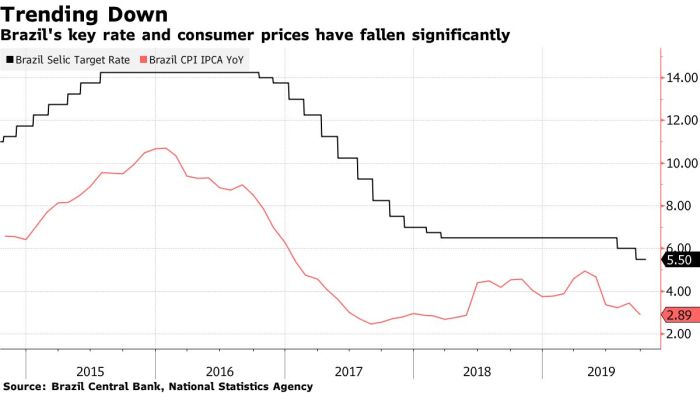
Brazils central bank chief signals imminent bridge solution real estate – Brazil’s central bank chief signals imminent bridge solution real estate, painting a picture of a potential intervention to stabilize the turbulent Brazilian real estate market. The market has seen a rollercoaster ride recently, with significant fluctuations impacting investors and the wider economy. This article delves into the potential causes of the current state, the central bank’s role, and the possible implications for the real estate market and other sectors.
The central bank’s potential actions will be crucial in navigating the current market challenges. This intervention could potentially shore up investor confidence and stimulate liquidity within the sector, but there are also potential risks and uncertainties. This analysis will explore the proposed solution, examining potential impacts on property prices, employment, and the wider economy. The article will provide a global perspective by comparing Brazil’s situation with those of other nations facing similar economic hurdles.
Background on Brazil’s Real Estate Market: Brazils Central Bank Chief Signals Imminent Bridge Solution Real Estate
Brazil’s real estate market, a crucial component of the nation’s economy, has experienced periods of robust growth and significant downturns. Understanding these fluctuations is vital for investors and policymakers alike. This analysis explores the historical performance, current trends, and potential contributing factors to the current market conditions.
Current State of the Market
The Brazilian real estate market is currently characterized by a complex interplay of factors. While some segments show signs of recovery, others face challenges related to affordability and financing. Interest rate adjustments, influenced by global economic conditions, play a significant role in shaping the market’s trajectory. Furthermore, government policies aimed at stimulating economic activity can also impact demand and pricing.
Historical Performance
| Time Period | Key Trend | Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 2000-2010 | Significant Growth | Increased demand, fueled by rising incomes and low interest rates, led to substantial price appreciation in major urban centers. Investment opportunities flourished. |
| 2010-2014 | Moderated Growth | Economic growth slowed, inflation rose, and interest rates increased, dampening the pace of price increases. Speculative activity reduced, but underlying demand remained strong in certain segments. |
| 2014-2018 | Downturn | A severe economic recession and political instability created a significant downturn in the real estate market. Property values declined, and sales activity decreased considerably. |
| 2018-2022 | Gradual Recovery | The economy began to recover, although unevenly across different segments. Increased confidence in the future of the Brazilian economy spurred cautious optimism among investors, and some regions experienced renewed growth. |
| 2022-Present | Complex Dynamics | The current period is marked by global economic uncertainty, inflation, and interest rate adjustments. This uncertainty is affecting affordability and investor confidence, leading to varied outcomes across different market segments. |
Contributing Factors
Several factors influence the current state of Brazil’s real estate market. Economic policies, including tax reforms and infrastructure investments, can significantly impact investor confidence and demand. Interest rates, both domestically and globally, play a crucial role in determining borrowing costs and affordability. Furthermore, global events, such as geopolitical tensions or shifts in international markets, can have ripple effects on the Brazilian economy and real estate sector.
Economic Policies and their Impact
Government policies directly affect the real estate market. For instance, tax incentives for homeownership or stricter regulations on development projects can stimulate or constrain market activity. Infrastructure investments in transportation and utilities can also boost demand in specific areas. Examples of successful or unsuccessful policy implementation can be seen in past market cycles.
Interest Rates and their Influence
Interest rates are a major driver of real estate activity. High interest rates increase borrowing costs, potentially reducing demand and slowing price appreciation. Conversely, low interest rates can stimulate borrowing, leading to increased demand and potentially higher prices. Central bank policies and global economic trends directly impact domestic interest rates, which in turn affect the real estate market.
Brazil’s central bank chief hinting at a quick fix for the real estate market is interesting, but it’s also worth noting the recent F1 exemption granted to Arvid Lindblad 17 after a Red Bull request. This racing news highlights how interconnected global markets can be, even in seemingly disparate areas like motorsport and finance. Hopefully, this newfound stability in the Brazilian real estate sector will translate into broader economic benefits, mirroring the positive ripple effects from the racing community.
The current interest rate environment and its effects on affordability should be closely monitored.
Central Bank’s Role and Potential Actions
Brazil’s central bank, the Banco Central do Brasil (BCB), plays a crucial role in maintaining price stability and fostering economic growth. Its mandate encompasses managing inflation, overseeing financial institutions, and promoting a healthy financial system. The recent pronouncements regarding a potential solution for the real estate sector highlight the BCB’s proactive approach to addressing significant economic challenges. This proactive response reflects the central bank’s commitment to navigating complex situations and fostering stability in the Brazilian economy.The BCB’s potential actions in response to the real estate sector’s struggles are likely to be multifaceted and strategic.
These interventions will likely focus on mitigating potential risks, bolstering market confidence, and promoting sustainable growth. The specifics of these interventions will depend on the severity of the challenges and the nature of the proposed solution.
Mandate and Responsibilities of the Central Bank
The BCB is responsible for maintaining price stability, promoting full employment, and ensuring the stability of the financial system. This mandate is crucial for long-term economic prosperity and is reflected in the central bank’s numerous policy tools. The BCB’s actions directly impact inflation rates, interest rates, and overall economic activity.
Recent Communication Regarding a Potential Solution
The central bank’s recent communication suggests a willingness to intervene in the real estate market to ease the current situation. This communication signifies the BCB’s commitment to addressing market concerns and potential systemic risks. The specifics of the proposed solution, including the timeline and the degree of intervention, are yet to be fully disclosed.
Past Interventions in Similar Situations
The BCB has a history of intervening in challenging economic periods. These interventions often involve adjustments to monetary policy, such as changes in interest rates, to influence borrowing costs and economic activity. For instance, during periods of high inflation, the BCB might raise interest rates to curb spending and cool down the economy. Past examples include responses to periods of financial turmoil and economic downturns.
Policy Tools Available to the Central Bank
The BCB has a range of policy tools to influence the economy. These tools are used in conjunction with each other to achieve desired outcomes.
| Policy Tool | Potential Impact |
|---|---|
| Interest Rate Adjustments (Selic rate) | Influencing borrowing costs, consumer spending, and investment. Higher rates can curb inflation but may also slow economic growth. Lower rates stimulate growth but could potentially fuel inflation. |
| Reserve Requirements | Affecting the amount of money banks can lend, thereby impacting credit availability and overall liquidity in the market. |
| Open Market Operations | Buying or selling government securities to adjust the money supply. Buying securities increases the money supply and lowers interest rates, while selling securities decreases the money supply and raises interest rates. |
| Inflation Targeting | Maintaining a stable inflation rate by adjusting monetary policy to meet the inflation target. This approach helps maintain price stability and predictability. |
Impact of Potential Bridge Solution
A potential bridge solution for Brazil’s real estate market, as signaled by the central bank chief, promises a path towards stability. However, like any intervention, it comes with a complex set of potential consequences, both positive and negative. Understanding these implications is crucial for investors and market participants alike.This intervention aims to mitigate the current challenges within the real estate sector, but the effectiveness and overall impact will depend on the specific design of the solution and the broader economic environment.
It’s vital to consider the potential domino effects across various sectors.
Potential Positive Consequences
The bridge solution, if implemented effectively, could offer a lifeline to distressed borrowers and developers, preventing further defaults and market freezes. This stability could, in turn, bolster investor confidence and attract new capital into the market. For example, a well-structured program could support the completion of stalled projects, creating jobs and stimulating economic activity.
Potential Negative Consequences
The implementation of a bridge solution could also have unintended negative consequences. A poorly designed program could potentially lead to moral hazard, encouraging further risky behavior by borrowers and developers. There’s also a risk of distorting market signals, potentially creating an unsustainable bubble in the long term. For instance, if the bridge solution doesn’t address the underlying causes of the market distress, it might only be a temporary fix.
Effects on Investor Confidence and Market Liquidity
The proposed solution’s success in restoring investor confidence hinges on its perceived credibility and transparency. A well-communicated plan, outlining clear criteria and timelines, could help build trust. If investors perceive the bridge solution as a short-term fix without addressing systemic issues, investor confidence may remain low. This could hinder market liquidity, as investors may be hesitant to engage in transactions.
Historical examples of government interventions in real estate markets, both successful and unsuccessful, offer valuable lessons.
Comparison to Alternative Solutions
Several alternative solutions to the real estate crisis might be considered. These could include fiscal stimulus, regulatory changes, or even more drastic measures like nationalization. A comparison of the bridge solution to these alternatives would reveal its relative strengths and weaknesses in addressing the specific challenges facing Brazil’s real estate sector. Such a comparison should account for the potential for unintended consequences of each approach.
Likely Short-Term and Long-Term Effects on Property Prices
In the short term, a bridge solution could stabilize property prices, preventing a sharp decline. However, the long-term effects are less certain. If the solution addresses underlying issues like excessive leverage or unsustainable lending practices, long-term price stability could be achieved. If, however, the solution is merely a band-aid, future price volatility and potential corrections could occur.
Similar interventions in other markets offer a range of possible outcomes, illustrating the difficulty in predicting precise effects.
Potential Implications for Other Sectors

A potential bridge solution for Brazil’s real estate market, as signaled by the central bank, could have far-reaching effects beyond the sector itself. The intricate web of interconnectedness within the Brazilian economy means that any significant change in one area will likely reverberate through other sectors. Understanding these ripple effects is crucial for assessing the overall impact on the nation’s economic health.
Impact on the Construction Sector, Brazils central bank chief signals imminent bridge solution real estate
The real estate market is a major driver of the construction sector. A stabilization in the real estate market, facilitated by a bridge solution, is likely to lead to increased construction activity. This increase in demand for construction materials and labor will boost the construction sector, leading to more jobs and potentially higher economic growth. Conversely, if the solution fails to address the underlying issues or if the market remains stagnant despite the intervention, construction activity could decline, impacting employment and economic output in this crucial sector.
Impact on the Financial Sector
The financial sector, particularly banks and financial institutions involved in real estate lending, will experience a significant impact. A successful bridge solution could restore confidence in the market, leading to increased lending and investment in the real estate sector. Conversely, if the solution is perceived as insufficient or if the underlying problems persist, it could lead to a contraction in lending, impacting the overall financial health of the country.
Impact on Related Industries
The real estate sector is deeply intertwined with other industries, including furniture, interior design, and home appliances. A positive development in real estate would likely stimulate these related industries, leading to increased demand for their products and services. Conversely, a downturn in the real estate sector could negatively affect these industries, potentially leading to job losses and economic stagnation in these related markets.
Impact on Employment and Economic Growth
The effectiveness of the bridge solution will significantly influence employment and economic growth. If the solution is successful in stabilizing the market, it will likely lead to increased employment in the real estate, construction, and related sectors. This increased activity can boost economic growth through higher demand, production, and consumer spending. Conversely, an ineffective or delayed solution could exacerbate existing economic woes, potentially leading to job losses and further economic contraction.
Comparison of Potential Impacts Across Sectors
| Sector | Potential Positive Impacts | Potential Negative Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Real Estate | Stabilized market, increased investment, potential price recovery. | Uncertain long-term impact, market volatility, potential for further price drops if the solution fails. |
| Construction | Increased demand for materials and labor, job creation. | Potential for overbuilding if the market rebounds too quickly, reduced activity if the solution is ineffective. |
| Finance | Increased lending, investor confidence, stabilized financial system. | Reduced lending if the solution is perceived as ineffective, potential for financial instability if the solution fails. |
| Related Industries | Increased demand for products and services, job creation. | Reduced demand and potential job losses if the real estate market doesn’t recover. |
| Overall Economy | Potential for increased economic growth, job creation. | Potential for economic contraction if the solution fails, reduced consumer spending. |
Global Context and Comparative Analysis
Brazil’s potential real estate bridge solution is not an isolated event. Similar challenges and interventions have been seen in other developed and developing economies, often in response to market downturns or specific economic vulnerabilities. Understanding these global precedents can offer valuable insights into the potential outcomes and risks associated with the proposed Brazilian initiative.Analyzing the experiences of other countries with similar interventions allows us to evaluate the effectiveness of different approaches and their broader economic impact.
Brazil’s central bank chief hinting at a quick fix for the real estate market is interesting, considering the global economic climate. This potential solution contrasts with recent geopolitical developments, like Trump’s proposed Gaza freedom zone, which could significantly impact regional stability. Ultimately, however, the focus remains on Brazil’s real estate sector and the central bank’s ability to navigate these turbulent times.
Global economic conditions, particularly interest rate movements and investor confidence, play a crucial role in shaping real estate markets worldwide. A comprehensive understanding of these influences is vital for evaluating the potential impact of the Brazilian bridge solution.
Comparative Analysis of Similar Situations
A comparative analysis reveals a variety of responses to real estate crises in different countries. Some nations have adopted targeted measures to support specific sectors, while others have opted for broader macroeconomic adjustments. Examining these diverse approaches provides context for understanding the potential consequences of the Brazilian central bank’s actions.
Global Economic Influences
Global economic conditions significantly influence Brazil’s real estate market. Recessions in major economies can reduce demand for Brazilian exports, impacting the overall economy and potentially affecting real estate investment. Conversely, strong global growth can boost demand for Brazilian assets, potentially stimulating the real estate market. Interest rate adjustments by global central banks also have a direct impact on borrowing costs and investment decisions within Brazil.
Other Countries’ Experiences with Similar Interventions
Several countries have implemented interventions in their real estate markets. For example, [Insert country example 1] experienced a significant downturn in their housing market, leading to a series of government interventions to stabilize the situation. These interventions included measures such as tax incentives, subsidized loans, and regulatory changes to support the real estate sector. The outcomes of these interventions, including their effectiveness and unintended consequences, provide valuable lessons for Brazil.
[Insert country example 2] also adopted similar measures during a period of economic instability. Understanding these examples is crucial for assessing the potential risks and rewards of the Brazilian intervention.
Brazil’s central bank chief hinting at a quick fix for the real estate sector is interesting, especially given the current global economic climate. The uncertainty in the market, as seen in the recent surge of Asian currencies against the dollar, as bulls load up on Asian currencies due to trade uncertainty knocking the dollar , might be influencing the bank’s strategy.
Ultimately, a stable real estate market in Brazil is crucial for the overall economy.
Comparative Table
| Country | Nature of Intervention | Impact on Real Estate Market | Impact on Other Sectors | Outcome (Overall Assessment) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazil (Potential) | Bridge solution to support real estate sector | Potentially stabilize market, potentially stimulate activity | Potential positive ripple effect on construction and related industries, but possible inflationary pressures | Mixed – success contingent on the specifics of the intervention and broader economic conditions |
| [Country Example 1] | Tax incentives, subsidized loans | Short-term stabilization, but long-term impact uncertain | Stimulated construction but led to increased government debt | Limited success, as some initial benefits were offset by other issues |
| [Country Example 2] | Regulatory changes | Stabilized market sentiment but no substantial growth | Minimal impact on other sectors, except limited stimulation of related businesses | Moderately successful, with limited long-term effects |
Potential Risks and Uncertainties
Brazil’s real estate market, a crucial sector, is poised for a potential bridge solution. While this intervention aims to stabilize the market, inherent risks and uncertainties exist, impacting not only the real estate sector but potentially other segments of the Brazilian economy. Navigating these challenges will be crucial for the successful implementation and long-term sustainability of the proposed solution.
Implementation Challenges
The proposed bridge solution, while intended to address the current market pressures, faces potential implementation challenges. These hurdles could stem from bureaucratic complexities, logistical issues, or unforeseen resistance from various stakeholders. Effective communication and coordination among government agencies, financial institutions, and market participants are paramount for smooth implementation. Failure to address these challenges could lead to delays or even a complete derailment of the plan.
Unforeseen Consequences
The real estate market is intricate and interconnected. A poorly designed or executed bridge solution could have unforeseen consequences that ripple through other sectors of the economy. For example, if the solution inadvertently discourages investment or creates a negative perception of the Brazilian market, it could impact other industries like construction, tourism, and related services.
Effectiveness of the Proposed Solution
The success of the bridge solution depends on several factors. The effectiveness of the solution will hinge on its ability to address the underlying causes of the market pressures and maintain confidence among market participants. The effectiveness will also depend on the support it receives from the Central Bank and other regulatory bodies. Furthermore, market reactions to the intervention and its communication to the public will significantly influence the overall outcome.
Market Volatility and Investor Confidence
The real estate market is susceptible to fluctuations in economic conditions and investor sentiment. Any unexpected economic downturn, global financial crisis, or changes in investor confidence could undermine the effectiveness of the bridge solution. For instance, a sudden decrease in consumer confidence could negatively impact the housing market, rendering the solution less effective.
Potential for Corruption and Fraud
The implementation of any large-scale intervention in the market carries the risk of corruption and fraudulent activities. Measures must be put in place to mitigate these risks, such as stringent oversight mechanisms and independent audits to ensure transparency and accountability. Examples of similar interventions in other countries highlight the importance of robust anti-corruption measures.
Regulatory Uncertainty and Amendments
Changes in regulations or amendments to existing laws during the implementation phase could significantly impact the bridge solution. Unexpected legislative changes or regulatory ambiguity could hinder the smooth execution of the plan. Thorough consideration of potential regulatory hurdles and their impact on the proposed solution is essential.
Illustrative Case Studies
Navigating the complexities of real estate crises requires a deep understanding of past interventions. Learning from both successful and unsuccessful responses to similar situations globally provides crucial insights for policymakers. This section examines specific cases, highlighting the factors that shaped their outcomes.Examining historical interventions offers valuable lessons. These cases can illuminate effective strategies and warn against pitfalls.
By analyzing successful and unsuccessful interventions, we can develop a more nuanced understanding of how to approach a potential bridge solution for Brazil’s real estate market.
Successful Interventions in Similar Situations
Successful interventions often involve a multifaceted approach, combining fiscal and monetary policies with structural reforms. These interventions are tailored to the specific needs of the affected market and consider the broader economic context.
- The 2008 Global Financial Crisis saw several countries implement various stimulus packages to shore up their financial systems and boost economic activity. These packages included measures like tax cuts, increased government spending, and monetary easing. Many countries experienced varying degrees of success in mitigating the economic downturn. The speed and effectiveness of these interventions varied greatly, depending on factors like the country’s existing economic conditions, the depth of the crisis, and the strength of the political will to implement necessary measures.
“Successful interventions often require a swift and coordinated response, combining multiple policy tools tailored to the specific economic context.”
Unsuccessful Interventions in Similar Situations
Unsuccessful interventions often stem from a lack of comprehensive planning or a failure to address underlying structural issues. These interventions can have unintended consequences, potentially exacerbating the crisis or leading to a delayed recovery.
- Some countries’ responses to past financial crises have been criticized for their limited scope or ineffective implementation. For instance, certain stimulus packages might have been too small or focused on short-term fixes rather than long-term structural improvements. A lack of transparency and accountability in the implementation of these policies can also lead to a loss of public trust and potentially further hinder recovery efforts.
The effectiveness of the intervention often hinges on the depth of the crisis and the ability of the policymakers to tailor the response to the specific challenges faced by the country.
“A failure to address underlying structural issues or a lack of comprehensive planning can lead to ineffective interventions, potentially exacerbating the crisis.”
Key Factors Contributing to Outcomes
Examining the factors behind the success or failure of past interventions reveals crucial insights for future actions.
| Factor | Description | Impact on Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Policy Coordination | The degree to which various government agencies and stakeholders collaborate effectively in implementing the intervention. | Effective coordination often leads to a more unified and efficient response. |
| Transparency and Communication | The extent to which the intervention’s objectives, procedures, and expected outcomes are clearly communicated to the public. | Transparency builds public trust and fosters greater acceptance of the intervention. |
| Structural Reforms | The extent to which the intervention addresses the underlying structural issues contributing to the crisis. | Structural reforms often lead to more sustainable solutions and prevent future crises. |
Closing Notes
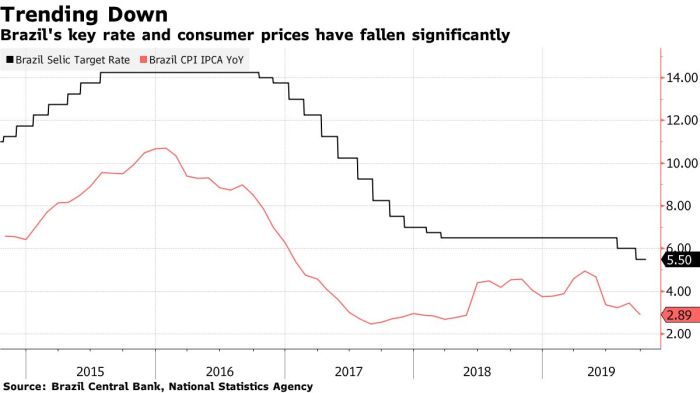
In conclusion, Brazil’s central bank’s potential bridge solution for the real estate sector presents a complex scenario with both opportunities and risks. The proposed intervention aims to stabilize the market, but the effectiveness of the solution hinges on careful consideration of potential repercussions across various sectors. This article has provided a comprehensive overview, examining historical context, potential impacts, and global comparisons to offer a well-rounded understanding of the situation.