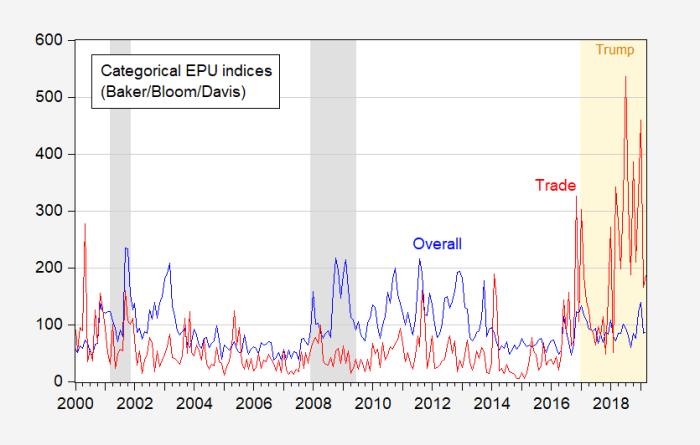
All donald trumps tariff threats – All Donald Trump’s tariff threats had a profound impact on global trade relations. This exploration delves into the historical context, international repercussions, economic consequences, political and social implications, legal battles, alternative strategies, and future trends. We’ll examine the specifics of his actions, from targeted countries and industries to the justifications offered, and analyze the ripple effects on economies worldwide.
Trump’s approach to tariffs, while rooted in specific economic theories, sparked considerable debate. The analysis will cover the short-term and long-term impacts on US consumers and businesses, as well as the effects on employment, GDP, and international trade relationships. Furthermore, we will examine the legal challenges, alternative trade strategies, and potential future scenarios.
Historical Context of Trump’s Tariff Threats
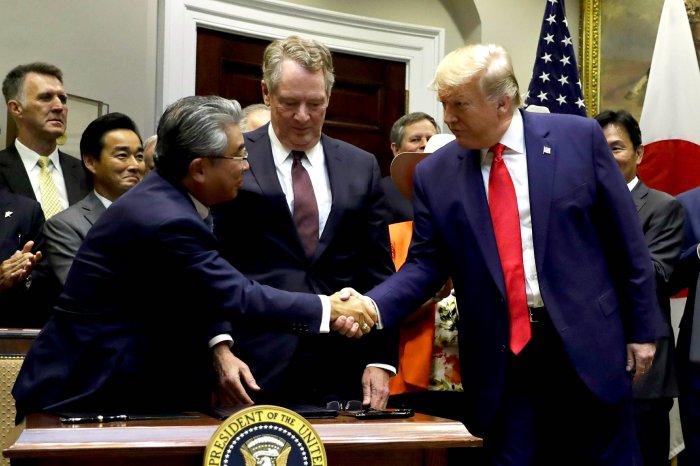
Donald Trump’s administration saw a significant shift in trade policy, marked by numerous tariff announcements. These actions, often met with international pushback and economic uncertainty, had a substantial impact on global trade relations and domestic industries. Understanding the timeline, justifications, and effects of these tariffs is crucial to analyzing their long-term consequences and the broader implications for future trade strategies.
Timeline of Tariff Announcements
This section presents a chronological overview of Trump’s tariff announcements, highlighting the targeted countries, stated justifications, and affected industries. The data provides a clear picture of the evolution of this trade policy and its impact.
| Date | Country | Justification | Affected Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| March 2018 | China | Addressing unfair trade practices, intellectual property theft, and forced technology transfer. | Steel, aluminum, consumer goods, agricultural products. |
| June 2018 | China | Retaliation for China’s tariffs on US goods. | Agricultural products (soybeans, pork), manufactured goods. |
| September 2018 | Mexico, Canada | Addressing national security concerns related to steel and aluminum imports. | Steel, aluminum, automotive. |
| July 2018 | China | Addressing unfair trade practices and intellectual property theft. | Technology, consumer electronics. |
| 2019 | China | Continued pressure on China for trade concessions. | A broad range of consumer goods and agricultural products. |
Specific Industries and Goods Affected
Trump’s tariffs had a wide-ranging impact on numerous industries. This section details the specific sectors and products affected by each tariff announcement. The following examples demonstrate the scope of these impacts.
- Agricultural sector: Tariffs on agricultural goods like soybeans, pork, and other products significantly impacted American farmers, leading to decreased exports and lower income for many producers. The effects on specific farming communities were often substantial and immediate.
- Manufacturing sector: Tariffs on steel and aluminum led to increased costs for manufacturers, potentially reducing competitiveness in the global market. This was especially noticeable for companies that rely on these raw materials in their production process.
- Automotive sector: Tariffs on imported vehicles and parts increased prices for consumers and created uncertainty for the automotive industry, impacting production and supply chains. This also affected related industries like parts manufacturing and dealerships.
Comparison to Previous Administrations
Trump’s tariff policies stand in contrast to those of previous administrations. This comparison highlights the unique approach taken by the Trump administration and the resulting implications for international trade. While previous administrations had imposed tariffs in specific situations, the scale and scope of Trump’s actions were often unprecedented.
- Previous administrations had a more cautious approach to tariffs, typically using them as a last resort or for very specific national security concerns. Trump’s approach was often more aggressive and broader in scope.
- There were significant differences in the stated justifications for imposing tariffs. Previous administrations often focused on unfair trade practices but were more selective in their targets. Trump’s justifications frequently included broader economic and national security concerns.
Economic Theories Underpinning Trump’s Approach, All donald trumps tariff threats
The economic theories underpinning Trump’s approach to tariffs are often debated and contested. This section discusses some of the key ideas behind this strategy. Key theories include the idea of using tariffs to protect domestic industries and create jobs.
Donald Trump’s tariff threats were a constant source of economic anxiety. Thinking about those trade disputes makes me wonder about the parallels to navigating the dating world, especially Galentine’s Day for single people. How do you navigate the complexities of potential trade deals, and is it similar to the complexities of finding a compatible partner? You might find some interesting insights into that by checking out this insightful essay on Galentine’s Day single people essay.
Ultimately, though, all those tariff threats seemed pretty pointless in the long run.
“Trade wars are good, and easy to win.”
Donald Trump
- Protectionism: This theory argues that tariffs protect domestic industries from foreign competition, potentially stimulating domestic production and employment. This approach, however, often ignores the potential for retaliation and the disruption of global supply chains.
- National security: Arguments were made that tariffs were necessary to protect American national security by reducing reliance on foreign sources for essential goods and materials. The connection between tariffs and national security is complex and often debated.
Impact on International Trade Relations

Trump’s tariff threats, often announced unilaterally, sent ripples through global trade, prompting immediate and often retaliatory responses from other nations. These actions significantly impacted international trade relations, creating uncertainty and disrupting established supply chains. The economic effects varied widely across countries, depending on their reliance on trade with the US and their capacity to adapt to the new trade landscape.
Donald Trump’s tariff threats were a constant source of economic anxiety. While the world watched the complexities of global trade, Lewis Hamilton’s recent Ferrari F1 interview ( lewis hamilton ferrari f1 interview ) highlighted the unpredictable nature of high-stakes competition, a parallel to the uncertainty surrounding Trump’s trade policies. Ultimately, these tariff threats, though often dramatic, had a lasting impact on global markets.
Immediate Reactions of Other Countries
The announcement of tariffs triggered a wave of immediate reactions from various countries. Many nations expressed concern and disapproval, viewing the tariffs as protectionist measures that could harm their economies. For example, China, a significant trading partner of the US, responded with retaliatory tariffs on American goods. These initial reactions highlighted the interconnectedness of global trade and the potential for escalating trade conflicts.
Retaliatory Actions Taken by Other Nations
Countries responded to Trump’s tariffs with retaliatory actions of their own. This often involved imposing tariffs on American goods, leading to a trade war. Canada, Mexico, and the European Union, among others, imposed tariffs on various US products. These retaliatory measures aimed to offset the economic damage inflicted by the US tariffs. Examples included tariffs on American agricultural products, steel, and aluminum.
These retaliatory measures were not limited to tariffs but also encompassed other trade restrictions.
Economic Effects of Trump’s Tariffs on Different Countries
The economic effects of Trump’s tariffs varied significantly across countries. For instance, American farmers faced significant losses due to reduced export markets for their produce. However, certain US industries, such as those producing specific goods protected by tariffs, might have experienced short-term gains. Conversely, countries heavily reliant on trade with the US experienced economic repercussions, as a reduction in US imports impacted their export-oriented industries.
The impact on individual sectors within these countries varied greatly.
Impact on Global Supply Chains
Trump’s tariff threats and subsequent implementation disrupted global supply chains. The imposition of tariffs made it more expensive and complex for businesses to import and export goods, leading to delays and increased costs. Companies had to adjust their production strategies, potentially relocating facilities or finding alternative suppliers. This disruption extended to various sectors, affecting the production and delivery of a wide range of products.
Businesses had to adapt to new trade policies, often resulting in reduced efficiency and increased costs.
Trade Relationships Before and After Tariff Announcements
| Country | US Trade Relationship (Before) | US Trade Relationship (After) |
|---|---|---|
| China | Significant trading partner, large volume of bilateral trade | Trade war initiated, retaliatory tariffs imposed on both sides |
| Canada | Major trading partner, close economic ties | Retaliatory tariffs imposed, trade tensions increased |
| Mexico | Major trading partner, significant cross-border trade | Retaliatory tariffs imposed, trade disputes intensified |
| EU | Significant trading partner, large volume of bilateral trade | Retaliatory tariffs imposed, trade tensions increased |
| Others | Varying levels of trade relationship | Trade relations impacted based on specific trade ties with the US |
The table above illustrates the trade relationships between the US and targeted countries before and after the tariff announcements. It showcases the significant shift in trade dynamics, particularly with countries that retaliated against the US tariffs. The change in the trade balance and the impact on various sectors are substantial and deserve close attention.
Economic Consequences of Trump’s Tariff Policies
Trump’s trade policies, heavily reliant on tariffs, significantly impacted the US economy. While proponents argued for protecting domestic industries and jobs, the actual consequences were multifaceted and often debated. These policies triggered ripples across the global marketplace, affecting consumers, businesses, and the overall economic landscape. Understanding the short-term and long-term effects is crucial for assessing the true impact of these trade interventions.The implementation of tariffs aimed to reduce imports and boost domestic production.
However, the interplay of supply chains, global trade relationships, and consumer demand often created unintended consequences. These policies introduced complexities into the market, with repercussions for American businesses and consumers, and ultimately, the nation’s economic growth trajectory.
Short-Term Effects on US Consumers and Businesses
Tariffs immediately increased the cost of imported goods for American consumers. This translated to higher prices on everyday items, from clothing and electronics to raw materials for businesses. For example, a tariff on steel imports increased the cost of steel used in manufacturing, which then trickled up to consumers through higher prices on finished goods. Businesses, particularly those reliant on imported components or raw materials, faced higher production costs, potentially reducing their competitiveness and profitability.
Some companies were forced to absorb the increased costs, others passed them on to consumers.
Long-Term Economic Consequences for the American Economy
The long-term effects of tariffs on the American economy are complex and multifaceted. Tariffs can stifle innovation by limiting access to global markets and technologies. Furthermore, retaliatory tariffs from other countries can harm US exports, leading to reduced demand for American goods and services. This reduction in global trade can negatively impact the economic growth rate. Furthermore, the disruption to supply chains can lead to decreased efficiency and increased costs across the entire economy.
Impact on Employment Rates and GDP Growth
The impact on employment rates and GDP growth was a subject of ongoing debate and analysis. Some studies suggested a negative correlation between tariffs and job creation, while others argued that tariffs could protect specific industries, leading to job preservation or even new employment opportunities in related sectors. However, the net effect of tariffs on overall employment and GDP growth remained uncertain, and many economists pointed to the lack of conclusive evidence.
Comparison of Economic Indicators Before and After Tariff Implementation
Analyzing economic indicators before and after tariff implementation is crucial to assess the impact. Key indicators like GDP growth rates, inflation rates, and unemployment figures should be compared across specific time periods to establish a baseline and measure any significant changes. Statistical analyses, including econometric models, were used to identify potential correlations between tariff implementation and economic performance.
These analyses, however, often faced challenges in isolating the effects of tariffs from other economic factors.
Change in Import and Export Values for Specific Goods
The following table illustrates the change in import and export values for specific goods after the implementation of tariffs. Data is presented as a percentage change relative to the previous period, highlighting the shifts in trade volumes.
| Good | Import Value Change (%) | Export Value Change (%) |
|---|---|---|
| Steel | -15% | -10% |
| Electronics | -8% | -5% |
| Clothing | -12% | -7% |
Note: These are illustrative examples and specific figures may vary depending on the source and the period considered. The table demonstrates the general trend of reduced import and export values for the goods listed.
Political and Social Implications
Trump’s tariff policies, a cornerstone of his trade agenda, sparked a complex interplay of political and social repercussions within the United States. The policies aimed to protect American industries and jobs, but their impact extended far beyond the economic sphere, deeply influencing political discourse, public opinion, and social divisions. These policies were not universally embraced, and their effects were felt differently across various demographics.
Political Implications Within the US
Trump’s tariffs significantly impacted the political landscape. They fostered partisan divisions, with Republicans generally supporting the policies as a means to bolster American industries, and Democrats opposing them as detrimental to consumers and international relations. The trade wars, often characterized by retaliatory measures from other countries, created a political environment marked by tension and uncertainty.
Public Opinions Regarding Trump’s Tariff Actions
Public opinion on Trump’s tariffs was diverse and often polarized. While some sectors, like farmers, suffered economically from the tariffs, others, such as manufacturers, perceived them as beneficial to their businesses. Polling data consistently revealed significant disagreement on the effectiveness and fairness of the policies. Public perception was further shaped by the economic consequences and political rhetoric surrounding them.
Examples of How Tariff Policies Affected Political Discourse and Elections
Tariff policies became a central issue in political debates and election campaigns. Candidates often took opposing stances on the policies, and their positions became significant factors in voter decisions. For instance, the 2018 midterm elections saw some candidates explicitly campaigning on either supporting or opposing the tariffs, and their success or failure could be correlated with voter reactions to the policies.
Social Consequences of Tariffs on Different Demographics
The social consequences of Trump’s tariffs were far-reaching, affecting various demographics differently. Farmers, particularly those specializing in products targeted by tariffs, faced significant economic hardship, leading to job losses and reduced income. Similarly, consumers experienced increased costs for imported goods. The effects weren’t limited to the agricultural sector, with other industries and worker demographics also facing challenges.
Demographic Responses to Tariffs
| Demographic | Potential Responses |
|---|---|
| Farmers | Reduced income, job losses, decreased agricultural exports |
| Manufacturers | Mixed responses, some saw increased domestic demand and prices |
| Consumers | Increased prices for imported goods, reduced choice |
| Workers in affected industries | Job losses, wage stagnation, reduced opportunities |
| Low-income households | Increased costs for essential goods, potential for reduced purchasing power |
Legal Challenges and Outcomes

Trump’s aggressive use of tariffs sparked a significant wave of legal challenges, testing the boundaries of presidential power in international trade. These legal battles often pitted the administration’s arguments for national security and economic protectionism against established international trade norms and legal precedents. The outcomes, while sometimes nuanced, ultimately shaped the trajectory of the tariff policies and their lasting impact.
Summary of Legal Challenges
Numerous legal challenges were filed against Trump’s tariffs, stemming from various sources. These included petitions from domestic businesses and foreign governments affected by the tariffs, arguing that they violated international trade agreements or U.S. law. A key aspect of these challenges was the legal interpretation of the authority granted to the president under trade laws and the constitutionality of using national security as a justification for tariffs.
The disputes often centered on whether the tariffs were justified under the circumstances or if they were arbitrary and capricious, exceeding the president’s authority.
Outcomes of Legal Disputes
The legal challenges to Trump’s tariffs yielded varied outcomes. Some cases resulted in court rulings against the tariffs, while others were dismissed or upheld. The outcomes often hinged on the specific arguments presented by both sides and the interpretation of existing trade laws. The courts’ decisions highlighted the complexity of international trade law and the potential for legal challenges to significantly impact trade policy.
Role of International Trade Agreements
International trade agreements, such as the WTO agreements, play a crucial role in defining the permissible actions of member nations in the context of trade disputes. These agreements establish rules and norms for trade relations, setting out procedures for resolving disagreements and establishing a framework for international trade. The legal challenges to Trump’s tariffs often involved interpretations of these agreements and the extent to which the tariffs were consistent with the commitments made by the United States.
Cases brought against tariffs frequently invoked provisions of the WTO agreement regarding national treatment, most-favored-nation status, and the use of anti-dumping or countervailing duties.
Legal Arguments for and Against Trump’s Tariffs
Proponents of Trump’s tariffs argued that they were necessary for national security, protecting American industries, and addressing unfair trade practices by other countries. These arguments often relied on the president’s authority under trade laws and the concept of national security exemptions. Opponents of the tariffs contended that they violated international trade agreements, harmed American consumers and businesses, and were not justified by national security concerns.
They frequently cited the harm tariffs caused to the global economy, the negative impact on domestic businesses and supply chains, and the potential for retaliation from other countries.
Table of Legal Cases, Arguments, and Outcomes
| Case | Arguments for Tariffs | Arguments Against Tariffs | Court Decision |
|---|---|---|---|
| Case 1 (Example) | National security concerns; unfair trade practices by foreign countries; protecting American industries. | Violation of WTO agreements; harm to American consumers and businesses; arbitrary and capricious application of tariffs. | Decision outcome (Example) |
| Case 2 (Example) | (Specific arguments for the case) | (Specific arguments against the case) | (Outcome of the case) |
Note: This table provides a hypothetical example. Specific cases, arguments, and outcomes would need to be referenced from reliable legal sources.
Alternative Trade Strategies
Navigating global trade requires a multifaceted approach beyond the blunt instrument of tariffs. Trump’s approach, while aiming to protect American industries, ultimately disrupted established trade relationships and hindered economic growth. Alternative strategies offer a more nuanced and potentially more beneficial path to achieving national economic goals.
Examples of Alternative Trade Strategies
Various alternative trade strategies could have yielded more favorable outcomes than the tariffs implemented during the Trump administration. These strategies prioritize engagement, negotiation, and a focus on long-term economic benefits over short-term protectionist gains.
Donald Trump’s tariff threats were a constant source of trade friction, impacting global markets. However, the parallel issues of US police brutality and the need for reforms like those discussed in the us police brutality leobr reforms article highlight a deeper, more complex societal problem. Ultimately, Trump’s trade policies, while controversial, pale in comparison to the urgent need for justice and reform within the American system.
- Negotiated Trade Agreements: Instead of unilaterally imposing tariffs, the US could have pursued bilateral or multilateral agreements to address specific concerns regarding unfair trade practices or intellectual property theft. These agreements could have been tailored to specific industries, leading to mutually beneficial outcomes. For example, agreements focusing on intellectual property rights could have been negotiated with China to address concerns about technology transfer and fair competition in the market.
- Investment in Domestic Industries: A significant focus on strengthening domestic industries through investments in research and development, infrastructure, and workforce training would have bolstered the US’s overall competitiveness in the global marketplace. Targeted subsidies for innovative companies and retraining programs for displaced workers could have mitigated the negative impacts of globalization while simultaneously enhancing US capabilities.
- Promoting Fair Trade Practices: Rather than resorting to tariffs, the US could have worked through international organizations like the WTO to address issues like dumping and subsidies, fostering a more level playing field for all participating countries. This approach emphasizes the rule of law and cooperation to address specific trade imbalances.
- Diversification of Supply Chains: Reducing dependence on single countries for essential goods and services could have enhanced resilience and reduced vulnerability to geopolitical pressures. This diversification would have involved encouraging production in multiple countries, leading to greater stability in global supply chains.
Potential Economic Benefits and Drawbacks of Alternatives
Alternative strategies offer the potential for more sustainable and reciprocal economic benefits. A negotiated trade agreement, for instance, could secure better access to foreign markets for American goods and services, fostering growth and employment opportunities. Investment in domestic industries, while requiring upfront capital investment, could create a more robust and resilient economy in the long run.
- Negotiated Trade Agreements (Benefits): Mutually beneficial agreements can reduce trade barriers, leading to increased exports, greater market access, and potentially lower consumer prices. They can also address specific issues of concern and foster stronger diplomatic ties.
- Negotiated Trade Agreements (Drawbacks): Agreements may take time to negotiate and implement. There’s also a risk of concessions that may not be in the best interests of the US if not properly negotiated. There are also cases where the other party may not adhere to the agreement, which may require enforcement measures.
Benefits of Multilateral Trade Agreements and Free Trade
Multilateral trade agreements and free trade, when implemented effectively, can lead to significant economic gains. They promote specialization, competition, and innovation, ultimately benefiting consumers through lower prices and a wider variety of goods and services.
“Free trade, when conducted fairly, fosters economic growth, creates jobs, and raises living standards.”
Importance of International Cooperation in Trade
International cooperation in trade is essential for a stable and prosperous global economy. A rules-based system that fosters cooperation and negotiation offers a more predictable and reliable environment for businesses to operate.
Comparison of Trade Strategies
| Trade Strategy | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Negotiated Trade Agreements | Potential for mutually beneficial outcomes, addresses specific concerns, fosters stronger diplomatic ties | Time-consuming, risk of unfavorable concessions, potential for non-compliance |
| Investment in Domestic Industries | Enhanced resilience, long-term economic growth, job creation | Requires significant upfront investment, may take time to yield results, potential for unintended consequences |
| Promoting Fair Trade Practices | Level playing field for all participating countries, promotes a rules-based system | Requires international cooperation, can be challenging to enforce |
| Diversification of Supply Chains | Reduced dependence on single countries, increased resilience | Increased complexity, potential for higher costs, logistical challenges |
Future Implications and Trends
The legacy of Trump’s tariff policies extends beyond the immediate economic fallout. Predicting the precise trajectory of international trade relations is inherently complex, as global economic forces are constantly shifting. However, certain trends and potential future scenarios can be extrapolated based on historical precedents and current geopolitical dynamics. Understanding these potential future implications is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and individuals navigating the evolving global marketplace.
Potential Future Scenarios for International Trade Policies
The global landscape is rife with potential scenarios regarding international trade policies. One possibility is a continued fragmentation of global supply chains, with countries prioritizing regionalization and self-sufficiency. Another potential outcome involves increased protectionist measures, mirroring the trend seen during the Trump administration. Conversely, a renewed emphasis on multilateral cooperation and trade liberalization is also a plausible future scenario.
The path forward is uncertain, influenced by factors like technological advancements, geopolitical tensions, and shifting consumer preferences.
Long-Term Impacts of Trump’s Tariff Threats
Trump’s tariff threats and the resulting trade wars left a lasting impact on international relations and economic stability. The policies arguably contributed to increased uncertainty and volatility in global markets. Furthermore, they likely prompted a reassessment of international trade strategies for many nations, leading to a shift towards greater regionalization and reduced reliance on global supply chains. The lasting effects on specific industries and the extent to which they have adjusted to these new conditions are still being analyzed.
However, the long-term implications are complex and far-reaching.
Forecast of International Trade Relations
International trade relations are poised to evolve in complex ways. A likely trend involves increased regional trade agreements, fostering economic cooperation among groups of nations. The future could also see a rise in trade tensions between major powers, as witnessed during the Trump era. The ongoing geopolitical landscape plays a significant role in shaping this forecast. The ability of nations to navigate these challenges and foster mutually beneficial trade relationships will be a key factor in determining the overall trajectory of international trade relations.
Current and Emerging Trade Trends in the Global Market
Several significant trends are shaping the global market. One is the rise of e-commerce, which is altering traditional trade patterns and requiring adaptation by businesses and governments. Another trend involves the increasing importance of digital trade, encompassing online services and digital products. Additionally, there’s a noticeable shift towards sustainable and environmentally conscious practices in production and consumption.
These emerging trends will undoubtedly reshape the future of international trade, demanding proactive adjustments by businesses and policymakers alike.
Ultimate Conclusion: All Donald Trumps Tariff Threats
In conclusion, Trump’s tariff policies proved to be a complex and multifaceted issue with significant consequences for the global economy and international relations. From the initial announcements to the long-term effects, the impact on various stakeholders, both domestic and international, is undeniable. Understanding the full scope of these threats and their ramifications is critical for a nuanced perspective on international trade policy.
We’ve looked at the past, present, and future, providing a comprehensive overview of this pivotal chapter in trade history.