
Domestic manufacturing isnt key to good jobs – Domestic manufacturing isn’t key to good jobs. This isn’t a simple case of outdated ideas; it’s a complex issue with deep historical roots, diverse perspectives, and a global context. We’ll explore the historical role of domestic manufacturing in job creation, compare it to alternative strategies, and examine the impact of globalization on the modern job market.
The narrative will delve into alternative job creation strategies, examining examples of successful initiatives in various sectors. We’ll also discuss the future of work, considering the evolving skills needed in a world shaped by automation and technological advancements. The role of government policies in fostering these changes will be explored, along with the pros and cons of different approaches.
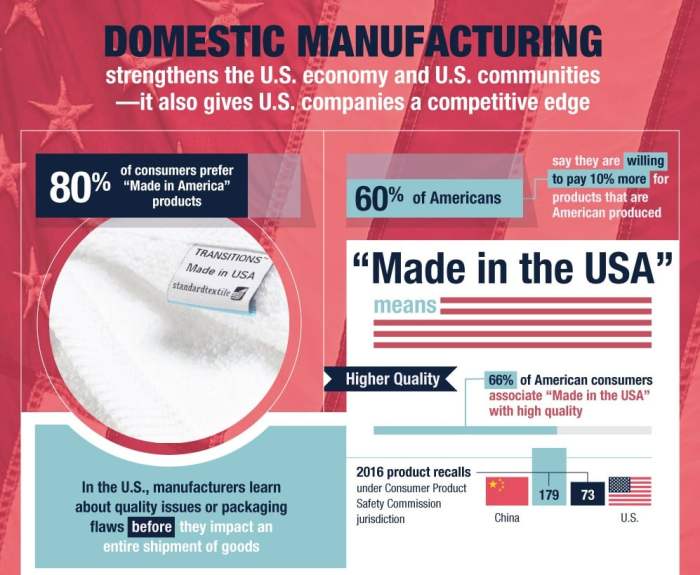
The Importance of Domestic Manufacturing
Domestic manufacturing has historically played a crucial role in economic growth and job creation. Its impact on national economies, from the Industrial Revolution onward, has been significant, shaping social and technological landscapes. Understanding its current relevance, considering both its benefits and drawbacks, is essential for informed economic policy.A strong domestic manufacturing sector often correlates with a stronger overall economy.
This sector fosters innovation, technological advancement, and skilled labor development. It’s a cornerstone of national resilience, allowing countries to produce essential goods and reduce reliance on external suppliers. However, the decline of domestic manufacturing in certain regions has raised questions about the best approaches to sustainable economic growth.
Focusing solely on domestic manufacturing isn’t the magic bullet for creating good jobs. While policies like those surrounding trump immigration crackdown executive orders might seem to address labor shortages, the reality is often more complex. Ultimately, a diverse and flexible economy, with robust trade and investment, is far more effective in fostering job growth than simply relying on domestic manufacturing.
Historical Overview of Domestic Manufacturing’s Role in Job Creation
Historically, domestic manufacturing has been a primary engine for job creation. The rise of factories and mass production in the 19th and 20th centuries led to a surge in employment opportunities. Industries like textiles, automobiles, and steel manufacturing provided substantial jobs, transforming communities and fostering economic growth. This period saw the development of specialized skills and the rise of a middle class, contributing to societal progress.
Different Perspectives on the Importance of Domestic Manufacturing
Advocates for domestic manufacturing emphasize its role in fostering national independence, building strong supply chains, and supporting domestic industries. They see it as a key element in economic stability and resilience, reducing reliance on foreign imports. Conversely, proponents of globalization and international trade emphasize the benefits of specialization and comparative advantage, arguing that focusing on domestic manufacturing may hinder overall economic growth.
Examples of Countries Successfully Transitioning Away from Heavy Reliance on Domestic Manufacturing
Several countries have successfully transitioned away from heavy reliance on domestic manufacturing while maintaining high employment rates. South Korea, for example, transitioned from an agricultural economy to a manufacturing powerhouse, then successfully diversified into high-tech industries, creating new employment opportunities. Singapore, similarly, developed a robust export-oriented economy through strategic investments in education and infrastructure, creating employment opportunities outside of manufacturing.
Factors Contributing to the Decline of Domestic Manufacturing in Some Regions
Several factors have contributed to the decline of domestic manufacturing in certain regions. Globalization, technological advancements, and shifts in consumer demand have all played a role. Rising labor costs, competition from lower-cost producers, and the pursuit of higher profit margins through outsourcing have also been significant factors.
Comparing Benefits of Domestic Manufacturing with Alternative Job Creation Strategies
Domestic manufacturing offers unique benefits, including the development of specialized skills, the fostering of innovation, and the creation of local supply chains. However, alternative strategies, such as investments in education, technology, and renewable energy, can also create jobs and stimulate economic growth. The optimal approach often depends on specific regional contexts and comparative advantages.
Potential Downsides of Prioritizing Domestic Manufacturing Over Other Economic Sectors
Prioritizing domestic manufacturing over other economic sectors can lead to misallocation of resources and potentially hinder the development of other potentially lucrative industries. It might also result in inflexibility in responding to changing market demands and technological advancements. A balanced approach that considers various sectors is crucial for long-term economic prosperity.
Relationship Between Domestic Manufacturing and Innovation
Domestic manufacturing fosters innovation through the development of new technologies, processes, and products. The need to improve efficiency, reduce costs, and adapt to changing market demands often drives innovation within manufacturing sectors. The creation of new jobs and the growth of related industries are often byproducts of these innovations.
Comparison of Pros and Cons of Domestic Manufacturing and Foreign Sourcing
| Feature | Domestic Manufacturing | Foreign Sourcing |
|---|---|---|
| Job Creation | High, localized job creation | Potentially lower, potentially offshored job creation |
| Economic Independence | Higher | Lower |
| Control over Production | Higher | Lower |
| Labor Costs | Potentially higher | Potentially lower |
| Environmental Impact | Potentially higher if not sustainable | Potentially lower or higher, depending on location and practices |
| Supply Chain Resilience | Higher | Lower |
Stages of a Product’s Lifecycle and Domestic Manufacturing
The flow chart below demonstrates how domestic manufacturing fits into a product’s lifecycle. From initial design and research to production, distribution, and eventual obsolescence, manufacturing plays a key role in each stage. This integrated approach allows for greater control over quality and efficiency.[Insert a flow chart here. It should visually depict the stages of a product’s lifecycle, highlighting the role of domestic manufacturing at each stage.
Example stages: Research & Development, Design, Production, Distribution, and Disposal.]
Alternative Job Creation Strategies
Beyond the traditional focus on manufacturing, diverse strategies can effectively drive job creation. These strategies encompass various sectors, from technology and services to renewable energy and sustainable practices. This approach recognizes that economic vitality isn’t solely dependent on a single industry, but rather on a thriving ecosystem of interconnected sectors. Successful implementation of these strategies necessitates adaptability, innovation, and proactive investment in human capital.Focusing solely on domestic manufacturing overlooks the dynamic potential of alternative job creation avenues.
These alternative pathways offer opportunities for economic growth, skill development, and a more resilient and adaptable economy. The key lies in recognizing the evolving landscape of work and proactively preparing the workforce for the demands of a future shaped by technological advancements and changing global trends.
Strategies for Job Creation Outside Manufacturing
A diversified economy offers a more robust and sustainable approach to job creation. This strategy necessitates a shift in focus from relying solely on traditional manufacturing industries to embracing a broader range of sectors. The emphasis should be on fostering an environment that encourages innovation, entrepreneurship, and the development of new industries.
Examples of Successful Alternative Initiatives
Numerous successful initiatives exist in diverse sectors. For example, the tech sector has created millions of jobs globally, fueled by innovation and technological advancement. The renewable energy sector is growing rapidly, creating jobs in solar panel manufacturing, wind turbine installation, and energy storage solutions. Similarly, the healthcare sector, encompassing medical research, pharmaceuticals, and healthcare services, offers a consistent source of employment.
These examples highlight the potential of diverse sectors to drive economic growth and job creation.
Potential Future Job Sectors
- Renewable Energy: This sector is poised for significant growth, driven by global efforts to transition to cleaner energy sources. Opportunities exist in solar panel installation, wind turbine maintenance, and energy storage technologies.
- Technology and Software Development: The demand for skilled software developers, data scientists, and cybersecurity professionals continues to rise, creating substantial employment opportunities.
- Healthcare Services: The aging global population and rising healthcare costs contribute to the ongoing need for doctors, nurses, therapists, and other healthcare professionals.
- Sustainable Agriculture and Food Production: As concerns about food security and environmental sustainability grow, the sector of sustainable farming practices and innovative food technologies is gaining importance.
- Green Building and Construction: The demand for energy-efficient and sustainable buildings is driving job creation in green construction, renewable energy integration, and sustainable building materials.
Long-Term Economic Impacts
Alternative job creation strategies offer a more sustainable and resilient economic model compared to solely relying on domestic manufacturing. A diversified economy is less vulnerable to economic downturns or industry-specific shocks. The focus on innovation and new technologies can lead to long-term economic growth and increased competitiveness in the global market.
Skills and Training Needs for Non-Manufacturing Jobs
The skills required for jobs in non-manufacturing sectors are constantly evolving. Training programs need to adapt to the changing demands of the job market. Emphasis should be placed on developing skills in technology, data analysis, communication, problem-solving, and adaptability.
Government Policies for Fostering Alternative Job Creation
Government policies play a critical role in fostering alternative job creation. This includes investing in education and training programs, promoting research and development, and providing incentives for entrepreneurship and innovation. Attracting foreign investment in these emerging sectors can also stimulate job creation.
Projected Sector Growth
| Sector | Projected Growth Rate (2024-2030) |
|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | 10-15% |
| Technology and Software Development | 8-12% |
| Healthcare Services | 6-8% |
| Sustainable Agriculture | 5-10% |
| Green Building and Construction | 7-9% |
Note: These figures are estimates and may vary based on economic conditions and policy changes.
Impact of Automation and Technology
Automation and technology are transforming the job market. While some jobs may be displaced, automation also creates new job opportunities in areas like robotics, artificial intelligence, and data analysis. Adaptation and upskilling are essential to navigate these changes.
Diversified Economy and Job Security
A diversified economy fosters greater job security. By spreading economic activity across multiple sectors, a nation reduces its vulnerability to downturns in any one industry. This approach promotes resilience and creates a more stable and sustainable economic future.
Globalization and its Impact: Domestic Manufacturing Isnt Key To Good Jobs
Globalization has profoundly reshaped the world economy, impacting virtually every facet of modern life, including the job market. The interconnectedness fostered by global trade and investment has created both opportunities and challenges for workers and businesses worldwide. Understanding these effects is crucial for navigating the complexities of the 21st-century economy.The interconnected nature of global supply chains and the ease of international movement of goods and capital have significantly altered the landscape of manufacturing and employment.
This shift necessitates a nuanced understanding of the interplay between globalization and domestic manufacturing, recognizing both the benefits and drawbacks for workers and economies.
The Role of Globalization in Shaping the Current Job Market
Globalization has dramatically altered the job market by increasing competition and driving specialization. The ease of transferring production to countries with lower labor costs has led to job displacement in developed nations, but simultaneously, new opportunities have emerged in emerging economies. This complex dynamic requires careful consideration of the long-term implications for workers and industries.
Impact of International Trade Agreements on Domestic Manufacturing
International trade agreements, such as the North American Free Trade Agreement (NAFTA) and the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP), have significantly influenced domestic manufacturing. These agreements, while aiming to foster economic growth, often lead to shifts in production locations and can result in job losses in sectors exposed to increased foreign competition. The long-term consequences of such agreements are a subject of ongoing debate and analysis.
Examples of Globalization’s Impact on Employment in Different Countries
The impact of globalization on employment varies considerably across countries. For example, China’s rapid industrialization, facilitated by globalization, has led to significant job creation in manufacturing, while developed nations like the United States have experienced job losses in certain sectors. These examples highlight the uneven distribution of benefits and burdens associated with globalization. The impact is not uniform and is affected by a multitude of factors, including a country’s level of industrialization, its workforce’s skillset, and the nature of its industries.
Economic Benefits and Drawbacks of Globalization for Workers
Globalization presents both economic benefits and drawbacks for workers. In some countries, increased access to foreign markets and investment can stimulate economic growth and create new jobs. However, the same process can lead to job displacement and wage stagnation in other sectors, particularly in developed nations. A comprehensive assessment must weigh these competing forces to understand the overall impact on workers’ livelihoods.
Challenges and Opportunities for Domestic Manufacturing in a Globalized World
Domestic manufacturing faces both challenges and opportunities in a globalized world. The need for adaptation and innovation is paramount. Companies must either become more efficient to compete with global players or differentiate their products in order to maintain a foothold in the market. A successful strategy involves embracing technology, upgrading skills, and finding niches where they can excel.
The Role of Foreign Investment in Job Creation
Foreign investment can play a crucial role in job creation, particularly in developing countries. Foreign companies often bring capital, technology, and management expertise, which can stimulate economic growth and create employment opportunities. However, the impact of foreign investment can vary depending on the specific industry and the policies of the host country.
Companies That Have Successfully Adapted to Global Competition
Numerous companies have successfully adapted to global competition by adopting innovative strategies. Companies that have prioritized product differentiation, invested in technology, and built strong supply chains have been better positioned to thrive in a globalized market. Examples of such successful adaptations include companies like Nike and Adidas, who have built their supply chains to leverage global labor markets and maintain competitive pricing.
Impact of Globalization on Supply Chains
Globalization has fundamentally altered supply chains, leading to increased complexity and interconnectedness. Goods are often produced in multiple countries, with components sourced from different regions. This intricate web of global supply chains can be both efficient and vulnerable. Disruptions in one part of the chain can have ripple effects throughout the entire system.
Barriers to Entry for New Businesses in Global Markets
Potential barriers to entry for new businesses in global markets include high startup costs, intellectual property protection concerns, and navigating complex international regulations. Overcoming these hurdles requires careful planning, strategic partnerships, and a deep understanding of the specific market conditions in the target countries. A well-researched market entry strategy is vital to ensure a successful launch in a global market.
The Future of Work
The future of work is rapidly evolving, driven by technological advancements and shifting societal needs. This transformation demands a proactive approach to reskilling and upskilling the workforce to remain competitive and relevant in the ever-changing job market. The nature of work itself is undergoing a fundamental shift, requiring a careful assessment of how existing skills can be adapted and new skills acquired to navigate this new landscape.The current workforce is already experiencing the impact of automation and artificial intelligence.
While these technologies present challenges, they also unlock opportunities for growth and innovation. Understanding the interplay between human capabilities and technological advancement is crucial for preparing for the future.
Evolving Nature of Work and Changing Skills
The modern workplace is increasingly dynamic and demanding. Traditional job descriptions are becoming less rigid, replaced by roles that require adaptability and a blend of hard and soft skills. The ability to learn new skills quickly and continuously is paramount for success. Workers need to embrace lifelong learning and be open to evolving job roles. This adaptability will be essential for navigating the complexities of the future job market.
Role of Automation and Artificial Intelligence in the Job Market
Automation and artificial intelligence are transforming industries, creating new opportunities while simultaneously altering existing roles. Certain tasks previously performed by humans are now being automated, requiring workers to focus on higher-level cognitive skills and tasks that machines cannot replicate. Examples include complex problem-solving, critical thinking, and creativity. This shift necessitates a focus on developing skills that complement and enhance the capabilities of these technologies.
While some argue domestic manufacturing is crucial for good jobs, the reality is often more complex. The US-China robotics race, for instance, is highlighting how automation is rapidly reshaping the global landscape. This race isn’t just about robots; it’s about the future of work, and it suggests that focusing solely on bringing manufacturing back to the US might not be the silver bullet for creating high-quality jobs.
Ultimately, a broader approach, encompassing innovation and adaptation, is likely a better strategy for creating a robust and competitive job market.
Impact of Technological Advancements on Domestic Manufacturing, Domestic manufacturing isnt key to good jobs
Technological advancements are reshaping the domestic manufacturing sector. Robotics, automation systems, and advanced data analytics are becoming integral components of production processes. This necessitates a shift in the skills required for manufacturing jobs. Future roles will demand expertise in operating and maintaining sophisticated machinery, interpreting data, and ensuring quality control.
Comparison of Manufacturing Skills Now and in the Future
Current manufacturing jobs often involve repetitive tasks and manual labor. Future roles will require a greater emphasis on technical expertise, data analysis, and problem-solving. Workers will need to understand and utilize complex software and machinery, and have a comprehensive understanding of process optimization. This transition necessitates proactive investment in training and education.
Potential Areas of Growth for Workers in the Face of Automation
Despite automation’s impact, several areas are likely to experience significant growth. These include roles in robotics engineering, data science, AI development, and machine learning. These fields demand expertise in advanced technologies and offer high potential for career advancement.
Industries Likely to Experience Significant Growth
The healthcare industry, renewable energy sector, and the technology sector are predicted to experience substantial growth in the coming decades. These industries demand skilled workers with expertise in areas such as medical technology, renewable energy systems, and software development.
While some argue that domestic manufacturing is essential for good jobs, a deeper look reveals a more nuanced picture. Recent research, and even a fascinating interview with Keith McNally, author of a new memoir, keith mcnally memoir interview , highlights the evolving job market. It suggests that focusing solely on domestic manufacturing might not be the key to creating high-quality, sustainable employment opportunities.
The globalized economy and technological advancements often dictate the types of jobs most in demand, and a shift in focus is arguably more beneficial.
Importance of Continuous Learning and Upskilling
In the dynamic modern job market, continuous learning and upskilling are essential for long-term success. Workers must actively seek opportunities to acquire new skills and adapt to changing industry needs. This commitment to continuous improvement will be critical for navigating the future job market.
Potential Skills Gaps and Solutions
| Potential Skills Gap | Solution |
|---|---|
| Lack of expertise in advanced technologies (AI, robotics) | Investment in educational programs focused on AI and robotics. Partnerships between industry and educational institutions. |
| Insufficient data analysis skills | Promoting data literacy through training and certifications. Developing specialized courses focused on data analysis and interpretation. |
| Gap in soft skills (communication, collaboration) | Integration of soft skills training into existing educational programs. Encouraging collaborative projects and teamwork in the workplace. |
Role of Education and Training in Preparing the Workforce
Education and training play a critical role in equipping the workforce with the skills necessary to succeed in the future. Curricula should be updated to reflect the evolving demands of the job market, focusing on transferable skills, critical thinking, and problem-solving. Collaboration between educational institutions and industry partners is vital for creating relevant and effective training programs.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies play a crucial role in shaping the domestic manufacturing sector. Effective policies can foster growth, attract investment, and create jobs, while poorly designed policies can stifle innovation and hinder competitiveness. Understanding the nuances of these policies is essential for crafting strategies that support the sector’s long-term health and prosperity.Government intervention, when thoughtfully implemented, can provide a supportive environment for domestic manufacturing.
This can involve tax incentives, targeted subsidies, regulatory frameworks that protect workers’ rights, and strategic investments in infrastructure. Conversely, poorly conceived policies can inadvertently harm the sector by creating unnecessary burdens or by failing to address the specific needs of manufacturers.
Impact of Government Policies on Domestic Manufacturing
Government policies significantly influence the domestic manufacturing sector by either promoting or hindering its growth and competitiveness. These policies can take many forms, from tax incentives and subsidies to regulations that affect worker safety and environmental standards. Effective policies attract investment, encourage innovation, and promote job creation, while poorly designed ones can create barriers to entry and stifle economic activity.
Examples of Policies Supporting or Hindering Domestic Manufacturing
Numerous examples illustrate the impact of government policies on the domestic manufacturing sector. Policies that support domestic manufacturing often include tax breaks for investments in new equipment, grants for research and development, and subsidies for training programs for workers. Conversely, excessive regulations or tariffs can hinder growth by increasing production costs and reducing competitiveness.
Role of Tax Incentives and Subsidies in Attracting Investment
Tax incentives and subsidies play a critical role in attracting investment in domestic manufacturing. By reducing the financial burden on manufacturers, these incentives encourage them to expand operations, invest in new technologies, and create new jobs. For example, tax credits for capital investments or research and development can stimulate innovation and competitiveness. Targeted subsidies, such as grants for training programs or infrastructure development, can further bolster the sector’s capabilities.
Comparison and Contrast of Different Approaches to Supporting Domestic Manufacturing
Different approaches to supporting domestic manufacturing have varying degrees of effectiveness. Some strategies focus on reducing the overall tax burden for manufacturers, while others target specific sectors or technologies. Policies that provide direct financial support, such as grants or subsidies, can be more impactful in the short term, but may require careful oversight to ensure their effectiveness. Other approaches, such as streamlining regulations or improving infrastructure, can have long-term benefits for the entire economy.
Role of Regulations in Protecting Workers’ Rights
Regulations play a vital role in protecting workers’ rights and ensuring fair labor practices within the domestic manufacturing sector. Robust regulations regarding workplace safety, minimum wages, and working hours contribute to a healthy and productive workforce. These regulations can also promote a more stable and predictable environment for businesses, encouraging long-term investment and growth.
Potential Government Interventions to Stimulate Job Creation
Government interventions can stimulate job creation by focusing on areas where domestic manufacturing can thrive. This can include investing in infrastructure improvements, streamlining regulations to reduce bureaucratic burdens, and providing targeted training programs to equip workers with the skills needed for the modern manufacturing environment. Investments in research and development can also support the development of innovative technologies, which can lead to the creation of new industries and jobs.
Table Outlining Pros and Cons of Different Government Policies
| Policy | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|
| Tax incentives for investment | Encourages capital investment, potentially boosts production, creates jobs. | May not reach smaller businesses, potential for misuse of funds. |
| Subsidies for R&D | Stimulates innovation, creates opportunities for new technologies, potentially boosts productivity. | Can be difficult to target effectively, potential for wasteful spending. |
| Streamlining regulations | Reduces bureaucratic burden on businesses, potentially increases investment and job creation. | May compromise worker safety or environmental protection, potentially harm consumers. |
Successful Government Initiatives to Support Job Creation in Specific Sectors
Successful government initiatives to support job creation in specific sectors demonstrate the potential for targeted interventions. Examples include programs that provide grants and training for workers in renewable energy or advanced manufacturing industries. These initiatives often involve collaborations between government agencies, businesses, and educational institutions to ensure that the training aligns with industry needs.
Effectiveness of Different Policy Approaches in Creating Jobs
The effectiveness of different policy approaches in creating jobs depends on several factors, including the specific context of the economy, the targeted industry, and the overall regulatory environment. Policies that combine various approaches, such as tax incentives, infrastructure investments, and workforce development programs, often produce more robust and sustainable results in job creation. The success of these policies also hinges on careful evaluation and adjustment based on ongoing data and feedback from the affected industries.
Concluding Remarks

In conclusion, while domestic manufacturing has played a significant role in the past, focusing solely on it may not be the optimal strategy for creating good jobs in the future. A diversified economy, supported by alternative job creation strategies and adaptable government policies, is crucial for ensuring a robust and resilient job market. The global landscape, characterized by technological advancements and international trade, requires a forward-thinking approach that embraces innovation and continuous learning.

