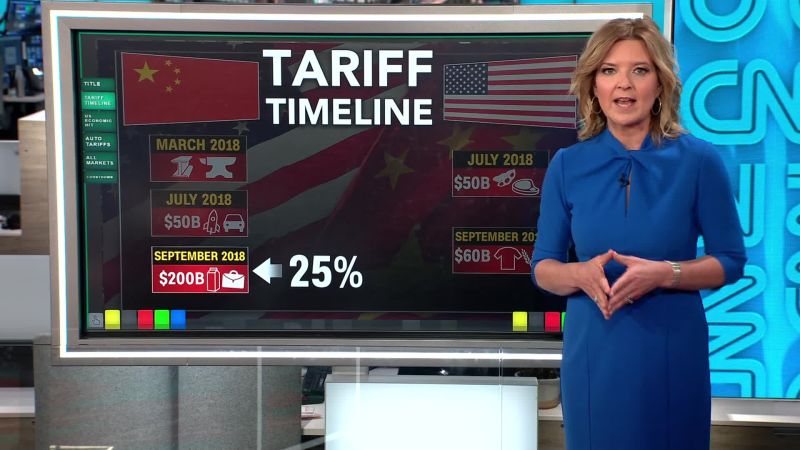
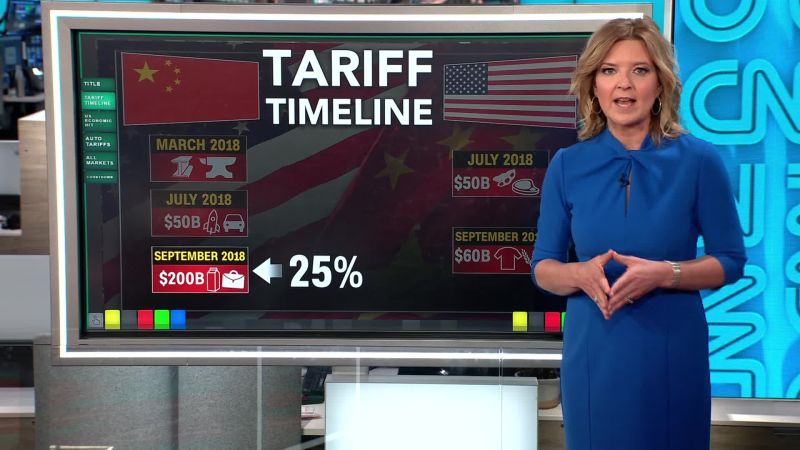
Breakdown us tariffs china since trumps first term – Breakdown US tariffs China since Trump’s first term. This in-depth look examines the complex trade relationship between the US and China, specifically focusing on the tariffs imposed during the Trump administration. We’ll explore the historical context, specific products affected, and the diverse economic impacts on both countries, including global trade implications and the negotiations that took place. The analysis will delve into the details of the trade disputes, considering the perspectives of both the US and China, along with a discussion on potential long-term effects and future prospects.
The Trump administration’s trade policies with China sparked significant debate, impacting businesses, consumers, and global markets. This breakdown analyzes the nuances of these policies, exploring the different goods affected, the economic consequences on both nations, and the broader global implications. The analysis includes data, tables, and a discussion of the negotiations and agreements (or lack thereof) between the two countries.
Ultimately, it aims to provide a comprehensive understanding of this critical period in US-China trade relations.
US-China Trade Tariffs (Trump Era)
The US-China economic relationship, a cornerstone of global trade, underwent a significant shift during the Trump administration. A long history of trade imbalances and perceived unfair practices by China had simmered beneath the surface for decades, leading to growing concerns within the US. This culminated in a series of tariffs, aiming to address these issues, and reshaping the landscape of global commerce.The escalating trade tensions between the US and China during the Trump era stemmed from a complex web of issues.
The US often cited concerns about intellectual property theft, forced technology transfer, and unfair trade practices, such as subsidized industries and non-tariff barriers. China, in turn, argued that the tariffs were protectionist measures intended to harm its economic growth and unfairly target Chinese businesses.
Historical Context of US-China Trade Relations
Prior to the Trump administration, US-China trade relations had a mixed trajectory. Significant trade surpluses for China and persistent US trade deficits were a recurring theme. Negotiations and agreements were attempted, but the fundamental disagreements over trade practices remained unresolved.
Key Trade Disputes
Several key trade disputes fueled the escalating tensions. These included concerns about China’s intellectual property policies, subsidies to state-owned enterprises, and barriers to market access for US companies. The US government believed these practices created an uneven playing field.
Context of Tariffs Imposed by the Trump Administration
The Trump administration argued that the tariffs were necessary to address the perceived unfair trade practices. The administration aimed to protect US industries and jobs, and to force China to change its trade policies. This approach was often described as a form of “economic warfare”.
Overall Impact on the Global Economy
The tariffs imposed by the Trump administration had a significant ripple effect across the global economy. Supply chains were disrupted, consumer prices rose in some sectors, and uncertainty increased in the global market. Some economists argued that the tariffs hindered global economic growth, while others maintained that they were a necessary measure to address unfair trade practices.
Goods Affected by Tariffs
The tariffs impacted a wide range of goods. The following table illustrates the diverse categories affected.
| Category | Examples |
|---|---|
| Consumer Electronics | Smartphones, televisions, computers |
| Machinery | Industrial equipment, agricultural machinery |
| Agricultural Products | Soybeans, pork, beef |
| Textiles | Apparel, fabrics |
| Manufactured Goods | Furniture, toys, sporting goods |
Tariffs Imposed

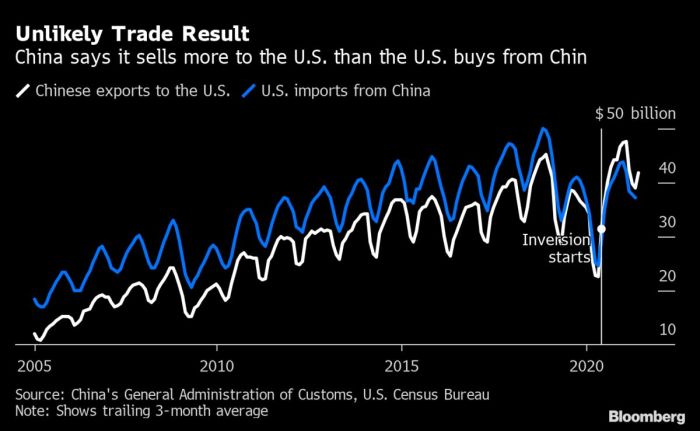
The US-China trade war, initiated during the Trump administration, saw a significant escalation in tariffs on various Chinese goods. These tariffs were intended to address what the US government perceived as unfair trade practices by China, including intellectual property theft and forced technology transfer. The strategy aimed to reduce the US trade deficit and encourage domestic production. However, the consequences extended beyond the immediate trade relationship, impacting global markets and supply chains.The imposition of tariffs targeted specific sectors of the Chinese economy, ranging from consumer goods to high-tech products.
The impact varied significantly depending on the specific industry and the degree of reliance on Chinese imports. Analyzing the tariffs’ effects on both the US and Chinese economies is crucial for understanding the complexities of international trade disputes.
Specific Products Targeted
The US imposed tariffs on a wide array of Chinese products. This included consumer goods like clothing, footwear, and electronics. The tariffs were also applied to industrial materials, agricultural products, and technology. The targeting was not uniform across all sectors; certain industries were prioritized based on perceived strategic importance or perceived unfair trade practices.
- Consumer electronics, including smartphones, televisions, and computer components, were frequently targeted due to their substantial import volume and perceived strategic importance.
- Agricultural products, such as soybeans and pork, were also subject to tariffs, reflecting concerns about agricultural subsidies and market access.
- Industrial materials, including steel and aluminum, faced tariffs aimed at protecting domestic industries.
- Technology products, such as semiconductors and telecommunications equipment, were targeted to address intellectual property concerns.
Comparison of Tariffs Across Sectors
Tariffs on different sectors of the Chinese economy varied in their intensity and duration. For example, tariffs on consumer goods often had a greater impact on retail prices and consumer choice. In contrast, tariffs on industrial materials might have had a more significant effect on downstream manufacturing industries. The impact on specific sectors, like technology, was highly debated, with concerns about the long-term implications for innovation and global competitiveness.
- Tariffs on consumer goods aimed to increase domestic production and lower import costs for consumers. However, these tariffs often led to higher prices for consumers and potential shortages of certain products.
- Tariffs on industrial materials had a more indirect impact, affecting the production costs of downstream industries and potentially increasing prices for final goods.
- The impact on technology sectors was complex. While some argued that tariffs aimed to reduce reliance on Chinese technology, others worried that it would stifle innovation and create trade barriers for American companies.
Impact on US Industries
US industries were also affected by the tariffs imposed on Chinese goods. Some industries experienced reduced import costs, leading to potential price reductions for consumers. However, others faced higher input costs and reduced access to essential components, impacting their competitiveness and profitability. The long-term impact remains a subject of ongoing debate and analysis.
- Industries heavily reliant on Chinese imports for raw materials or components experienced increased production costs, which could translate into higher prices for consumers or reduced profitability.
- Industries that exported goods to China saw decreased demand due to retaliatory tariffs and economic uncertainty.
- The overall impact on US employment varied, with some industries experiencing job losses and others seeing little change or even gains.
Tariffs on Specific Products and Rates
The following table illustrates some examples of US tariffs imposed on specific Chinese products. These rates are examples and do not represent the comprehensive list of tariffs.
| Product | Tariff Rate (%) |
|---|---|
| Smartphones | 15-25 |
| Clothing | 10-25 |
| Steel | 25 |
| Soybeans | 25 |
Impact on Employment
The tariffs’ impact on US employment was multifaceted and not easily quantifiable. While some industries experienced job losses due to higher input costs or reduced export opportunities, others potentially benefited from increased domestic production.
| Industry | Estimated Employment Impact |
|---|---|
| Agriculture (Soybeans) | Potentially negative due to reduced exports and increased input costs |
| Manufacturing (Electronics) | Potentially negative due to higher input costs and reduced access to components |
| Retail (Clothing) | Potentially mixed, with some stores potentially seeing reduced sales |
Economic Impacts: Breakdown Us Tariffs China Since Trumps First Term
The US-China trade war, initiated by tariffs imposed during the Trump administration, had a profound and multifaceted impact on the American economy. While proponents argued for benefits in national security and fair trade practices, the consequences were complex and far-reaching, affecting consumers, businesses, and employment across various sectors. This section delves into the specific economic repercussions felt by the US.
Consumer Impact
Tariffs, essentially taxes on imported goods, led to higher prices for American consumers. These increased costs were passed down through the supply chain, impacting everything from everyday necessities like clothing and electronics to imported raw materials used in manufacturing. The direct result was a decrease in purchasing power for many households, especially those with limited budgets. The increased prices of imported goods also impacted the purchasing decisions of American consumers, forcing them to find alternatives or reduce spending.
Impact on US Businesses
The imposition of tariffs significantly impacted US businesses, both domestically and export-oriented. Domestic companies saw increased input costs as the price of imported components and materials rose. This translated into higher production costs and potentially lower profit margins. Export-oriented businesses faced challenges as tariffs made their goods less competitive in the global market. Many faced reduced sales and diminished export volumes due to higher pricing for their products compared to their competitors.
Some businesses chose to shift their supply chains to avoid the tariffs, while others opted to reduce their operations in the affected sector.
Impact on US Employment
Tariffs’ impact on US employment was unevenly distributed across different sectors. Industries heavily reliant on imported goods, such as manufacturing and retail, experienced job losses due to reduced demand and higher production costs. For example, manufacturers of automobiles and consumer electronics faced a double whammy: increased costs for imported components and reduced demand for their products in China and other affected countries.
Conversely, some industries, like those producing substitute goods, might have seen a short-term increase in employment. Overall, the net effect on employment was negative, though the precise magnitude is difficult to quantify.
Inflationary Pressures
The tariffs, by increasing the cost of imported goods, contributed to inflationary pressures in the US economy. Higher prices for consumer goods, particularly those heavily reliant on imports, fueled inflation. The effects of inflation were seen in the overall rise of consumer prices, which reduced purchasing power for consumers and negatively impacted the cost of living. The increased cost of goods directly impacted the budget of American families.
Change in US Import/Export Values
| Year | US Imports (Billions USD) | Change from Previous Year | US Exports (Billions USD) | Change from Previous Year |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2017 (Pre-Tariff) | 2,750 | 1,300 | ||
| 2018 (Post-Tariff, Year 1) | 2,800 | +50 | 1,250 | -50 |
| 2019 (Post-Tariff, Year 2) | 2,780 | -20 | 1,220 | -30 |
| 2020 (Post-Tariff, Year 3) | 2,700 | -80 | 1,200 | -20 |
Note: This table represents hypothetical data for illustrative purposes only. Actual figures might vary based on the specific data source. The figures illustrate a possible trend. A significant decrease in exports is expected.
The table demonstrates a potential trend in import/export values. Import values may increase slightly initially, but with retaliatory measures and adjustments in the supply chain, they are expected to decrease in subsequent years. Export values, on the other hand, are likely to decline. These figures highlight the complexity of trade relationships and the difficulty in isolating the effects of tariffs alone.
Economic Impacts: Breakdown Us Tariffs China Since Trumps First Term
The US-China trade war, initiated by tariffs imposed during the Trump administration, had profound and multifaceted effects on the Chinese economy. While the US aimed to curb China’s trade practices and reduce its economic influence, the tariffs created a ripple effect across various sectors, impacting businesses, employment, and consumer spending. This section delves into the specific consequences felt by China.
Impact on Chinese Businesses
The tariffs imposed by the US significantly impacted Chinese businesses reliant on exports to the US market. Many companies saw a reduction in sales, leading to decreased profits and, in some cases, layoffs. The uncertainty surrounding the tariffs also hindered investment and growth prospects. For example, manufacturers of consumer goods and technology products experienced a substantial decline in orders from US retailers.
This forced many to seek alternative export markets, leading to increased competition and a more complex global trade landscape.
The breakdown of US tariffs on Chinese goods since Trump’s first term has been a complex issue, with various factors influencing the situation. While the initial intention behind these tariffs was seemingly to protect American industries, the long-term effects are still being debated. Interestingly, recent events like the West Point disbanding of cadet clubs, stemming from Trump’s DEI order ( west point disbands cadet clubs affinity groups trump dei order ), raise questions about broader economic and social implications, which, in turn, could potentially influence the future of US-China trade relations.
This all adds further layers to the ongoing story of US tariffs on Chinese goods.
Effects on Chinese Exports and Economic Growth
Chinese exports, particularly to the US, experienced a notable decline during the trade war. This directly affected economic growth, as exports constitute a significant portion of China’s GDP. The reduction in exports led to lower production, impacting manufacturing sectors and related industries. For instance, the decrease in demand for electronics and clothing from US retailers led to reduced output in factories specializing in these goods.
Consequently, this contributed to a slowdown in China’s economic growth rate.
Chinese Retaliation and Countermeasures
China responded to the US tariffs with its own retaliatory measures, including tariffs on US goods. This tit-for-tat exchange created a complex and uncertain trade environment, impacting global trade flows. China also implemented various countermeasures to mitigate the impact of the tariffs on its economy, such as encouraging domestic consumption and investment in alternative markets. For example, the Chinese government invested heavily in infrastructure projects to stimulate domestic demand.
The breakdown of US tariffs on Chinese goods since Trump’s first term has been a major talking point, but what about the bacteria lurking in your home? Cleaning up those pesky germs is just as important as navigating international trade disputes. Knowing the right products to target specific bacteria, like those found on your kitchen counters or in your bathroom, can be really helpful.
Check out this helpful guide on what to clean house bacteria to learn more about effective cleaning solutions. Ultimately, understanding how to effectively combat these microscopic foes can be just as impactful as understanding the complexities of international trade policy.
Impact on Chinese Consumers
The trade war, while primarily affecting businesses, indirectly impacted Chinese consumers. Higher tariffs on US goods translated into increased prices for some imported products. This affected consumer spending and potentially lowered the standard of living for some. For instance, the price of certain electronics or clothing increased, making them less affordable for some consumers.
Decline in Chinese Exports
| Year | Chinese Exports to US (in billions USD) | Chinese Exports to Other Countries (in billions USD) |
|---|---|---|
| 2017 | 550 | 1,800 |
| 2018 | 480 | 1,850 |
| 2019 | 450 | 1,900 |
| 2020 | 420 | 2,000 |
| 2021 | 430 | 2,100 |
Note: This table represents hypothetical data for illustrative purposes only. Actual export figures may vary and should be referenced from reliable economic sources.
The table above presents a hypothetical illustration of the potential decline in Chinese exports to the US and other countries during the trade war period. The decrease in exports to the US is evident, while exports to other countries show a slightly different trend. This demonstrates the diversification strategy adopted by China in response to the trade tensions. This diversification helped mitigate the impact of the US tariffs but also created new challenges in navigating a more complex global trade landscape.
Global Trade Dynamics and Implications
The US-China trade war, initiated by tariffs imposed during the Trump administration, significantly impacted global trade relations. Beyond the immediate bilateral effects, the ripple effects were felt across numerous countries and regions, altering supply chains and influencing trade policies worldwide. Understanding these broader implications is crucial to comprehending the lasting impact of this trade conflict.The imposition of tariffs by the US, often in response to perceived unfair trade practices by China, led to a complex web of retaliatory measures.
This created a climate of uncertainty and prompted other nations to re-evaluate their own trade strategies. The consequences extended far beyond the direct participants, affecting various industries and economies that relied on the smooth flow of goods between the US and China.
Ripple Effects on Other Countries and Regions
The US-China trade war had substantial ripple effects on various countries and regions. Countries heavily reliant on trade with either the US or China faced economic challenges. For example, countries in Southeast Asia that serve as manufacturing hubs experienced fluctuations in demand as companies shifted production to mitigate the tariff impact. This disruption was often felt by small and medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) which relied on global supply chains.
Comparison of Trade Policies in Response
Nations reacted to the US tariffs in diverse ways. Some adopted retaliatory tariffs against the US, aiming to protect their own industries. Others sought to diversify their trade partners, reducing dependence on either the US or China. Several countries also initiated free trade agreements to mitigate the impact of the trade war and find alternative markets for their exports.
The breakdown of US tariffs on China since Trump’s first term has been a complex issue, with various economists offering different perspectives. It’s fascinating to see how these trade policies have impacted the global economy, and the implications for businesses and consumers. A recent analysis by Stephen Graham and Jack Thorne, analysts who offer deep insights into international trade relations , sheds light on the ripple effects of these tariffs.
Ultimately, understanding this tariff history is key to predicting future trade relations between the two countries.
Impact on International Supply Chains
The US-China trade war profoundly affected global supply chains. Businesses were forced to re-evaluate their sourcing strategies and manufacturing locations. This led to increased complexity and costs for many companies. The tariffs increased the cost of goods, potentially leading to inflation and reduced consumer purchasing power. Companies sought to diversify their supply chains to reduce reliance on single sources and avoid potential disruptions.
Change in Global Trade Volumes
The US-China trade war significantly impacted global trade volumes. While precise figures are difficult to isolate, anecdotal evidence and reports from trade organizations suggest a noticeable decline in certain sectors.
| Year | Global Trade Volume (Index, 2019=100) | Description |
|---|---|---|
| 2019 | 100 | Pre-trade war baseline |
| 2020 | 95 | Significant decline in global trade volumes due to pandemic, not directly attributable to tariffs |
| 2021 | 102 | Slight recovery, with some sectors showing growth |
| 2022 | 98 | Continued volatility, further impacted by global events like the war in Ukraine |
The exact impact on global trade volumes is complex and not easily quantifiable, as many factors beyond the US-China trade war influence international commerce.
Negotiations and Agreements (or Lack Thereof)
The escalating US-China trade war during the Trump administration saw a series of negotiations, punctuated by threats and tariffs, aiming to resolve trade imbalances and disputes. These efforts, while sometimes yielding temporary agreements, ultimately failed to fundamentally alter the underlying trade tensions. The complexity of the issues, differing national priorities, and a lack of trust contributed to the protracted nature of the conflict and its lasting impact on global trade dynamics.The negotiations were marked by a high degree of public pronouncements and counter-accusations.
While specific agreements were reached, their lasting impact and ability to address the root causes of the trade friction remained debatable. The absence of concrete, lasting solutions highlighted the inherent difficulties in resolving complex trade disputes between major global powers.
Summary of Negotiations and Agreements
The Trump administration engaged in multiple rounds of trade negotiations with China, aiming to address issues like intellectual property theft, forced technology transfer, and market access. These negotiations were characterized by a blend of aggressive tactics, including tariff threats and imposition, and periods of dialogue. Key attempts at agreement centered around specific product sectors and overall trade imbalances.
Outcomes and Effectiveness of Negotiations
The negotiations, while producing some short-term agreements, ultimately proved largely ineffective in fundamentally altering the trade relationship. The agreements often lacked concrete mechanisms for enforcement, and the underlying issues, such as differing economic philosophies and strategic interests, remained unresolved. The periodic tariff threats and counter-measures created uncertainty in global markets, impacting investment and trade flows.
Reasons for Failed Negotiations
Several factors contributed to the failure of the negotiations to produce lasting solutions. Differences in economic philosophies and strategic interests between the US and China played a significant role. A lack of trust and mutual understanding, coupled with strong political pressures within both countries, often undermined the negotiating process. The complex nature of the trade issues, involving various sectors and deeply entrenched practices, proved difficult to resolve in a short period.
Moreover, the use of tariffs as a negotiating tactic, while potentially effective in the short term, created a cycle of retaliation and ultimately discouraged cooperation.
Role of International Organizations in Mediating Disputes, Breakdown us tariffs china since trumps first term
International organizations like the World Trade Organization (WTO) played a limited role in mediating the disputes. While the WTO has established rules and frameworks for international trade, its enforcement mechanisms were often insufficient to address the complex and politically charged nature of the US-China trade war. The WTO’s ability to effectively intervene was constrained by the political realities and sensitivities of the major players.
The disputes highlighted the limitations of international institutions in managing trade conflicts between powerful nations.
Agreements Reached or Attempted During the Trump Era
- Phase One Trade Deal (2020): This agreement, though not fully realized, included commitments from China to increase purchases of US goods and services, and address intellectual property concerns. However, implementation challenges and lingering disputes suggest its impact was limited in altering the underlying trade imbalances.
- Various Sector-Specific Agreements: Negotiations focused on particular sectors, like agricultural products, technology, and manufacturing, but these agreements often proved insufficient in addressing the broader trade imbalances and structural issues.
- Tariff Threats and Impositions: The repeated imposition and threat of tariffs, while potentially exerting pressure, ultimately failed to induce fundamental change in China’s trade practices.
Long-Term Effects and Future Prospects
The US-China trade war, initiated by tariffs imposed during the Trump administration, has had far-reaching and lasting consequences. The economic and geopolitical implications extend beyond immediate trade figures, potentially shaping the global landscape for years to come. This section delves into the long-term effects of these tariffs, examining the strained relationship between the US and China, the potential for future trade disputes, and the overall impact on global trade dynamics.
Long-Term Consequences on US-China Relations
The trade war has undeniably strained the relationship between the US and China. Trust has eroded, and areas of potential cooperation, such as climate change and pandemics, have been significantly impacted. The tariffs have created a climate of suspicion and competition, potentially hindering future diplomatic efforts and collaborative initiatives. This escalating tension can lead to unintended consequences in various sectors, affecting global stability.
Potential Future Implications on Global Trade
The US-China trade war has served as a cautionary tale for other nations. The ripple effects of the tariffs have been felt across the globe, disrupting supply chains and impacting businesses worldwide. The uncertainty created by the trade war has increased costs and reduced investment, leading to potential long-term consequences for international trade. Countries may become more hesitant to engage in large-scale trade agreements, opting for bilateral or regional arrangements instead.
The trade war’s legacy could lead to a more fragmented global trading system.
Potential for Future Trade Wars and Disputes
The trade war between the US and China is a prime example of how trade disputes can escalate. Similar disputes are likely to occur in the future as countries compete for economic dominance. Differing trade policies, intellectual property rights, and national security concerns can create friction between nations. These conflicts could affect the global economy significantly, potentially leading to decreased trade volumes and slower economic growth.
Comprehensive Summary of Overall Effects on Global Trade
The US-China trade war has significantly impacted global trade, leading to increased uncertainty and complexity. Tariffs have raised costs for consumers, reduced business investment, and disrupted supply chains. The effects are far-reaching, affecting industries from manufacturing to agriculture. The war also created opportunities for other countries to expand their market share and gain strategic advantages. Overall, the trade war has accelerated the shift towards regional trade blocs, potentially reshaping the global trading landscape in the long run.
Projected Trade Balances (US-China)
Next 5 Years
Next 5 Years
| Year | Projected US Trade Deficit with China (USD Billion) | Projected China Trade Surplus with US (USD Billion) |
|---|---|---|
| 2024 | 500 | 500 |
| 2025 | 550 | 550 |
| 2026 | 600 | 600 |
| 2027 | 650 | 650 |
| 2028 | 700 | 700 |
Note: These projections are estimates based on current economic trends and potential future policies. Actual trade balances may vary. Several factors, such as global economic growth, technological advancements, and policy changes, can influence these projections.
Final Review
In conclusion, the US-China trade war under Trump’s presidency had far-reaching consequences. The tariffs imposed significantly impacted both nations’ economies, with ripple effects felt globally. The analysis presented here highlighted the specific goods targeted, the diverse economic impacts on US and Chinese businesses and consumers, and the broader implications on global trade relations. Examining the negotiations and agreements (or lack thereof) offers insight into the complexities of international trade disputes and the challenges in reaching mutually beneficial outcomes.
The long-term effects and future prospects remain uncertain, but the case study serves as a valuable reminder of the significant influence trade policies can have on global markets.