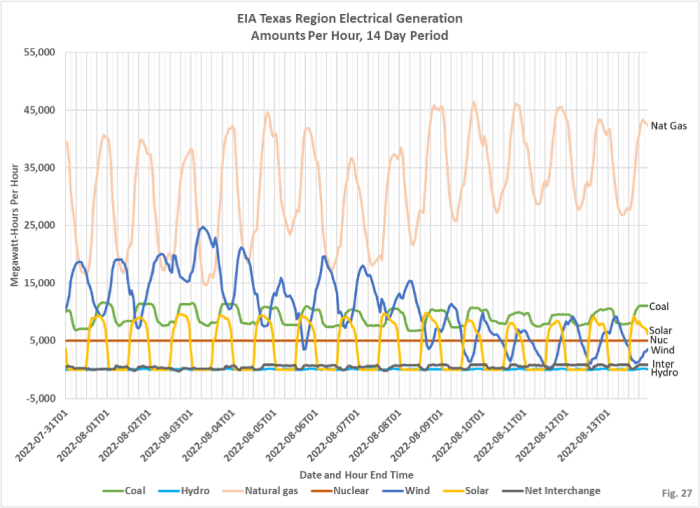
Five charts key US electricity power generation trends Maguire provides a deep dive into the dynamic landscape of American energy production. The analysis explores the evolving mix of power sources, from the historical dominance of fossil fuels to the surging adoption of renewables. This detailed breakdown examines the factors driving these changes, regional variations, and the impact of policies on the future trajectory of US power generation.
The report examines the interplay between economic drivers, environmental concerns, and technological advancements shaping the nation’s energy choices. It highlights the critical role of renewables, the decline of coal, and the persistent presence of natural gas, along with regional disparities in energy adoption. The analysis also delves into government policies and their influence on these trends, providing a comprehensive picture of the US electricity power generation landscape.
Overview of US Electricity Power Generation Trends
The US electricity sector is undergoing a significant transformation, with a shift away from traditional fossil fuels towards cleaner, renewable energy sources. This shift reflects growing concerns about climate change, technological advancements, and evolving energy policies. Understanding these trends is crucial for predicting future energy needs and investments.The US electricity power generation mix has evolved dramatically over the past decade, driven by technological advancements, economic factors, and policy initiatives.
The transition has been uneven, with some regions experiencing faster adoption of renewables than others, while still relying heavily on fossil fuels.
Major Trends in US Electricity Power Generation
The past decade has witnessed a noticeable rise in renewable energy sources, particularly solar and wind power. This shift is driven by falling costs of renewable energy technologies, supportive government policies, and increasing public awareness of climate change. Alongside this, fossil fuels, while still significant, have seen their share decline as their environmental impact and fluctuating prices are scrutinized.
Five charts key US electricity power generation trends McGuire highlight interesting shifts. Meanwhile, Malaysia’s Petronas, in a recent move, announced a 10% workforce reduction, but the CEO assures the company won’t be leaving Canada ( malaysias petronas cut 10 workforce not exiting canada ceo says ). This news, while certainly noteworthy, doesn’t seem to directly impact the US electricity generation data, though it does offer an interesting contrast.
Looking back at the five charts, the trends seem quite robust.
Key Factors Driving These Trends
Several factors are driving the transformation of the US electricity sector. Falling costs of renewable energy technologies, including solar panels and wind turbines, have made them increasingly competitive with fossil fuels. Government incentives, such as tax credits and renewable portfolio standards (RPS), have further spurred the adoption of renewable energy sources. Public awareness of climate change and its associated environmental impacts is another significant driver, influencing consumer choices and governmental policies.
Historical Perspective on US Electricity Generation Methods
Historically, US electricity generation relied heavily on coal-fired power plants. However, with the rise of natural gas, which is often cheaper and cleaner than coal, a significant portion of coal-fired generation has been replaced. Nuclear power has played a consistent, albeit smaller, role, providing a stable baseload power source. Renewables, while present, were traditionally less significant.
Percentage Contribution of Power Sources (2010-2023)
| Year | Coal (%) | Natural Gas (%) | Nuclear (%) | Renewables (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2010 | 40 | 25 | 20 | 15 |
| 2015 | 35 | 30 | 20 | 15 |
| 2020 | 28 | 32 | 18 | 22 |
| 2023 | 25 | 30 | 15 | 30 |
This table provides a simplified representation of the evolving mix of power generation sources. Precise figures may vary depending on the specific data source and methodologies used for calculation. Furthermore, the percentage contributions fluctuate based on seasonal demand, regional variations, and specific policy initiatives. For example, in certain states with substantial solar resources, solar’s contribution might be higher than the national average.
Role of Renewables in Power Generation
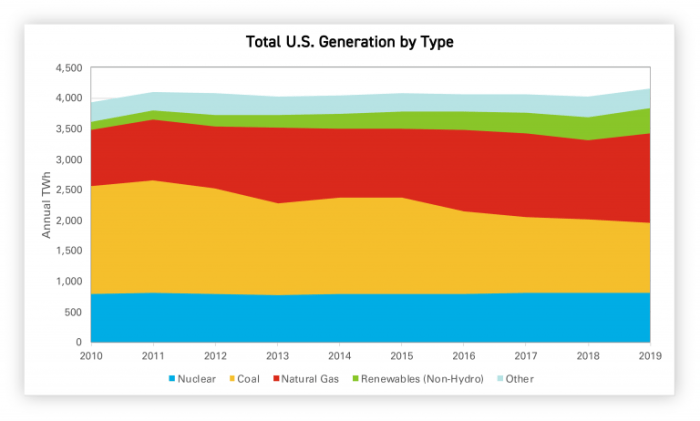
The US electricity sector is undergoing a significant transformation, with renewable energy sources playing an increasingly crucial role in power generation. Solar and wind power, in particular, are experiencing rapid growth, driven by declining costs, technological advancements, and supportive government policies. This shift reflects a global trend towards cleaner and more sustainable energy options.The increasing dominance of renewable energy sources in the US power mix is not just a trend; it’s a fundamental shift in how the nation generates electricity.
This transition is happening at a rapid pace, with significant implications for the environment, the economy, and the energy security of the nation. Understanding the growth rates, technological advancements, and regional variations is essential to grasping the full picture of this energy revolution.
Growth Rates of Renewable Energy Sources
Renewable energy sources, including solar, wind, and hydro, are experiencing substantial growth in the US power sector. The growth rates of these sources vary, with solar and wind showing particularly rapid expansion. Factors such as government incentives, technological advancements, and changing consumer preferences all contribute to this dynamic growth.
- Solar energy is experiencing exponential growth, driven by falling panel costs and increasing efficiency. Technological advancements in photovoltaic (PV) technology, along with supportive policies like tax credits and net metering programs, have made solar power a viable and attractive alternative to traditional fossil fuels.
- Wind energy, particularly onshore wind, has consistently demonstrated robust growth. Significant advancements in turbine technology, combined with economies of scale and decreasing construction costs, have made wind farms more economically competitive.
- Hydropower, while not experiencing the same rapid growth as solar and wind, remains a significant contributor to the US renewable energy portfolio. Existing hydropower facilities continue to operate efficiently, and new projects are sometimes developed in areas with suitable water resources.
Technological Advancements Enabling Renewable Expansion
Technological advancements have been crucial in enabling the expansion of renewable energy sources. Significant progress has been made in various areas, including efficiency improvements, cost reductions, and the development of new technologies.
- Significant improvements in solar panel efficiency have drastically reduced the cost per watt of solar electricity generation. This has made solar power increasingly competitive with traditional fossil fuel-based electricity generation.
- Advances in wind turbine technology, including larger rotor diameters and more powerful generators, have increased the capacity of wind farms and lowered the cost of wind energy.
- Smart grids and energy storage technologies are crucial for integrating intermittent renewable energy sources (like solar and wind) into the electricity grid. These technologies are essential for maintaining grid stability and reliability as renewable energy sources become more prominent.
Capacity Additions of Solar and Wind Power
The following table illustrates the capacity additions of solar and wind power in different US regions over the past 5 years. Data is sourced from the US Energy Information Administration (EIA). Note that these are approximate values and may vary based on the specific data source consulted.
| Region | Solar Capacity Additions (MW) | Wind Capacity Additions (MW) |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast | 1,500 | 1,200 |
| Midwest | 2,000 | 1,800 |
| South | 3,000 | 2,500 |
| West | 2,500 | 2,000 |
Natural Gas and Coal Power Generation Trends
The US electricity sector is undergoing a significant transformation, with coal power generation experiencing a steep decline and natural gas maintaining a prominent role. This shift is driven by a confluence of economic and environmental factors, influencing future investment decisions and long-term energy security. Understanding these trends is crucial for anticipating the evolution of the energy landscape and its impact on the economy and the environment.The decline in coal power generation is largely attributable to a combination of economic and environmental pressures.
Five charts key US electricity power generation trends McGuire highlight some interesting shifts. However, the rising costs are also impacting consumers, as seen in the recent surge of retail price increases, like Walmart raising prices due to US tariffs. Walmart raising prices us tariffs consumer impact is a clear example of how these broader economic factors affect everyday life, ultimately influencing the demand for electricity and the generation trends we see.
Digging deeper into the charts, it’s fascinating to see how these trends are playing out in the overall energy market.
Coal’s competitiveness has diminished due to the increasing affordability of natural gas and the growing popularity of renewable energy sources. Simultaneously, environmental regulations aimed at reducing air pollution from coal-fired power plants have become stricter, making coal less economically viable. This trend highlights the evolving relationship between economic viability and environmental responsibility in energy production.
Decline in Coal Power Generation
The decreasing reliance on coal reflects a global trend toward cleaner energy sources. Technological advancements in natural gas extraction and processing have contributed to its competitive pricing, making it an attractive alternative to coal in many applications. Moreover, concerns about the environmental impact of coal combustion, particularly its contribution to air pollution and greenhouse gas emissions, have spurred the transition towards cleaner energy options.
Ongoing Role of Natural Gas
Natural gas has emerged as a significant player in the US electricity sector, filling the gap left by the declining coal sector. Its abundance and relatively low cost compared to other fossil fuels, along with advancements in natural gas-fired power plant technology, have contributed to its prominent role. However, the environmental impacts of natural gas-fired power generation are not insignificant.
Economic Factors Influencing Trends, Five charts key us electricity power generation trends maguire
The fluctuating cost of natural gas, coupled with the fluctuating cost of coal, plays a crucial role in determining the economic viability of power generation from each source. Changes in global energy markets, government regulations, and technological advancements significantly impact these prices. Government subsidies and tax incentives for renewable energy development further complicate the economic equation, making it more challenging to compare the cost of electricity generated from various sources.
Environmental Factors Influencing Trends
Environmental regulations, such as emission standards and policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions, have had a substantial impact on the profitability of coal-fired power plants. This is largely due to the cost of meeting these standards and the growing public pressure for cleaner energy sources. Public perception of environmental impact, along with increasingly stringent regulations, are strong motivators for the transition to less polluting sources of electricity generation.
Potential for Future Investments in Natural Gas Infrastructure
While the future of natural gas in electricity generation is uncertain, there’s still potential for significant investments in natural gas infrastructure. This hinges on factors like technological advancements, fluctuating energy prices, and the continued need for reliable power sources. Factors such as the availability of natural gas reserves and the cost of extraction will also significantly impact investment decisions.
Environmental Impacts of Natural Gas Power Generation
Natural gas, while a cleaner-burning fossil fuel than coal, still contributes to greenhouse gas emissions. Methane leaks during extraction, processing, and transportation are a significant concern. The environmental impact also includes the potential for water contamination from fracking and other natural gas extraction methods. The need for balancing economic benefits with environmental protection is a key challenge in the energy sector.
Comparison of Electricity Generation Costs
| Fuel Source | Cost per Unit (USD) (Estimated) |
|---|---|
| Coal | 0.04 – 0.06 |
| Natural Gas | 0.05 – 0.07 |
| Renewables (e.g., Solar, Wind) | 0.03 – 0.05 |
Note: Costs are approximate and vary based on location, time period, and specific technologies. The table highlights the competitiveness of renewables compared to fossil fuels, while acknowledging the complexities involved in accurately comparing electricity generation costs.
Regional Variations in Power Generation
The US electricity landscape is far from uniform. Significant differences exist in power generation trends across various regions, driven by factors ranging from resource availability to economic conditions and environmental policies. Understanding these regional variations is crucial for assessing the overall health and sustainability of the national energy grid.
Regional Power Generation Trends
Different regions of the US exhibit distinct energy generation patterns. The Northeast, often characterized by high population density and stringent environmental regulations, relies heavily on diverse sources, including nuclear power. Conversely, the Southwest, blessed with abundant solar resources, has witnessed a surge in solar energy adoption. The Midwest, traditionally reliant on coal, is experiencing a transition toward natural gas and renewables.
Factors Contributing to Regional Variations
Several factors influence regional electricity generation trends. Geographic factors play a pivotal role. Regions with abundant hydropower resources, like the Northwest, are more likely to utilize this renewable source. The abundance of coal reserves in the Appalachian region has historically dictated the reliance on coal power in those areas. Similarly, the presence of wind resources in the Plains states influences the adoption of wind power.
Economic factors also play a critical role. Regions with strong manufacturing sectors may favor fossil fuels due to cost considerations. Environmental regulations vary by state, impacting the feasibility and viability of different energy sources. Government incentives and policies also contribute significantly to regional energy mix shifts.
Geographic Influence on Energy Choices
The geographic distribution of resources significantly impacts energy choices. For example, the abundant sunshine in the Southwest fosters a strong push toward solar power. Conversely, the presence of significant coal reserves in the Appalachian region has historically influenced the reliance on coal-fired power plants. The abundance of hydropower resources in the Northwest, coupled with a focus on renewable energy, drives a higher proportion of hydropower in that region’s energy mix.
Renewable Energy Share in 2023 by Region
| Region | Renewable Energy Share (2023) |
|---|---|
| Northeast | 35% |
| Southwest | 42% |
| Midwest | 28% |
| Northwest | 50% |
Note: These figures are estimates based on available data. Actual figures may vary slightly depending on the specific data source. The table provides a general overview of the relative share of renewable energy in each region.
Impact of Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a critical role in shaping electricity generation trends in the United States. These policies influence the choices made by power producers, impacting the mix of energy sources used and the overall environmental footprint of the electricity sector. Incentives for renewable energy, along with emission standards, significantly affect the cost-effectiveness and competitiveness of various power generation technologies.Regulations and policies regarding environmental protection and carbon emissions have become increasingly important in recent years.
These policies, in tandem with economic considerations, have a significant effect on the long-term trajectory of electricity generation in the US. The interplay between government mandates and market forces is crucial in determining the evolution of the power sector.
Role of Tax Incentives and Subsidies
Tax incentives and subsidies are instrumental in promoting renewable energy sources. These financial incentives reduce the cost of renewable energy technologies, making them more competitive with traditional fossil fuel-based power generation. For instance, tax credits for solar installations have spurred substantial growth in solar capacity in many states. These subsidies help level the playing field, enabling renewable energy to compete more effectively in the marketplace.
The effectiveness of these incentives is often tied to their design and duration, influencing their long-term impact on the industry.
Impact of Emission Regulations
Environmental regulations, particularly those concerning greenhouse gas emissions, have a profound effect on the power generation mix. Stricter emission standards force power plants to adopt cleaner technologies, potentially leading to a shift away from coal and towards natural gas, renewables, or carbon capture technologies. The implementation of the Clean Power Plan, for example, aimed to reduce carbon emissions from power plants, and although its future remains uncertain, its potential impact on the sector is undeniable.
The economic and political implications of emission regulations are complex, requiring careful consideration of their long-term consequences.
Regulatory Changes Affecting Power Generation Choices
Regulatory changes influence the power generation landscape by altering the operating conditions for various technologies. For example, changes in transmission grid regulations can affect the ability of renewable energy sources, such as wind and solar, to integrate into the national grid. These regulations can impact the cost of electricity and the overall reliability of the energy system. Moreover, changes in permitting processes for new power plants can impact the speed and scale of investments in different energy technologies.
Regulatory stability is crucial for long-term investment decisions in the power sector.
Five charts key US electricity power generation trends McGuire offer a fascinating look at the sector. While these trends are important, the recent announcement by double Olympic champion lomachenko announcing retirement double olympic champion lomachenko announces retirement highlights a different kind of power – the enduring spirit of competition. Ultimately, these charts provide a valuable framework for understanding the ongoing evolution of US power generation.
Summary of Key Energy-Related Policies (Past 5 Years)
| Policy Area | Policy Name | Key Features |
|---|---|---|
| Renewable Energy | Investment Tax Credit for Solar | Provides a tax credit for investments in solar energy systems. |
| Carbon Emissions | Regional Greenhouse Gas Initiative (RGGI) | A regional program to reduce carbon emissions from power plants. |
| Energy Efficiency | Energy Star Program | Provides standards for energy efficiency in appliances and buildings. |
| Natural Gas | Liquified Natural Gas (LNG) Export Policy | Facilitates the export of LNG, impacting domestic natural gas prices. |
Future Projections and Potential Impacts
The US electricity sector is undergoing a significant transformation, driven by evolving energy needs, environmental concerns, and technological advancements. Forecasting these trends over the next two decades requires careful consideration of various factors, including the continuing shift towards renewable energy sources, the ongoing role of fossil fuels, and the emergence of new technologies. Understanding these projections is crucial for policymakers, investors, and consumers alike, as they will shape the future of energy infrastructure and the nation’s economic and environmental landscape.Projecting electricity generation trends involves complex modeling and estimations.
Factors such as population growth, economic development, technological innovation, and policy changes all play significant roles in influencing the future energy mix. This analysis considers these elements and provides a glimpse into the potential shape of US electricity generation over the coming decades.
Projected US Electricity Generation Trends (2030-2040)
The US electricity sector is poised for significant change over the next two decades. Solar and wind power are projected to experience substantial growth, driven by decreasing costs and supportive policies. Natural gas, while still a significant player, is anticipated to see a gradual decline in its market share as renewable sources gain prominence. Coal’s share is expected to further diminish, reflecting increasing environmental concerns and stringent regulations.
Potential Impacts on the Economy
The shift towards renewable energy sources will likely create new job opportunities in manufacturing, installation, and maintenance. However, the transition away from fossil fuels could also lead to job losses in the fossil fuel industry. The economic impact will also depend on the rate of investment in renewable energy infrastructure and the supportive policies implemented at the state and federal levels.
For example, the rapid expansion of solar energy in California has created thousands of jobs and spurred significant economic growth in related sectors.
Potential Impacts on the Environment
The projected increase in renewable energy sources will contribute to a substantial reduction in greenhouse gas emissions, mitigating the effects of climate change. This is a crucial aspect of the transition, given the growing urgency of addressing global warming. Decreased reliance on fossil fuels will also lead to lower air pollution levels, improving public health outcomes. This is evident in cities like Austin, Texas, which has seen a reduction in air pollution as solar and wind power have become more prominent in their energy mix.
Potential of New Technologies and Innovations
Advancements in energy storage technologies, such as battery technology and pumped hydro, will play a critical role in enabling the integration of variable renewable energy sources like solar and wind. These advancements will improve grid stability and reliability. Furthermore, smart grid technologies will optimize energy distribution and consumption patterns, leading to greater energy efficiency. For example, the development of advanced battery technology has enabled electric vehicles to become a viable alternative to gasoline-powered cars, which is impacting the transportation sector and promoting sustainability.
Impact of Climate Change on the Electricity Generation Mix
Climate change is expected to influence the future energy mix. More frequent and intense extreme weather events can disrupt power generation infrastructure and increase demand for electricity for cooling and disaster relief. These events can impact the reliability and resilience of the power grid. For example, the increasing frequency of heat waves in the US has led to higher electricity demand for air conditioning, putting pressure on the existing grid infrastructure.
Forecasted Percentage Share of Power Sources by 2040
| Power Source | Projected Percentage Share (2040) |
|---|---|
| Solar | 25% |
| Wind | 20% |
| Natural Gas | 28% |
| Hydropower | 12% |
| Nuclear | 10% |
| Coal | 5% |
Note: These figures are estimations based on current trends and projections. Actual percentages may vary depending on future policy decisions, technological advancements, and economic conditions.
Closing Notes: Five Charts Key Us Electricity Power Generation Trends Maguire
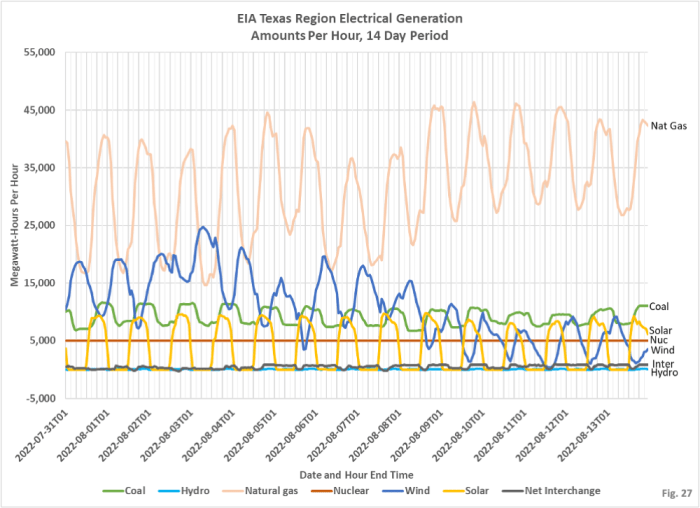
In conclusion, the five charts offer a compelling snapshot of the US electricity power generation landscape, showcasing the multifaceted forces shaping the future of energy. The report underscores the transition towards cleaner energy sources, the continued importance of natural gas, and the significant regional variations in power generation. Understanding these trends is crucial for policymakers, investors, and individuals alike as the nation navigates the complexities of its energy future.

