized pattern, with a life cycle spanning 17 years. This prolonged underground phase allows them to develop and mature without significant disruption. Their geographic distribution is primarily confined to the eastern United States, spanning from the southeastern parts of the country, encompassing parts of the Mid-Atlantic region.
Emergence Patterns and Timing
The emergence of Brood XIV cicadas follows a predictable pattern. Their emergence typically occurs over several weeks or months. The exact timing and duration of the emergence are influenced by local environmental factors such as temperature and rainfall. Early emergence is usually associated with warmer temperatures, while later emergence can be linked to cooler weather.
Ecological Significance of Emergence
The emergence of Brood XIV cicadas has a significant impact on the local ecosystem. Their massive numbers provide a vital food source for various animals, from birds and reptiles to mammals and insects. Their nymphs are also a food source for some animals. Furthermore, the decomposition of their shed exoskeletons contributes to soil nutrients, enhancing the fertility of the soil.
This impact is often temporary, but noticeable, and beneficial.
Brood XIV Emergence: A Regional Overview
| Location | Expected Emergence Date | Duration of Emergence | Key Ecological Impacts |
|---|---|---|---|
| Southeastern United States | Typically late spring or early summer | Several weeks to months | Significant impact on the food web; increased nutrient availability in the soil; potential for increased bird activity; increased predation on cicadas by other insects and animals |
| Mid-Atlantic region | Variable, depending on specific location | Variable, depending on location | Similar ecological impact to the Southeastern region, including increased food for various animals, increased predation on cicadas, and nutrient enhancement of the soil. |
| Specific regions within Brood XIV range | Consult specific regional resources for precise timing | Consult specific regional resources for precise timing | Specific ecological impacts may vary depending on local conditions, vegetation, and the presence of other species. |
Cicada Emergence Impacts
Brood XIV cicadas’ emergence, a spectacle for many, can also bring about noticeable changes to human activities, local ecosystems, and economies. The sheer volume of these insects during their brief, yet impactful, life cycle can affect various aspects of daily life, requiring careful consideration and proactive measures.The significant population of emerging cicadas will undoubtedly impact the landscapes, agricultural output, and transportation networks.
Their presence will be a visible and audible part of the environment, demanding adjustments in human routines and activities. Understanding these impacts allows for better preparedness and potential mitigation strategies.
Impacts on Human Activities
The sheer number of cicadas emerging can significantly affect various human activities. Landscaping efforts might need adjustments as cicadas can damage plants and trees. Agricultural operations could experience disruptions due to cicadas’ feeding habits, impacting crop yields. Transportation networks, especially in rural areas, may encounter issues with cicadas’ presence on roads, potentially leading to accidents or maintenance needs.
Understanding these potential impacts allows for proactive measures and better planning.
So, cicada Brood XIV is finally emerging, and it’s a fascinating phenomenon! While the sheer volume of these buzzing insects is quite something, it’s also a reminder of how important it is to understand the legal battles that paved the way for fair treatment in the workplace, like the real-life story behind the movie Lilly Ledbetter movie true story.
Knowing about these historical legal precedents adds another layer of understanding to the sheer scale of the cicada emergence and the larger context of societal shifts. It’s a good time to learn more about Brood XIV, including what to expect and where they’ll be most prevalent.
Impacts on Local Ecosystems and Biodiversity
The emergence of Brood XIV cicadas will have profound effects on the local ecosystems. Their presence will be a significant food source for many species, influencing the balance of the food web. Predators like birds, reptiles, and mammals will benefit from this abundant food source. Conversely, cicada emergence can potentially lead to competition for resources among various animal species.
The presence of cicadas will undoubtedly alter the dynamics of the ecosystem.
Impacts on Local Economies and Tourism
The emergence of Brood XIV cicadas can present both challenges and opportunities for local economies. Increased interest from tourists drawn to observe the phenomenon could boost tourism. However, potential disruptions to agriculture, landscaping, and transportation could negatively impact local businesses. Proactive planning and communication about the emergence can help mitigate these negative effects. For example, businesses could offer cicada-themed activities or merchandise to attract tourists, leveraging the unique event.
Impact Assessment Table
| Affected Area | Impact Type | Severity Level | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|---|
| Landscaping | Plant damage, pest control | Moderate | Regular monitoring, pest control measures, adjusting planting schedules |
| Agriculture | Crop damage, reduced yields | Moderate to High | Crop rotation, protective nets, timely pest control, insurance |
| Transportation | Road accidents, maintenance issues | Low to Moderate | Increased road maintenance, public awareness campaigns, adjusting travel schedules |
| Ecosystems | Food source, predator-prey dynamics | Low to Moderate | Monitoring of ecosystem changes, research on the effects of cicada emergence on local species |
| Tourism | Increased visitor interest, economic boost | High | Promoting cicada emergence as a tourist attraction, creating themed events and merchandise |
Cicada Life Cycle and Behavior
The emergence of Brood XIV cicadas is a fascinating natural event, and understanding their life cycle and behaviors is key to appreciating the spectacle. These periodical cicadas undergo a complex transformation from egg to adult, exhibiting specific behaviors during their brief adult stage. This detailed look at their life cycle will help us appreciate the intricate processes involved in their emergence.Brood XIV cicadas, like all periodical cicadas, have a remarkable life cycle, a subterranean existence punctuated by a sudden, massive emergence.
The time spent underground, feeding on tree roots, is crucial for their development and eventual emergence. Their behavior during this emergence phase is critical to their survival and the continuation of their species.
Egg Stage
The life cycle of Brood XIV cicadas begins with the female cicada laying eggs in the twigs of trees. The eggs hatch into nymphs that fall to the ground. These nymphs will spend the next 13-17 years developing underground, feeding on the roots of trees. This long period of development is a key factor in their ability to avoid predators and synchronize their emergence.
Nymph Stage
The nymphs of Brood XIV cicadas spend a significant portion of their lives underground. During this time, they undergo several molts, shedding their exoskeletons as they grow. They feed on the roots of trees, absorbing nutrients that fuel their development. This underground existence is a critical phase in their life cycle, providing a crucial source of energy and protection from predators.
Emergence Stage
Brood XIV cicadas emerge from the ground as adults, a phenomenon that typically occurs in the spring. The exact timing is dictated by environmental cues, including temperature and moisture levels. The synchronized emergence of millions of cicadas is a remarkable display of nature’s precision.
Adult Stage
The adult cicada stage is short-lived, lasting only a few weeks. During this time, the cicadas’ primary focus is reproduction. They feed on tree sap, using their sharp mouthparts to pierce the bark and suck the nutritious fluid within. This feeding behavior is crucial for providing the energy needed for reproduction. Mating rituals are important for the continuation of the species.
Females lay eggs in twigs of trees, completing the cycle.
Factors Influencing Emergence Timing
The emergence timing of Brood XIV cicadas is influenced by a complex interplay of environmental factors. Temperature and moisture levels are crucial determinants. Specific temperature thresholds trigger the nymphs’ development and their eventual emergence from the ground. These factors also affect the timing of the mating and egg-laying processes, ensuring the species’ continued existence.
Feeding Habits
Brood XIV cicadas, like other cicadas, are herbivores, feeding primarily on the sap of trees. This sap-sucking behavior is a critical aspect of their adult life cycle, providing the energy needed for reproduction and flight. Their sharp mouthparts are specifically adapted for piercing the bark and extracting the sap.
Mating Rituals
Mating rituals are an integral part of the Brood XIV cicada life cycle. Males attract females with their distinctive calls. These calls, often described as buzzing or chirping, are essential for attracting mates and for species recognition. The mating process is brief, focused on reproduction, and essential for the continuation of the species.
Nesting Patterns
Brood XIV cicadas have specific nesting patterns, dictated by the need to lay eggs in suitable tree twigs. This behavior is influenced by various factors, including the availability of suitable host trees. The eggs are laid in the twigs of trees, ensuring the survival of the next generation.
Cicada and Human Interactions
Brood XIV cicadas are a fascinating natural phenomenon, but their emergence also brings about a range of interactions with humans. From the awe-inspiring spectacle of their mass emergence to the potential for some minor inconveniences, understanding these interactions is key to appreciating the full picture of this significant ecological event. This section delves into common misconceptions, behavioral comparisons, potential health risks, and best practices for safe interaction with these magnificent insects.Brood XIV cicadas, like all cicadas, have a complex relationship with human activities.
Their sheer numbers can create a noticeable impact on our daily lives, sparking curiosity and even some apprehension. This section examines the ways in which these interactions manifest and the importance of accurate information to manage these interactions safely and effectively.
Common Misconceptions about Brood XIV Cicadas
Many misconceptions surround the emergence of Brood XIV cicadas. These misconceptions often stem from a lack of understanding about cicada biology and behavior. Clearing up these misunderstandings is crucial for appreciating the natural world and engaging with this phenomenon responsibly.
- Cicadas are harmful pests that need to be eradicated.
- Cicada emergence is a sign of impending doom or a major environmental disaster.
- Cicadas are a significant threat to human health, and their presence should trigger public health warnings.
Behavioral Comparisons with Other Cicada Species
Brood XIV cicadas share some behavioral similarities with other cicada species but also exhibit unique characteristics. Understanding these distinctions helps us appreciate the intricacies of their ecological role.Brood XIV cicadas, like other cicada species, are hemimetabolous insects, meaning they undergo incomplete metamorphosis. They have a relatively short adult lifespan, primarily focused on reproduction. Their emergence is a coordinated event, synchronized with other members of their brood.
This synchronous emergence is a defining characteristic that distinguishes Brood XIV from other cicadas.
Potential Health Risks Associated with Brood XIV Cicadas
While Brood XIV cicadas are generally harmless, some potential health risks associated with their emergence should be considered. This section examines these risks, and appropriate precautions.Although Brood XIV cicadas do not directly transmit diseases, their sheer numbers can cause some minor inconveniences. The sheer volume of cicadas can cause some individuals to experience allergic reactions, while the noise generated by the mating calls of male cicadas can be disruptive to some people.
It is important to be mindful of these possibilities.
Best Practices for Handling and Managing Brood XIV Cicadas Safely
Safe handling and management of Brood XIV cicadas are crucial for minimizing potential risks and ensuring responsible engagement with this natural phenomenon. The following guidelines are crucial for responsible interaction.
- Avoid direct contact with large numbers of cicadas.
- If you encounter cicadas on your property, use non-toxic methods to manage them, such as placing barriers or providing natural predators like birds or frogs.
- Do not attempt to capture or harm cicadas, as this is not only harmful to the insects but can also lead to unnecessary stress.
Misconception vs. Correct Information
| Misconception | Correct Information |
|---|---|
| Cicadas are harmful pests that need to be eradicated. | Cicadas are beneficial insects that play a role in the ecosystem, serving as a food source for various animals. Their presence is a natural phenomenon. |
| Cicada emergence is a sign of impending doom or a major environmental disaster. | Cicada emergence is a natural biological event that occurs in a cyclical pattern. It is a remarkable example of the interconnectedness of nature. |
| Cicadas are a significant threat to human health, and their presence should trigger public health warnings. | Cicadas are generally harmless to humans. While some individuals may experience allergic reactions or be bothered by the noise, there is no significant health risk associated with their presence. |
Brood XIV Emergence Predictions and Resources: Cicada Brood Xiv Emerging What To Know
Brood XIV cicadas, a magnificent and somewhat disruptive spectacle, emerge in cyclical patterns. Predicting their emergence is crucial for understanding and managing their impacts on various ecosystems and human activities. Accurate predictions allow for better preparation and mitigation strategies, minimizing disruptions to agriculture, infrastructure, and public life.
Methods for Predicting Brood XIV Emergence
Cicada emergence is intricately linked to environmental factors, particularly temperature and soil moisture. Researchers utilize various methods to pinpoint the emergence time, often combining multiple approaches for a more robust prediction. These methods rely on extensive historical data, coupled with advanced modeling techniques. A key component is identifying the precise timing of previous Brood XIV emergences, allowing for the establishment of a reliable baseline.
Available Resources for Tracking Emergence and Impacts
Several resources provide valuable information about Brood XIV emergence, allowing for public engagement and monitoring. These include dedicated websites, social media platforms, and scientific publications. Online forums and citizen science initiatives facilitate data collection, allowing the public to contribute to the understanding of the emergence. Monitoring the impact of the emergence on various ecosystems and human activities is critical for adaptive management strategies.
Role of Scientific Research in Understanding and Mitigating Impacts
Scientific research plays a vital role in understanding and mitigating the impacts of Brood XIV emergence. By studying the cicada life cycle, their interactions with other species, and the broader ecosystem, scientists can develop effective strategies to minimize negative effects. For example, studies can focus on the impact on agriculture, infrastructure, and public health. Research findings can then be disseminated to inform management strategies and public awareness campaigns.
So, Brood XIV cicadas are finally emerging! It’s a fascinating time to learn about these insects, but you might also be wondering about your gut health. Considering how these massive insect swarms might affect the ecosystem, it’s important to consider your own well-being, too. Perhaps you’re wondering if you should be taking a fiber supplement to support your digestive system during this time of abundance of natural wonders.
If so, check out this article on whether you should take a fiber supplement should you take fiber supplement. Regardless, keep an eye out for these amazing cicadas!
Prediction Methodologies and Their Accuracy
| Prediction Method | Accuracy | Limitations |
|---|---|---|
| Historical Data Analysis | High accuracy for regions with extensive historical records; Emergence timing is relatively consistent across similar geographic areas. | Limited predictive power for novel environments or locations without a well-documented history. |
| Temperature and Soil Moisture Modeling | Moderate accuracy; Models can predict emergence based on climate conditions, but factors like rainfall patterns can affect accuracy. | Models can be influenced by incomplete or inaccurate data. Regional variations in climate can also limit the model’s effectiveness. |
| Citizen Science Initiatives | Moderate accuracy; Public participation in reporting observations provides real-time insights and broader geographical coverage. | Accuracy depends on the quality and quantity of reported observations. Potential for bias or inconsistencies in reporting. |
| Combination of Methods | High accuracy when different methods are integrated. Combining historical data, modeling, and citizen science allows for a more comprehensive prediction. | Requires extensive resources and expertise in data analysis. Coordination among different research groups and stakeholders is essential. |
Visual Representation of Brood XIV
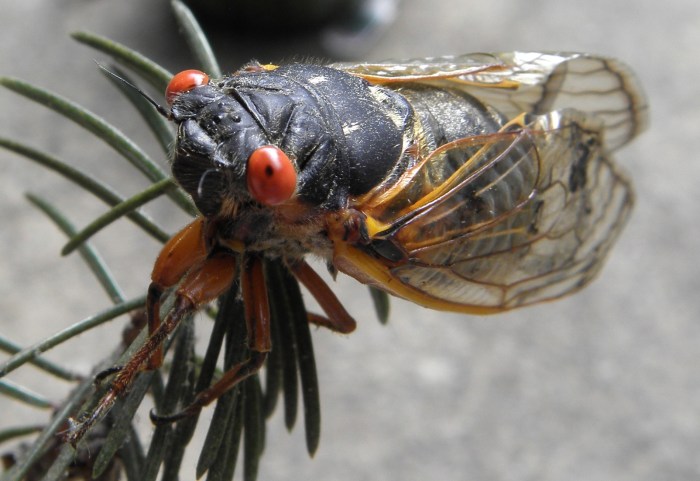
Brood XIV cicadas, a spectacle of nature’s rhythm, are poised to emerge in the coming weeks. Understanding their physical characteristics and sonic signatures is key to appreciating their presence and the impact they will have on the ecosystem. This section delves into the visual details of these insects, from their size and color to the unique sound they produce.Adult Brood XIV cicadas are a striking sight.
Their physical attributes contribute to their ecological role, both as a food source and as a significant component of the environment. The distinctive characteristics of the nymphs and adults are integral to the life cycle of the cicada.
So, Brood XIV cicadas are finally emerging – what’s the deal? While we’re all buzzing about these massive insect swarms, it’s worth noting that there’s a parallel happening in the US – a reality show where immigrants are pitching their cases for US citizenship, like in the Department of Homeland Security reality show. Regardless of whether you’re interested in the buzzing insects or the journey to citizenship, it’s a fascinating time for all sorts of transformations.
Lots to learn about Brood XIV’s emergence and life cycle.
Adult Cicada Characteristics
Brood XIV cicadas, when fully developed, are typically medium-sized insects. Their size varies, but they are generally robust, with a noticeable body. The color of the cicada is usually a rich brown or reddish-brown, though some individuals may show variations in their coloration. Their wings, when fully extended, typically span several inches. The wingspan, a crucial factor in flight and dispersion, is an essential characteristic that differentiates one species from another.
Nymph to Adult Transformation
The transformation from nymph to adult cicada is a remarkable process. The nymphs, typically found underground, undergo a series of molts, gradually increasing in size. As they progress through these stages, their physical appearance changes drastically. The nymph stage is characterized by a pale, often yellowish or light brown color, and lacks the wings and robust body structure of the adult.
The transition to adulthood is a remarkable feat of biological engineering. The adult form is equipped with the necessary features for reproduction and dispersal, playing a significant role in the continuation of the species.
Sound Production
The distinctive sound of Brood XIV cicadas is a product of the male cicadas’ specialized structures. They produce a loud, resonant buzzing sound using specialized tymbals on their abdomens. The frequency and intensity of the sound vary, but the overall effect is a powerful auditory experience. The sound is crucial for attracting mates and deterring predators. The sonic performance of these insects is a testament to the complexity of natural communication.
Comparison of Nymph and Adult
| Feature | Nymph | Adult ||—————-|——————————————-|——————————————–|| Color | Pale yellowish or light brown | Rich brown or reddish-brown || Size | Smaller, with a more slender body | Larger, with a more robust body || Wings | Absent | Present, often spanning several inches || Sound | No sound produced | Loud, resonant buzzing sound |
“Brood XIV cicadas are a symphony of color and sound. Their rich brown bodies, coupled with their impressive wingspan, create a striking visual contrast against the landscape. The male cicadas’ distinctive buzzing sound, a resonant hum that fills the air, is both a testament to their presence and a fascinating part of the natural world.”
Preparation and Management Tips
Brood XIV cicada emergence is a predictable event, allowing for proactive preparation. Understanding their life cycle and behavior enables effective strategies to mitigate their impacts and manage any potential infestations. These strategies range from simple preventative measures to more involved property-specific solutions.Knowing what to expect and how to react to the emergence can significantly reduce stress and disruption.
By taking the necessary steps, homeowners and communities can navigate the cicada season with greater ease and minimize the impact on their lives and properties.
Preparing for Brood XIV Emergence
Understanding the emergence timeline and anticipated peak activity allows for proactive preparation. This includes planning for potential noise and visual disturbances. Proper preparation ensures minimal disruption to daily routines and activities.
- Establish a Monitoring System: Keep track of local emergence reports and use online resources to track the emergence in your area. This will give you an estimated timeframe for the peak activity, allowing you to plan accordingly. For instance, if you know the emergence is predicted for late May, you can plan your outdoor activities and projects around this time to avoid major disruptions.
- Prepare Outdoor Spaces: If you have outdoor activities or events planned, schedule them before the peak emergence period. Protective measures, like covering sensitive plants, can be implemented if necessary. Consider adjusting outdoor activities, such as yard work or outdoor gatherings, during the peak emergence to minimize potential noise or visual disturbances.
- Stock up on Noise-Reducing Materials: If noise from cicadas is a concern, have materials like white noise machines, earplugs, or noise-canceling headphones on hand to help mitigate the impact.
Minimizing Impacts on Property
Several strategies can be implemented to reduce the impact of Brood XIV cicadas on your property. These methods focus on preventing damage and minimizing the nuisance factor.
- Protect Plants: Cover sensitive plants with netting or protective coverings. This will shield them from potential damage caused by cicada molting or their presence.
- Seal Entry Points: Inspect your property for any entry points that cicadas might use to enter your home or other structures. Seal cracks, gaps, or openings in walls, foundations, or windows to prevent them from entering.
- Clean Regularly: Regular cleaning and maintenance can prevent potential infestations. Remove dead leaves, branches, or debris that might attract cicadas or create breeding grounds.
Managing Brood XIV Cicada Infestations, Cicada brood xiv emerging what to know
If a cicada infestation occurs, it’s important to implement proper management techniques. The goal is to minimize the impact and prevent further issues.
- Monitor the Situation: If you notice an increase in cicada numbers, monitor the situation to assess the severity of the infestation. Document the extent of the infestation to understand its growth and decide on the appropriate management strategy.
- Consult with Professionals: For large-scale infestations or if you have specific concerns about damage, consider consulting with pest control professionals. They have experience in managing cicada infestations and can provide tailored solutions.
- Use Natural Methods: There are some natural methods to deter cicadas, but their effectiveness can vary. Consider using natural deterrents such as certain scents or sounds, though these might not be universally effective.
Actionable Steps for Cicada Emergence Preparation
A structured approach can greatly ease the transition through the emergence period. The following steps Artikel a practical method for preparing for Brood XIV cicada emergence.
- Identify Emergence Timeframe: Research the predicted emergence timeframe for your area. This information is crucial for planning activities and minimizing disruptions.
- Inspect Property for Entry Points: Carefully examine your property for potential entry points for cicadas. Seal any cracks, crevices, or gaps to prevent them from entering your home.
- Prepare Protective Measures: Consider covering sensitive plants or taking steps to shield them from potential damage.
- Plan Outdoor Activities: Schedule outdoor activities and events before the peak emergence period.
Concluding Remarks

In conclusion, understanding cicada brood XIV emerging what to know is key to navigating their impact. From their complex life cycle to their profound effects on ecosystems and human activities, these insects are more than just a nuisance; they’re a vital part of the natural world. Armed with this information, you can prepare for their arrival, minimize any negative impacts, and even appreciate the beauty and wonder of this natural event.
Prepare for the buzz!

