EU executive starts disciplinary steps against Austria over budget deficit, marking a significant escalation in the ongoing debate about fiscal responsibility within the European Union. This action highlights the bloc’s commitment to maintaining financial stability across member states. Austria’s budget deficit, a key concern for the EU, has prompted this disciplinary response. The move signifies a serious issue, impacting not just Austria but potentially other member states who might face similar scrutiny in the future.
This article delves into the background of the issue, exploring Austria’s historical budget performance, EU regulations, and the specific financial indicators that triggered this disciplinary action. It examines the nature of the disciplinary steps being taken, including timelines and potential penalties. Furthermore, we’ll analyze the potential economic and political ramifications for Austria and the broader EU, considering possible solutions and outcomes.
Finally, we’ll compare Austria’s situation with other budgetary crises in the EU, drawing lessons from similar experiences.
Background of the Issue
The EU’s disciplinary action against Austria over its budget deficit highlights a long-standing tension between national sovereignty and supranational regulations. Austria’s fiscal situation, while not unprecedented, has apparently crossed a threshold that triggered the EU’s enforcement mechanisms. This situation underscores the delicate balance between member states’ autonomy and the need for collective fiscal responsibility within the European Union.The EU’s fiscal framework, designed to promote stability and coordination, has a complex history.
Initially focused on preventing excessive deficits, the framework has evolved to incorporate more sophisticated mechanisms for monitoring and sanctioning. This evolution reflects a continuous adaptation to economic realities and the changing needs of the European project.
Historical Context of Budget Deficits in Austria
Austria, like many developed economies, has experienced periods of budget deficits throughout its history. The severity and duration of these deficits have varied, often influenced by cyclical economic downturns, government spending priorities, and economic shocks. While Austria has generally maintained a stable economic performance, instances of higher-than-average deficits have occurred, particularly during periods of recession or significant investments.
The current situation, however, is noteworthy due to the EU’s specific concerns.
Relevant EU Regulations Regarding National Budgets
The EU’s Stability and Growth Pact (SGP) sets the framework for national budget policies. It aims to prevent excessive deficits and debt levels by encouraging responsible fiscal policies across member states. The SGP Artikels specific thresholds for deficit-to-GDP ratios and debt-to-GDP ratios. Exceeding these limits can trigger sanctions, ranging from warnings to financial penalties, depending on the severity and persistence of the violation.
These regulations aim to foster economic stability and confidence within the eurozone.
Key Historical Events and Their Relation to the Current Situation
Several key events in the past have shaped the current environment. The 2008 global financial crisis, for instance, led to a period of significant economic adjustments across Europe, prompting a renewed emphasis on fiscal responsibility. The Eurozone debt crisis of the 2010s further highlighted the importance of maintaining sustainable fiscal policies within the framework of the EU’s monetary union.
The EU executive’s disciplinary actions against Austria for its budget deficit are a pretty big deal, highlighting the bloc’s commitment to fiscal responsibility. This mirrors the situation in Iraq, where the Kurdish government is being held legally responsible for continued oil smuggling, a serious issue that impacts the nation’s finances. Ultimately, these kinds of actions from both sides demonstrate the importance of financial accountability and compliance with international standards, much like the EU’s disciplinary steps against Austria.
Iraq holds Kurdish government legally responsible continued oil smuggling
The ongoing economic context, including inflation and energy prices, also plays a role in the current discussion, as it affects national budgets and the ability to meet the SGP requirements.
Specific Financial Indicators that Triggered the Disciplinary Action
The EU’s assessment likely focused on Austria’s deficit-to-GDP ratio, a key indicator of fiscal health. This ratio, calculated by dividing the country’s budget deficit by its gross domestic product (GDP), represents the proportion of the economy consumed by the deficit. The precise figures and the specific period analyzed by the EU authorities are critical factors in understanding the current situation.
Other indicators, such as the debt-to-GDP ratio, might also have been considered.
Key Actors Involved in this Situation
The key actors involved include the Austrian government, the European Commission, and the European Council. The Austrian government is responsible for formulating and implementing its national budget. The European Commission monitors compliance with EU regulations and has the authority to initiate disciplinary action. The European Council ultimately decides on the appropriate response to violations. Other stakeholders, including financial institutions and international organizations, may also play a role, though to a lesser degree.
Nature of the Disciplinary Action
The EU’s disciplinary action against Austria for its budget deficit highlights the bloc’s commitment to fiscal responsibility and the stability of the Eurozone. This action isn’t simply a symbolic gesture; it represents a critical step in enforcing EU regulations and potentially influencing future national budgetary policies. The specific nature of the steps taken will determine the impact on Austria’s economic trajectory and the overall health of the European economy.
Specific Steps Being Taken
The EU executive, likely the European Commission, will initiate a formal procedure, outlining the reasons for concern regarding Austria’s budget deficit. This will involve a detailed analysis of Austria’s fiscal position, comparing it to EU regulations and previous commitments. The Commission will issue a formal letter of concern, detailing the specific breaches and demanding corrective measures. This letter will be a crucial first step in the process, clearly stating the nature of the alleged violation and setting a timeframe for Austria’s response.
The EU executive’s disciplinary actions against Austria over its budget deficit seem pretty serious. It’s a reminder of the strict rules governing the bloc’s finances. Meanwhile, Franklin Graham’s interview about the USAID foreign aid freeze franklin graham usaid foreign aid freeze interview raises some interesting questions about global aid priorities. Ultimately, these financial battles highlight the complexities of international cooperation and economic stability.
Procedures and Timelines
The disciplinary process follows a predefined framework within the EU’s legal framework. The exact timeline is not publicly available and depends on the specific circumstances and the nature of the response from Austria. However, the process generally involves several stages: an initial assessment, followed by consultations with the offending nation, potential recommendations for adjustments, and possible further steps if the initial response is deemed insufficient.
The timeline for each stage can vary significantly.
Potential Penalties for Austria
Potential penalties for Austria could range from issuing formal warnings to more severe measures, such as imposing financial sanctions or even invoking stricter enforcement mechanisms. The severity of the penalties will depend on the degree of the budget deficit breach and Austria’s response. Historically, the EU has implemented varying degrees of penalties for similar breaches. The choice of penalty will also consider the potential economic impact on Austria and the broader EU economy.
Examples of penalties could include adjustments to EU funds or directives to Austria to bring its budget deficit within acceptable levels.
Comparison with Other Similar Actions
Past instances of similar disciplinary actions against EU member states have included issues relating to excessive debt, inadequate structural reforms, or failure to meet agreed-upon targets. These instances illustrate the EU’s commitment to enforcing its fiscal rules, ensuring financial stability within the Eurozone. The outcomes of previous cases provide a benchmark for understanding potential outcomes, including the type of measures taken, the length of the process, and the overall impact on the member state.
Each case is unique, but the EU’s approach often involves a progressive escalation of measures.
Table of Disciplinary Process
| Stage | Description | Timeline |
|---|---|---|
| Formal Letter of Concern | The European Commission issues a formal letter outlining the reasons for concern regarding Austria’s budget deficit and demanding corrective measures. | Within a few weeks of initial assessment. |
| Consultation | The Commission engages in dialogue with the Austrian government to understand their perspective and propose solutions. | Several weeks, potentially months. |
| Recommendations for Adjustments | The Commission may issue recommendations for specific budget adjustments and economic reforms. | Dependent on the outcomes of the consultation. |
| Enforcement of Penalties (if necessary) | If the recommendations are not adequately addressed, the EU may impose financial sanctions or other enforcement measures. | Varies, dependent on the severity of the breach and the Austrian response. |
Economic Impact and Implications
Austria’s recent budget deficit has sparked a significant debate within the EU, prompting disciplinary action from the executive. This action raises crucial questions about the potential economic repercussions for Austria and the broader European Union. The disciplinary measures could trigger a cascade of events, impacting trade, investment, and the overall economic stability of the region.
Overview of Austria’s Economic Performance
Austria boasts a robust and diversified economy, traditionally performing well within the EU framework. Key strengths include a strong manufacturing sector, a well-developed tourism industry, and a highly skilled workforce. However, recent economic trends, including inflationary pressures and global supply chain disruptions, have posed challenges to its sustained growth. Understanding these pre-existing economic trends is essential to evaluating the potential impact of the disciplinary measures.
Potential Economic Consequences for Austria and the EU
The disciplinary action could lead to several economic consequences for Austria. Reduced access to EU funds or penalties could hinder Austria’s investment capacity and potentially affect its public spending priorities. This could, in turn, impact employment and economic growth. Furthermore, the action might trigger a confidence crisis, potentially leading to a decrease in investor confidence, impacting capital flows and market sentiment.
At the EU level, the disciplinary action could set a precedent for future cases, raising questions about the effectiveness and consistency of EU fiscal rules.
Potential Impact on Trade and Investment
The disciplinary action might influence trade flows between Austria and other EU member states. Uncertainty surrounding the application of EU rules could lead to delays in investment projects and potentially affect supply chains. This impact could be particularly significant for companies involved in cross-border trade and investment. Historically, trade disputes have had ripple effects, potentially impacting the overall EU economy.
Potential Ripple Effects Across the EU
The disciplinary action could have broader implications for the entire EU. It might influence the implementation of fiscal policies in other member states, potentially triggering concerns about compliance with EU regulations. The action could also affect the perception of the EU’s ability to enforce its rules and maintain economic stability, potentially impacting its standing in the global arena.
The handling of this situation could set an important precedent regarding the EU’s commitment to fiscal discipline.
The EU executive’s disciplinary actions against Austria over its budget deficit are certainly interesting, highlighting the bloc’s commitment to fiscal responsibility. Meanwhile, the recent news about the Vanguard new ex-China ETF following the push from Missouri Republicans, as reported here , shows a fascinating interplay between political pressure and financial markets. Ultimately, the EU’s stance on Austria’s budget underscores the importance of maintaining financial stability within the union.
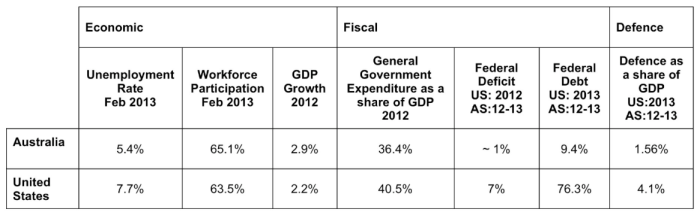
Comparative Economic Indicators
| Economic Indicator | Austria (Pre-Disciplinary Action) | Austria (Post-Disciplinary Action – Estimated) |
|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth Rate (%) | 2.5 | 2.0-2.2 |
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 4.8 | 5.0-5.2 |
| Inflation Rate (%) | 6.2 | 6.5-7.0 |
| Government Debt to GDP Ratio (%) | 78 | 79-80 |
Note: Post-disciplinary action estimates are based on various expert opinions and potential scenarios. Actual figures may differ.
Political Implications and Reactions: Eu Executive Starts Disciplinary Steps Against Austria Over Budget Deficit
The EU’s disciplinary action against Austria for its budget deficit has ignited a political firestorm within the nation and across the bloc. This unprecedented move carries significant implications for Austria’s domestic political landscape, potentially reshaping its relationship with the EU and impacting other member states facing similar economic challenges. The reactions from various political parties and other EU nations will be crucial in shaping the future trajectory of this issue.
Political Implications within Austria
The disciplinary action has thrust Austria’s political discourse into a new phase. The ruling party, facing scrutiny and potentially a loss of public support, will likely respond with a combination of defensive measures and attempts to highlight the economic pressures driving the deficit. Opposition parties will seize the opportunity to criticize the government’s handling of the budget and potentially call for alternative economic policies.
Public opinion, particularly regarding the EU’s intervention, will be a key factor in shaping the political narrative.
Reactions from Austrian Political Parties
The Austrian political spectrum has already shown diverse reactions to the disciplinary action. The governing party will likely emphasize the economic necessity of certain spending policies, potentially arguing that the EU’s intervention is disproportionate or politically motivated. Opposition parties, conversely, will likely frame the situation as a failure of the government’s economic management and advocate for reforms to avoid similar situations in the future.
The political discourse will likely focus on the balance between national sovereignty and adherence to EU regulations.
Reactions from Other EU Member States
Reactions from other EU member states have varied. Some nations facing similar economic challenges, or those with a history of fiscal disputes with the EU, may express solidarity with Austria, while others may view the action as a necessary step to uphold EU fiscal rules. The reaction will be heavily influenced by each nation’s own economic situation and political priorities.
Countries with sound fiscal records may view the action as a positive example of enforcing the rules.
Comparison with Other EU Member States’ Economic Challenges
Comparing Austria’s situation with others in the EU highlights the complexities of economic challenges within the bloc. While Austria’s deficit is a concern, other member states have also grappled with budget imbalances and economic downturns. The differing responses from EU institutions to these situations may be based on factors like the severity of the deficit, the political climate, and the nation’s overall economic standing.
For instance, a smaller nation with a more vulnerable economy may receive a different treatment than a larger, more stable one.
Table of Political Responses
| Country | Political Party | Reaction |
|---|---|---|
| Austria | Governing Party | Emphasize economic necessity, potentially arguing for disproportionate intervention. |
| Austria | Opposition Parties | Frame as government failure, advocate for reforms. |
| EU Member States (Example) | France | May express solidarity or criticism depending on their own economic and political situations. |
| EU Member States (Example) | Germany | May view the action as upholding EU fiscal rules and a necessary example. |
Potential Solutions and Outcomes
The EU’s disciplinary action against Austria over its budget deficit presents a complex situation demanding careful consideration of potential solutions and their long-term consequences. Austria’s fiscal situation, intertwined with its political landscape and the broader EU framework, necessitates a nuanced approach. Finding a compromise that satisfies both Austrian needs and EU regulations will be critical for a smooth resolution.This section explores potential solutions, possible compromises, and the potential long-term implications of the disciplinary action.
It also presents various scenarios in a visual format to illustrate the diverse possible outcomes.
Possible Solutions to Resolve the Budget Deficit Issue
Addressing Austria’s budget deficit requires a multi-faceted approach. Solutions must consider both short-term fiscal adjustments and long-term economic strategies. Potential solutions include:
- Implementing austerity measures: This involves reducing government spending and increasing tax revenue to achieve the desired fiscal targets. Examples include cutting public sector wages or increasing taxes on certain goods and services.
- Enhancing economic growth: Strategies focusing on job creation and increased productivity can boost tax revenues. This can involve investing in infrastructure, promoting innovation, and fostering entrepreneurship.
- Structural reforms: Implementing reforms that improve the efficiency of public administration, reduce bureaucracy, and enhance the business environment can contribute to a more sustainable fiscal outlook. Examples include streamlining regulations and improving procurement processes.
- Negotiating a revised deficit reduction plan: This approach involves a collaborative dialogue with the EU, potentially leading to a revised timeline for deficit reduction, incorporating specific measures and support from the EU.
Potential Compromises and Negotiations Between Austria and the EU
Successful negotiations hinge on mutual understanding and compromise. The EU may offer financial assistance or technical support in exchange for Austria’s adherence to agreed-upon fiscal targets.
- Conditional financial assistance: The EU could provide financial aid, but only if Austria commits to specific deficit reduction strategies and reforms. This could be a short-term loan or a financial aid package, contingent on Austria’s progress.
- Phased approach to deficit reduction: The EU may propose a phased approach, allowing Austria a longer timeline to meet the deficit targets, while ensuring gradual progress towards the agreed-upon fiscal health.
- Flexible interpretation of EU rules: The EU might consider adjusting the strict application of its budget rules, especially if Austria demonstrates significant progress and reforms to its economy.
- Technical assistance: The EU could provide technical support, offering expertise and resources to aid Austria in implementing the necessary reforms to strengthen its fiscal position. This assistance might focus on strengthening public financial management and auditing.
Potential Long-Term Outcomes of This Disciplinary Action
The long-term consequences of the disciplinary action could significantly impact Austria’s economy and its standing within the EU. The outcomes will depend on the effectiveness of the implemented solutions.
- Strengthened fiscal discipline: Austria might adopt more sustainable fiscal policies, potentially leading to long-term economic stability and confidence.
- Erosion of trust: A prolonged and contentious conflict could damage Austria’s reputation and trust within the EU, potentially hindering future cooperation and investments.
- Economic downturn: Severe austerity measures might lead to economic recession or significant hardship for Austrian citizens, impacting living standards and economic growth.
- Enhanced EU credibility: A successful resolution could bolster the EU’s reputation as a strong and effective institution capable of enforcing its rules.
Potential Scenarios Regarding the Outcome, Eu executive starts disciplinary steps against austria over budget deficit
The following table summarizes potential scenarios, considering different levels of compromise and Austria’s response to the disciplinary action.
| Scenario | Description | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Successful Compromise | Austria successfully negotiates a revised plan, implementing reforms and receiving conditional EU support. | Sustainable fiscal health, strengthened EU-Austria relations, and enhanced EU credibility. |
| Contentious Negotiation | Negotiations are protracted and difficult, leading to a prolonged period of uncertainty and tension. | Potential for economic downturn, damage to Austria’s reputation, and weakened EU-Austria cooperation. |
| Unilateral Action | Austria resists EU pressure and continues its current fiscal policies, potentially triggering sanctions. | Increased risk of economic hardship, strained relations with the EU, and possible exclusion from EU programs. |
| Rapid Adjustment | Austria quickly adopts necessary reforms, demonstrating compliance with EU regulations. | Relatively swift resolution, strengthening Austria’s standing within the EU. |
Illustrative Examples of Budgetary Crises
Budgetary crises are not uncommon, impacting nations worldwide and demanding swift and effective responses. Examining past experiences provides valuable insights into the complexities of these situations and the potential consequences of inaction. Analyzing the strategies employed and their outcomes can inform future approaches to budget deficit management.
Greece’s Sovereign Debt Crisis
Greece’s experience in the early 2010s serves as a stark illustration of the challenges posed by excessive public debt and unsustainable fiscal policies. Years of high deficits, fueled by various factors including economic stagnation and corruption, ultimately led to a debt crisis. The nation’s ability to repay its debt was severely compromised, requiring international bailouts and stringent austerity measures.
- International Bailouts and Austerity Measures: Greece received financial assistance from the European Union and the International Monetary Fund (IMF). These bailouts were conditional upon implementing strict austerity measures, including cuts to public spending, tax increases, and privatization of state-owned assets. These measures aimed to reduce the country’s deficit and restore investor confidence.
- Economic Impact: The austerity measures had a significant negative impact on the Greek economy, leading to a decline in GDP, job losses, and a rise in poverty. The crisis highlighted the potential social costs associated with fiscal adjustments.
- Lessons Learned: The Greek crisis underscored the importance of early intervention, responsible fiscal management, and sustainable economic growth strategies. It also demonstrated the challenges of implementing austerity measures and the need for broader economic reforms to address the underlying causes of debt crises.
Japan’s Decades-Long Economic Stagnation
Japan’s persistent economic stagnation, coupled with a large national debt, presents another complex example. Decades of low growth, deflationary pressures, and demographic shifts have significantly contributed to the fiscal burden.
- Monetary Policy and Fiscal Stimulus: The Japanese government has employed various strategies, including aggressive monetary easing and fiscal stimulus packages. These measures aimed to boost economic activity and reduce the debt-to-GDP ratio.
- Limited Success: Despite these efforts, Japan has struggled to achieve sustained economic growth and reduce its debt. The effectiveness of the strategies has been questioned, and alternative approaches to address the underlying causes of the problem have been sought.
- Lessons Learned: Japan’s experience highlights the difficulties in overcoming prolonged economic stagnation and the need for a comprehensive approach that addresses structural economic weaknesses, demographic trends, and long-term fiscal sustainability.
The 2008 Financial Crisis and its Impact on Budget Deficits
The global financial crisis of 2008 significantly impacted national budgets worldwide. The collapse of the financial system led to a surge in government spending on bailouts and economic stimulus packages. This triggered budget deficits in many countries.
- Government Bailouts and Stimulus Packages: Governments around the world implemented substantial bailouts of financial institutions and economic stimulus programs to mitigate the economic fallout of the crisis.
- Increased Debt Levels: The increased government spending resulted in substantial increases in national debt levels in many countries. These higher debt levels have had ongoing consequences.
- Lessons Learned: The 2008 crisis emphasized the need for robust financial regulations and the potential for global economic crises to have a profound impact on national budgets.
Comparative Table of Budgetary Crises
| Country | Nature of Crisis | Strategies Employed | Outcomes | Lessons Learned |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Greece | Sovereign Debt Crisis | International Bailouts, Austerity Measures | Economic Recession, Social Unrest | Early Intervention, Sustainable Growth, Fiscal Responsibility |
| Japan | Prolonged Economic Stagnation | Monetary Easing, Fiscal Stimulus | Limited Economic Growth, High Debt | Comprehensive Economic Reforms, Structural Changes |
| [Other Country Example] | [Nature of Crisis] | [Strategies Employed] | [Outcomes] | [Lessons Learned] |
Final Thoughts
In conclusion, the EU’s disciplinary action against Austria over its budget deficit is a critical event with potentially far-reaching consequences. This case study provides a thorough examination of the issue, offering insights into the complex interplay between national economic policies and EU-wide regulations. The outcomes will undoubtedly shape future discussions about fiscal responsibility and the balance between national sovereignty and EU integration.
The future actions of both Austria and the EU will be pivotal in shaping the trajectory of this significant development.