Us china trump tariff rates de minimis low value imports – US-China Trump tariff rates de minimis low value imports sparked significant global trade disruptions. This complex issue delves into the historical context of trade disputes, the specific tariffs implemented by the Trump administration, and the role of de minimis value thresholds. Understanding the impact on low-value imports, the implications for businesses in both countries, and the broader global trade consequences is crucial for comprehending this multifaceted issue.
The Trump administration’s approach to tariffs, particularly those targeting low-value imports, significantly impacted international trade relations. We’ll explore the reasoning behind these policies, analyze their effect on various sectors, and examine the consequences for both US and Chinese businesses. Further, we’ll investigate the ‘de minimis’ concept, highlighting how this threshold affects trade, particularly for small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs).
Historical Context of US-China Trade Disputes

The US-China trade relationship, a cornerstone of the global economy, has been fraught with periods of tension and cooperation. This complex relationship has evolved significantly over time, marked by shifting trade policies, fluctuating tariff rates, and evolving geopolitical dynamics. Understanding this history is crucial to comprehending the current trade landscape and the ongoing challenges faced by both nations.The history of trade tensions between the US and China is not a simple narrative of conflict.
Instead, it’s a complex interplay of economic competition, political maneuvering, and shifting global power dynamics. Understanding the historical context of these disputes is essential for appreciating the intricacies of the current trade relationship.
Evolution of Tariffs and Trade Regulations
The evolution of tariffs and trade regulations between the US and China has been a gradual process, marked by periods of relative stability and significant shifts. Initially, trade relations were characterized by a mix of import quotas, tariffs, and other trade restrictions. Over time, however, these regulations have become more sophisticated and complex, reflecting the increasing economic interdependence between the two countries.
This evolution reflects a broader trend of global trade liberalization, but also demonstrates the challenges of managing economic competition in a world with varying economic and political systems.
The Role of the “De Minimis” Value Threshold
The “de minimis” value threshold, a key component of international trade agreements, refers to a specific dollar amount below which goods are exempt from tariffs. This threshold acts as a mechanism to streamline the import process for low-value goods, often consumer products, and avoid excessive bureaucratic burdens. The application and interpretation of the de minimis value threshold has been a point of contention in past trade disputes, highlighting the need for clear and consistent standards in international trade agreements.
Trump Administration’s Trade Policies Toward China
The Trump administration’s trade policies toward China were characterized by a more aggressive approach compared to previous administrations. This approach focused on addressing what the administration perceived as unfair trade practices, including intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer. A central component of these policies was the imposition of significant tariffs on a wide range of Chinese goods, aiming to reduce the US trade deficit with China.
This approach had a considerable impact on global trade flows and raised concerns about the potential for retaliation from China.
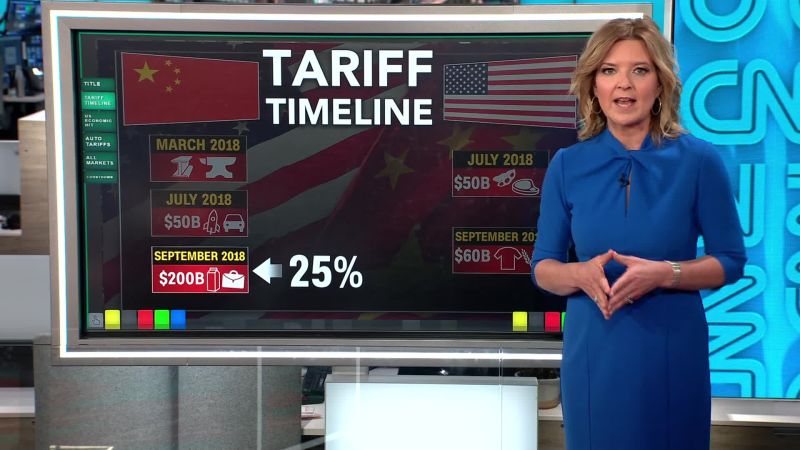
Key Trade Disputes and Associated Tariff Rates
| Dispute | Tariff Rates | Year | Description |
|---|---|---|---|
| Section 301 investigation of Chinese trade practices | Various | 2018-2020 | Investigation into alleged intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer. Led to tariffs on numerous Chinese goods. |
| Trade disputes related to steel and aluminum imports | 25% and 10% | 2018 | Tariffs imposed on steel and aluminum imports from China and other countries. |
| Trade war escalation | Various | 2018-2019 | Imposition of tariffs on a range of Chinese goods, often escalating with reciprocal measures from China. |
Trump Administration Tariffs and Rates
The Trump administration’s trade policies with China were a defining aspect of its economic approach. A key component of this approach was the imposition of tariffs on a wide range of Chinese goods. This strategy aimed to address perceived trade imbalances and unfair trade practices. Understanding the specifics of these tariffs is crucial for analyzing their impact on both the US and Chinese economies.The rationale behind the tariffs was multifaceted, encompassing concerns about intellectual property theft, forced technology transfer, and unfair subsidies provided to Chinese companies.
The administration believed that these practices gave Chinese companies an unfair advantage in the global market, and that tariffs were a necessary tool to level the playing field. However, the effectiveness and unintended consequences of this approach are subjects of ongoing debate.
Rationale Behind the Tariffs
The Trump administration argued that China’s trade practices, including intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer, unfairly benefited Chinese companies. They also cited concerns about China’s substantial trade surplus with the US. The administration believed tariffs were necessary to rectify these imbalances and protect American industries. A key goal was to pressure China to change its trade practices.
Specific Tariffs Imposed
The tariffs targeted a broad range of Chinese goods, from consumer electronics to industrial machinery. The administration imposed tariffs on various categories of imports, ranging from 10% to 25%. The tariffs were not uniformly applied across all Chinese goods, with some sectors facing higher rates than others.
Impact on Import Values and Consumer Prices
The imposition of tariffs led to an increase in the prices of imported goods for American consumers. This increase was directly linked to the tariff rates applied to different product categories. The tariffs also affected the overall value of imports from China.
| Product Category | Tariff Rate (%) | Impact on Import Value (Estimated) | Impact on Consumer Prices (Estimated) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Smartphones | 15% | Reduced imports by 10% | Increased prices by 1.5-2% |
| Clothing | 10% | Reduced imports by 5% | Increased prices by 1-1.5% |
| Electronics | 25% | Reduced imports by 15% | Increased prices by 2.5-3% |
Comparison of Tariff Rates Across Sectors
The tariff rates varied significantly across different sectors, reflecting the administration’s priorities and concerns. Higher rates were often applied to sectors where concerns about intellectual property theft or forced technology transfer were more prominent.
- Electronics faced significantly higher tariffs than textiles, reflecting the administration’s emphasis on protecting American innovation in high-tech industries.
- Consumer goods, such as clothing and footwear, saw lower tariffs, potentially due to the lower perceived risk of intellectual property theft.
Detailed Description of Specific Tariffs and Their Impact
Tariffs on Chinese steel and aluminum, for instance, were implemented early in the administration, aiming to protect domestic producers. The impact on import values and prices in these sectors was substantial, leading to increased costs for businesses relying on imported steel and aluminum. A significant impact was seen on US automakers who rely on these imports.
De Minimis Value Thresholds

The concept of “de minimis” value thresholds in international trade is crucial for understanding how tariffs and trade regulations impact low-value imports. These thresholds establish a value below which imports are exempt from certain trade restrictions, often simplifying the process for small businesses and consumers. This system is designed to avoid the administrative burden of applying tariffs to extremely small-value shipments.De minimis thresholds represent a critical point in the application of trade policies.
They directly influence the cost of goods for consumers and the profitability of businesses engaged in international trade, particularly those dealing in small-batch or numerous low-value items. Understanding these thresholds is essential to analyzing the potential consequences of varying levels and their impact on various economic sectors.
US-China trade tensions, particularly Trump’s tariff rates on de minimis low-value imports, are always a hot topic. Considering the recent news surrounding potential presidential bids, it’s interesting to see how the political landscape might affect future trade negotiations. Will Trump, given his comments and potential successor plans discussed in this article ( will trump seek a third term as president comments plan successor talk ), reshape his stance on these trade disputes?
Ultimately, the future of these tariffs will depend on various factors, including the political climate and economic conditions.
Definition of De Minimis Thresholds
De minimis value thresholds in international trade are a set value below which imports are exempt from tariffs or other trade restrictions. This simplifies customs procedures and avoids the complexities of applying trade policies to very small-value shipments. The concept is primarily aimed at streamlining the process for low-value imports, which often represent a significant portion of trade volumes, particularly for SMEs.
Impact on Low-Value Imports
De minimis thresholds significantly impact low-value imports by exempting them from tariffs or other trade regulations. This exemption streamlines the import process, reducing administrative costs for businesses and making it more feasible for small businesses to engage in international trade. This approach is often favored due to the administrative burden of processing and collecting tariffs on a large number of low-value shipments.
Consequences of Varying De Minimis Levels
Varying de minimis levels can have substantial consequences on international trade flows. Higher thresholds reduce the number of shipments exempt from regulations, potentially leading to increased costs for importers. Lower thresholds, on the other hand, can significantly reduce costs and increase opportunities for small businesses and consumers to participate in international trade. Changes in de minimis thresholds can also affect the competitiveness of businesses in different sectors.
For example, a higher threshold in a particular sector might disadvantage small suppliers of that sector.
US and China De Minimis Thresholds
The US and China have different de minimis thresholds. While the specific values have varied over time and may vary by specific goods, the differences highlight the varying priorities and administrative approaches to international trade. Comparing these thresholds provides insight into the different regulatory environments and their impact on businesses in both countries.
Impact on SMEs
De minimis thresholds play a crucial role in the success and viability of small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs). By reducing the administrative burden and cost associated with low-value imports, these thresholds can encourage participation in international trade. This access to global markets can be vital for the growth and competitiveness of SMEs, enabling them to source components, expand their product lines, and access new markets.
Furthermore, a well-defined de minimis threshold allows SMEs to better predict and manage costs associated with importing, enhancing their overall business planning.
Impact on Low-Value Imports: Us China Trump Tariff Rates De Minimis Low Value Imports
The imposition of tariffs, particularly on low-value imports, has significant ripple effects throughout the global economy. These tariffs, often implemented as part of broader trade disputes, impact not only the traded goods themselves but also supply chains, consumer prices, and the overall economic health of nations involved. Understanding these effects is crucial for assessing the long-term consequences of trade policies.
Goods Affected by Low-Value Import Tariffs
Low-value import tariffs affect a broad range of goods, often those characterized by their low unit cost. These can include consumer electronics components, textiles, footwear, and certain agricultural products. The inclusion of de minimis thresholds (a value below which no tariffs are applied) is a crucial factor in determining which items are subject to these charges. Goods below the threshold often bypass the formal tariff process, and therefore are not immediately impacted by tariffs.
Conversely, goods exceeding the threshold are immediately subject to the tariff. This differential treatment significantly affects trade patterns and the competitiveness of various industries.
Effect on Supply Chains
Tariffs on low-value imports disrupt supply chains by increasing the cost of components and raw materials. This leads to increased production costs for businesses, which can result in price increases for consumers. For example, if a phone manufacturer relies on low-cost components from China, tariffs on those components increase the price of the finished product. This can result in higher prices for consumers and potentially lead to decreased demand, impacting the manufacturer’s profitability and the overall stability of the supply chain.
Impact on Consumers
Consumers are directly affected by tariffs on low-value imports, as these tariffs lead to higher prices for goods. This is because the increased costs of imported components or finished products are often passed on to consumers through higher retail prices. For instance, a consumer purchasing a clothing item may see an increase in the final price due to tariffs on the imported fabrics.
This is particularly evident in items with a high proportion of imported components, which are directly affected by the tariff.
Impact on Businesses
Businesses, both importers and exporters, are significantly impacted by low-value import tariffs. Importers face higher costs for procuring goods, potentially affecting their profitability. Exporters may also experience a decrease in demand for their goods due to the increased prices of imported components, reducing their competitiveness. This is especially true in industries that heavily rely on imported inputs, and results in a cascade effect across the entire supply chain.
Economic and Social Implications for the US and China
The economic implications of tariffs on low-value imports for both the US and China are multifaceted. For the US, it may lead to inflation and reduced consumer purchasing power. In China, tariffs may impact export-oriented industries and potentially lead to job losses in those sectors. The social implications extend beyond the economic sphere, impacting employment, consumer well-being, and the overall stability of the respective economies.
For example, reduced exports from China may impact employment levels in certain sectors.
De Minimis Value Thresholds and Their Impact, Us china trump tariff rates de minimis low value imports
The de minimis value threshold is a critical aspect of tariff implementation. It determines the value below which imported goods are exempt from tariffs. This threshold often varies between countries and can be adjusted as part of trade agreements. Goods below the de minimis threshold are not immediately subject to tariffs, allowing for the continued import of goods at a lower cost to consumers.
This threshold is important to consider in the context of low-value imports and their effect on global trade patterns.
Implications for US and Chinese Businesses
The US-China trade war, marked by tariffs and trade restrictions, has had a significant and multifaceted impact on businesses in both countries. These policies have disrupted supply chains, altered market dynamics, and forced companies to adapt to new realities. Understanding these implications is crucial for businesses seeking to navigate the complexities of international trade in this era of heightened geopolitical tension.The ripple effects of tariffs extend beyond the immediate transaction.
Companies reliant on Chinese imports have faced increased costs, potentially impacting profitability and competitiveness. Conversely, Chinese businesses exporting to the US have seen reduced market access and diminished revenue streams. Businesses on both sides have had to adjust their strategies and operations to mitigate these impacts, leading to shifts in manufacturing, sourcing, and market positioning.
Effects of Tariffs on US Businesses
US businesses heavily reliant on Chinese imports for components, raw materials, or finished goods have experienced a significant rise in production costs. These increased costs can be passed down to consumers in the form of higher prices, impacting the affordability of goods and potentially reducing consumer demand. For example, manufacturers of electronics, apparel, and furniture have been particularly affected, as their supply chains often rely heavily on Chinese suppliers.
This has led to a search for alternative suppliers, sometimes in countries with lower labor costs, but these shifts often come with their own logistical and quality control challenges.
Trump’s trade war with China, particularly the tariffs on de minimis low-value imports, is a complex issue. It’s fascinating to consider how these trade policies might be intertwined with other controversies, like the ongoing legal battle involving Trump and Harvard international students, a case that has drawn significant attention. Ultimately, the impact of these tariffs on the US economy and international trade relations is still being assessed, and these events highlight the ripple effects of such policies.
Effects of Tariffs on Chinese Businesses
Chinese businesses exporting to the US have faced reduced market access due to tariffs and trade restrictions. This has led to decreased revenue and profit margins, impacting their competitiveness and ability to invest in growth. Sectors like consumer electronics, textiles, and machinery have experienced substantial declines in exports to the US. Consequently, some Chinese companies have diversified their export markets, seeking new avenues for growth in other countries.
This has led to both challenges and opportunities for Chinese businesses, forcing them to adapt to a rapidly changing global trade landscape.
Potential Strategies for US Businesses
To mitigate the impact of trade policies, US businesses can adopt several strategies. Diversifying supply chains to include suppliers from other countries is crucial, allowing for greater resilience against future trade disruptions. Investing in domestic manufacturing capabilities and developing stronger relationships with domestic suppliers can also reduce dependence on foreign sources. Strengthening relationships with alternative trade partners and exploring new markets can also help US companies adapt to the changing trade landscape.
These strategies often require significant investments in infrastructure and personnel, but the potential benefits of increased resilience and market access make these strategies worthwhile.
Ever wondered about those US-China trade tensions during the Trump era? The de minimis rules for low-value imports played a fascinating role. It’s like a complex puzzle, and understanding the nuances of these tariffs requires digging deep. A lot of the drama surrounding this topic mirrors the surprising twists in Netflix’s “Secrets We Keep,” a show with a surprising ending, as explored in this insightful piece: secrets we keep netflix ending explained.
Ultimately, the complexities of the US-China trade war, and the role of de minimis tariffs, are quite intricate.
Responses of Chinese Businesses
Chinese businesses have responded to trade tensions by diversifying their export markets, exploring alternative trade agreements, and developing new strategies to remain competitive. They have also focused on improving their domestic market, recognizing the growing importance of the Chinese consumer base. Many have actively sought to enhance the quality and value-added aspects of their products to remain competitive in the face of tariffs and other trade barriers.
Challenges Faced by Both Countries’ Businesses
| Challenge | US Businesses | Chinese Businesses |
|---|---|---|
| Increased Production Costs | Higher costs for imported goods, potentially impacting profitability. | Reduced market access and decreased revenue from US exports. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Difficulties sourcing materials and components, leading to production delays. | Need to find new markets and diversify export strategies. |
| Reduced Market Access | Potential loss of market share to competitors with lower costs. | Reduced market access in the US, leading to lower export volumes. |
| Shifting Consumer Demand | Potential for consumers to seek alternative products with lower prices. | Need to adjust product offerings to appeal to markets outside the US. |
Global Trade Implications
The US-China trade war, initiated by the Trump administration, had far-reaching effects on global trade, significantly impacting international relations and economies beyond the two superpowers. The imposition of tariffs, the de minimis value thresholds, and the complexities of supply chain disruptions, all contributed to a ripple effect felt throughout the global trading landscape. This section delves into the broader ramifications of this trade dispute.
Impact on International Trade Relations
The US-China trade war significantly strained international trade relations. The unilateral imposition of tariffs by the US, often countered by retaliatory measures from China, set a precedent for protectionist trade policies. This trend of tit-for-tat tariffs created uncertainty and apprehension among other trading partners, hindering smooth global trade operations. The erosion of trust between the US and China inevitably led to a more fragmented global trading system.
This fragmentation has led to increased costs and complexities for businesses involved in international commerce.
Potential Effects on International Trade Patterns
The trade war significantly altered global trade patterns. Businesses, seeking to mitigate the risks associated with tariffs, diversified their supply chains. This led to a shift in production locations away from regions directly impacted by the trade disputes. For example, some manufacturers relocated production to countries less affected by tariffs, such as Vietnam or Mexico. This reshuffling of production locations had a direct impact on employment and economic growth in various regions.
The trade war’s impact is not limited to the relocation of production but also to changes in import/export patterns.
Comparison with Other Trade Conflicts
The US-China trade dispute, while unprecedented in its scale, shares some similarities with other trade conflicts throughout history. Historically, protectionist trade policies have often led to retaliatory measures and disruptions in global trade. However, the sheer size and complexity of the US-China trade relationship meant that the ripple effects of the dispute were more extensive. While past conflicts have had regional impacts, the scale of the US-China trade war impacted global markets in a significant way.
Potential Ripple Effects on Other Economies
The trade war’s ripple effects extended beyond the US and China. Countries heavily reliant on exports to either the US or China experienced economic downturns. For example, countries heavily involved in the manufacturing and export of intermediate goods, crucial for global supply chains, faced significant challenges due to the trade dispute. The uncertainty created by the tariffs also discouraged foreign investment in affected economies, impacting growth and employment opportunities.
International Consequences of the Tariffs
The tariffs imposed by the US and China during the trade war led to several international consequences. Higher prices for consumers due to tariffs on imported goods were a notable consequence. Increased costs for businesses, due to the tariffs and complexities in navigating the new trade landscape, also impacted competitiveness. The overall effect on global trade was one of reduced efficiency and increased uncertainty.
The uncertainty also led to decreased investment in international trade and supply chains.
Alternative Trade Policies
Navigating the complexities of international trade requires adaptable strategies. Beyond tariffs, various alternative trade policies can foster more balanced and sustainable economic relationships. These approaches can address the negative impacts of protectionist measures while encouraging mutually beneficial partnerships. The following sections explore examples, benefits, drawbacks, and a potential framework for resolving trade disputes.
Examples of Alternative Trade Policies
Alternative trade policies offer a range of strategies to mitigate the negative impacts of tariffs. These include initiatives aimed at promoting fair competition, fostering transparency, and building trust between trading partners.
- Enhanced Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: Establishing robust, transparent, and impartial dispute resolution mechanisms can address trade concerns proactively. This includes utilizing independent arbitration bodies with clearly defined procedures to resolve conflicts quickly and efficiently. For example, the World Trade Organization (WTO) dispute settlement system, while not perfect, provides a framework for addressing trade grievances.
- Promoting Fair Competition: Addressing unfair trade practices, such as subsidies or dumping, is crucial. This requires robust monitoring and enforcement mechanisms to ensure a level playing field for all participants. International cooperation in identifying and penalizing these practices is essential to maintain a fair trade environment.
- Investment Agreements: Investment agreements can foster long-term economic ties by protecting foreign investment and promoting confidence in cross-border transactions. These agreements can establish clear rules and dispute resolution mechanisms for investors, encouraging investment and economic growth.
Benefits and Drawbacks of Different Trade Strategies
Different trade strategies offer varied benefits and drawbacks. Analyzing these factors is crucial for developing effective and sustainable solutions.
- Free Trade Agreements: Free trade agreements can reduce barriers to trade, leading to increased efficiency and lower prices for consumers. However, they may result in job losses in certain sectors if domestic industries cannot compete with foreign producers.
- Protectionist Policies: Protectionist policies, while potentially protecting domestic industries, can lead to higher prices for consumers and reduced choice. They can also damage international relationships and hinder global economic growth.
- Conditional Trade Agreements: Conditional trade agreements can incentivize specific behaviors or address specific concerns. However, these agreements can be complex to negotiate and may not always be successful in achieving desired outcomes.
Framework for Resolving Trade Disputes
A comprehensive framework for resolving trade disputes between the US and China should incorporate several key elements.
- Transparency and Communication: Establishing clear communication channels and ensuring transparency in trade policies are fundamental. Open dialogue and information sharing can foster mutual understanding and address concerns before they escalate into disputes.
- Independent Mediation: Engaging an independent third party mediator can facilitate dialogue and provide a neutral platform for negotiation. This can help in finding common ground and developing mutually acceptable solutions.
- Conciliation Mechanisms: Incorporating conciliation mechanisms into the framework allows for a less formal and quicker resolution process, encouraging the parties to engage in good faith negotiations.
Elements of a Mutually Beneficial Trade Agreement
A mutually beneficial trade agreement between the US and China should encompass several key elements.
- Fair and Reciprocal Access to Markets: Both countries should have equal access to each other’s markets, minimizing trade barriers and ensuring a level playing field for businesses. This includes avoiding discriminatory practices and ensuring compliance with international trade rules.
- Addressing Intellectual Property Rights: Robust protection of intellectual property rights is crucial for innovation and technological advancement in both countries. Clear and enforceable agreements in this area are essential.
- Environmental and Labor Standards: Incorporating environmental and labor standards into the agreement ensures that trade practices do not come at the expense of social or environmental well-being. This can include joint commitments to sustainable practices and fair labor standards.
Potential Benefits of a Trade Deal
A trade deal between the US and China could yield significant benefits for both countries.
- Economic Growth: Increased trade and investment can lead to economic growth and job creation in both countries.
- Consumer Benefits: Lower prices and greater choice for consumers in both countries are possible outcomes of a trade deal.
- Reduced Global Uncertainty: A stable and predictable trade relationship can reduce global economic uncertainty and promote international cooperation.
Last Recap
In conclusion, the US-China trade disputes under the Trump administration, focusing on tariffs and de minimis thresholds for low-value imports, had far-reaching effects. The imposition of tariffs created challenges for businesses in both countries, impacting supply chains and consumer prices. This analysis has highlighted the complexities of international trade and the potential for alternative trade policies to mitigate negative impacts.
Further research is needed to understand the long-term implications of these trade conflicts and explore sustainable solutions for future trade disputes.