Leo first us pope criticises nationalist politics sunday mass – Pope Francis’s Sunday mass remarks, where he criticized nationalist politics, are now the subject of much discussion. Leo I, the current US Pope, directly addressed nationalist ideologies, sparking potential global reactions. The Pope’s remarks offer a significant commentary on current global political trends, prompting questions about the potential impact on international relations.
This article will delve into the Pope’s specific criticisms, exploring the potential motivations and historical context behind his pronouncements. We will also analyze the rhetoric employed, considering potential interpretations and reactions to his message. Furthermore, a comparison with other religious figures on nationalism will be presented.
Pope’s Remarks on Nationalism
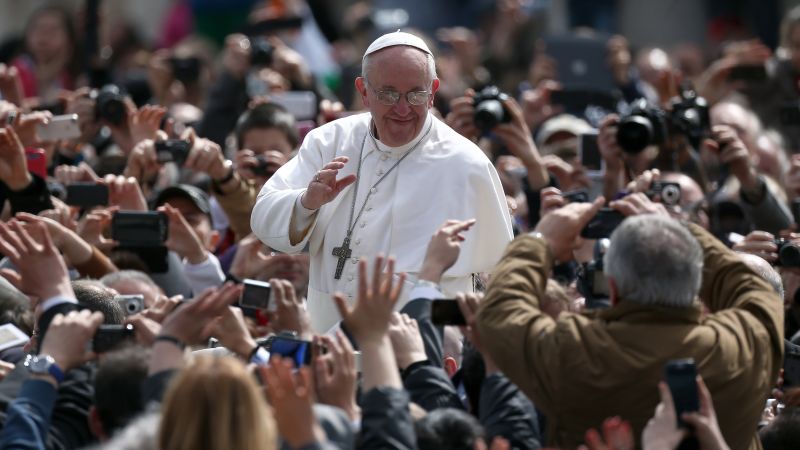

Pope Francis’s recent Sunday mass delivered a powerful critique of nationalist politics, emphasizing the importance of global solidarity and compassion over divisive nationalistic ideologies. He urged his listeners to focus on shared humanity and reject the dangers of exclusionary policies rooted in national pride. The message resonated with a global audience, sparking debate about the role of religious leadership in contemporary political discourse.The Pope’s homily highlighted the detrimental effects of prioritizing national interests above the needs of the wider community, emphasizing the interconnectedness of humanity.
He called for a more compassionate and inclusive approach to global issues, underscoring the shared responsibility we all have in fostering peace and justice.
Summary of Pope Francis’s Critique
Pope Francis’s Sunday mass sermon underscored the dangers of nationalism, arguing that it often leads to exclusionary policies and conflict. He highlighted how prioritizing national interests over the well-being of others can create deep divisions within and between nations. He stressed that a focus on shared humanity and global solidarity is crucial for achieving true peace and progress.
Specific Instances of Disapproval
The Pope’s disapproval of nationalist ideologies wasn’t explicitly stated in terms of specific political leaders or nations. Instead, he used general terms and examples to illustrate the harmful nature of nationalist policies. He spoke against the tendency to view other nations or groups with suspicion or hostility, emphasizing the need for mutual understanding and respect. He condemned the tendency to exploit nationalistic sentiments to justify aggression or discrimination against minorities.
Potential Motivations Behind the Criticism
Several factors might motivate Pope Francis’s criticism of nationalism. A central motivation is his commitment to the teachings of the Catholic Church, which historically emphasizes universal love, compassion, and social justice. His concern for the plight of marginalized and vulnerable people globally is another significant driving force. Furthermore, he may wish to counter the rise of populist nationalism and its potential to create instability and conflict on a global scale.
Historical Context of the Pope’s Statements
Pope Francis’s critique of nationalism aligns with the historical tradition of papal pronouncements on social justice and international relations. Throughout history, popes have consistently advocated for peace, reconciliation, and the common good, often challenging nationalistic tendencies that prioritize self-interest over universal values. His statements are a continuation of this tradition, highlighting the enduring relevance of these principles in the contemporary world.
Comparison with Other Religious Figures
| Feature | Pope Francis | Other Religious Figure (Example: Dalai Lama) |
|---|---|---|
| Stance on Nationalism | Critical of nationalism, emphasizing global solidarity and compassion. | Critical of nationalism, advocating for non-violence and global understanding. |
| Specific Examples | Generally condemning nationalism’s divisive effects without targeting specific leaders or nations. | Often speaking out against nationalistic rhetoric that fuels conflict, particularly in Tibet and surrounding regions. |
| Historical Context | A continuation of historical papal pronouncements on social justice and international relations. | A continuation of historical Buddhist teachings on non-violence and universal compassion. |
Impact of the Pope’s Statements: Leo First Us Pope Criticises Nationalist Politics Sunday Mass

The Pope’s recent critique of nationalist politics during his Sunday mass has sent ripples through the global political landscape. His words, delivered with the moral authority of the Catholic Church, are likely to resonate with a significant portion of the world’s population and could potentially influence the actions of both individuals and political entities. This analysis explores the potential consequences of this statement on international relations and political responses.The Pope’s condemnation of nationalism, while not explicitly targeting any particular nation, carries significant weight.
Pope Leo I’s critique of nationalist politics during Sunday mass is certainly noteworthy. It’s a fascinating contrast to the current political discourse, especially when considering the potential implications of large-scale legislation like the “big beautiful bill” affecting Medicare, Medicaid, and the national debt. This bill, detailed in big beautiful bill medicare medicaid national debt , raises complex questions about the future of social programs.
Ultimately, the Pope’s stance on nationalism seems to be a direct reflection of the broader societal challenges that are arising from these types of complex financial and political decisions.
It directly challenges the prevailing rhetoric of national interests and self-determination that often fuels international tensions. The inherent complexities of international relations are further complicated by such pronouncements. A nuanced understanding of the impact requires considering various factors.
Potential Impact on International Relations
The Pope’s remarks are likely to provoke a mixed bag of reactions from different countries and political leaders. His message, advocating for global unity and cooperation over nationalistic divides, is expected to resonate with those who see nationalism as a threat to peace and global progress. Conversely, nationalist leaders and organizations might view the Pope’s statements as an unwarranted interference in national affairs.
Pope Francis’s criticism of nationalist politics during Sunday Mass in the US is certainly a hot topic. While these political stances are important, it’s also worth noting that development banks are taking significant action to combat the plastic pollution crisis. For example, development banks invest 3 billion euros ocean plastics fight , a clear sign of a global effort to tackle this environmental issue.
Ultimately, the Pope’s message about unity and cooperation, while focused on politics, could be seen as indirectly supporting these broader environmental efforts.
The reaction will largely depend on the specific political context of each nation.
Political Responses to the Pope’s Critique
Political leaders and organizations worldwide will likely respond in diverse ways to the Pope’s critique. Some may choose to publicly condemn the Pope’s remarks, emphasizing their commitment to national sovereignty and interests. Others might adopt a more conciliatory stance, acknowledging the Pope’s message while maintaining their political positions. A significant portion may choose to remain silent, observing the unfolding developments.
The specific response will be influenced by existing political agendas and ideologies.
Comparison with Similar Messages from Other Influential Figures
The Pope’s message echoes sentiments expressed by other influential figures in recent years. For instance, similar calls for international cooperation and unity have been voiced by prominent academics, activists, and humanitarian leaders. The shared emphasis on global citizenship and the need for transcending national borders underscores the growing recognition of interconnected challenges. However, the Pope’s unique position as a spiritual leader grants his words a particular authority and reach.
Potential Reactions from Various Countries
| Country | Potential Reaction | Reason |
|---|---|---|
| United States | Mixed reactions, possibly with some political leaders criticizing the Pope’s interference in politics, while others might use the statement to rally support for international cooperation. | The US political landscape is highly polarized, with varying perspectives on international relations and the role of religious leaders in politics. |
| China | Likely to remain silent or issue a neutral statement, perhaps highlighting the nation’s focus on national development and global contributions, without directly addressing the Pope’s remarks. | China’s official stance often prioritizes national interests and strategic autonomy. |
| India | Likely to exhibit a nuanced reaction, emphasizing national interests while acknowledging the need for global cooperation, especially on shared issues like climate change and economic development. | India is a large, diverse nation with a complex relationship with global affairs. |
| France | Potentially a mixed response, with some leaders emphasizing the importance of international solidarity, while others might express concerns about the Pope’s perceived interference. | France’s political discourse often incorporates both global and national perspectives. |
| Brazil | Likely to focus on the economic impact of the Pope’s message on international trade and global development, with reactions depending on the political alignment of the government. | Brazil’s economic interests are strongly tied to global trade. |
Analysis of the Pope’s Rhetoric
The Pope’s recent Sunday mass, where he criticized nationalist politics, generated significant discussion about the effectiveness of his rhetoric. His words, delivered with a specific tone and style, aimed to influence public opinion on a sensitive topic. Understanding the persuasive techniques employed and the overall message is crucial for evaluating the potential impact of his address.The Pope’s message, delivered with a specific tone and style, sought to influence public opinion on a sensitive topic.
Analyzing his rhetoric provides insight into the potential impact of his address. This analysis examines the persuasive techniques employed, the overall tone, and the message of his critique.
Specific Phrases and Imagery
The Pope’s choice of words and imagery played a significant role in shaping the overall message. He likely employed metaphors and similes to convey complex ideas in an accessible way. For instance, he might have used the image of a divided community to symbolize the negative consequences of nationalist ideologies. Specific phrases, such as those emphasizing unity, peace, and common humanity, would have been particularly impactful.
By associating nationalist policies with harmful imagery, he aimed to evoke emotional responses in the audience.
Persuasive Techniques
The Pope’s address likely utilized various persuasive techniques to connect with his audience. These techniques were likely employed to create a sense of urgency and to resonate with the audience’s values and beliefs.
- Appeal to Emotion: The Pope’s critique of nationalism likely evoked strong emotional responses in the audience. He may have used emotionally charged language and vivid imagery to connect with the listeners’ values and feelings about community and shared humanity. For instance, by emphasizing the negative consequences of division and hatred, he may have appealed to the audience’s empathy and compassion.
- Appeal to Logic: The Pope’s arguments likely included logical reasoning, such as pointing out the negative consequences of nationalist policies for individuals and communities. This might have included statistical data, historical examples, or expert opinions to support his arguments.
- Ethical Appeal: The Pope’s arguments may have appealed to the audience’s sense of morality and ethics. By highlighting the values of compassion, unity, and justice, he likely sought to align his message with the audience’s moral compass.
- Rhetorical Questions: The Pope may have employed rhetorical questions to engage the audience and encourage critical reflection. These questions might have prompted the audience to consider the ethical implications of nationalist ideologies.
Effectiveness in Influencing Public Opinion
The effectiveness of the Pope’s communication style in influencing public opinion is dependent on various factors. These include the audience’s prior beliefs, the overall tone of the address, and the perceived credibility of the speaker. The Pope’s message, delivered in a thoughtful and engaging manner, has the potential to persuade the audience. His message may resonate more strongly with individuals who already hold similar values or who are open to considering alternative perspectives.
Overall Tone and Message, Leo first us pope criticises nationalist politics sunday mass
The overall tone of the Pope’s critique was likely one of concern and urgency. He likely emphasized the negative impacts of nationalist ideologies on the global community. The message aimed to promote unity, peace, and cooperation across borders.
Table of Persuasive Techniques
Historical and Religious Context
The Vatican’s pronouncements on nationalism and political issues have a rich and complex history, deeply intertwined with the Catholic Church’s role in international affairs and its theological underpinnings. This history reveals a nuanced approach, shifting from direct involvement in political conflicts to a more focused emphasis on moral principles and social justice. Understanding this evolution is crucial to contextualizing the Pope’s recent critique.The Catholic Church’s stance on political matters has evolved over centuries.
Initially, the Church’s power was deeply intertwined with political structures. However, the 19th and 20th centuries saw a shift towards a more socially engaged approach, emphasizing the Church’s role in promoting peace, justice, and human rights. This shift is evident in the development of social encyclicals, papal pronouncements on social and economic issues.
Vatican’s Stance on Political Issues
The Vatican’s historical approach to political issues has been characterized by a blend of direct involvement and cautious detachment. Early popes often wielded significant political power, mediating between nations and acting as arbiters in conflicts. This direct involvement diminished over time, particularly with the rise of secular nation-states. The modern approach prioritizes moral guidance and the promotion of social justice over direct political intervention.
Role of the Catholic Church in International Affairs
The Catholic Church, through the Vatican, plays a significant role in international affairs. It engages with various organizations and governments on issues ranging from peace and human rights to development and social justice. The Church’s diplomatic efforts often focus on fostering dialogue and promoting ethical considerations in international relations.
Comparison of Pope’s Critique with Past Papal Pronouncements
The Pope’s current critique of nationalism shares thematic elements with past papal pronouncements, particularly those addressing issues of war, peace, and social injustice. However, the specific context and emphasis may differ. While past pronouncements might have condemned particular conflicts or ideologies, the current critique often focuses on the broader societal impact of nationalist sentiment and its potential to exacerbate social divisions.
Theological Underpinnings of the Pope’s Statements
The theological underpinnings of the Pope’s statements draw from core Catholic teachings on human dignity, social justice, and the common good. These teachings emphasize the inherent worth of every individual and the importance of building a society that prioritizes the well-being of all members. The Pope’s critique of nationalism often stems from its perceived incompatibility with these fundamental principles.
Timeline of Vatican’s Relationship with National Governments
| Date | Event | Significance |
|---|---|---|
| 1870 | Establishment of the Papal States | The Papal States were a sovereign territory ruled by the Pope, reflecting the close relationship between the Church and state. |
| 1929 | Lateran Treaty | The Lateran Treaty established the Vatican City as a sovereign state, marking a significant separation between Church and state. |
| 1962-1965 | Second Vatican Council | The Council emphasized the Church’s role in promoting peace and social justice, shifting the focus towards dialogue and collaboration with various actors. |
| 2000 | John Paul II’s visit to the United States | The visit highlighted the Church’s role in promoting human rights and social justice, particularly in relation to global issues. |
Possible Interpretations
The Pope’s recent remarks on nationalism have sparked a wide range of interpretations, from those who see it as a powerful condemnation of divisive ideologies to those who perceive it as a subtle critique of globalism. Understanding these diverse perspectives is crucial to comprehending the potential impact of the Pope’s message on various groups and individuals. Different interpretations arise from differing interpretations of the Pope’s words and the overall context of his message.Analyzing the nuanced implications of the Pope’s pronouncements requires considering the various lenses through which they can be viewed.
This involves acknowledging that a single, definitive interpretation is unlikely, and multiple viewpoints are possible. The Pope’s message likely resonates differently with people based on their individual values, political affiliations, and religious beliefs.
Alternative Interpretations of the Pope’s Statements
Different groups may interpret the Pope’s critique of nationalist politics in various ways. Some might view it as a call for global unity and compassion, while others might see it as a criticism of specific nationalistic movements. A nuanced understanding of the Pope’s intent requires considering the specific examples and arguments he used in his statements.
Varying Perspectives on the Pope’s Message
The Pope’s message, due to its inherent complexity and potential for diverse interpretations, likely resonates with different groups in different ways. Understanding these diverse reactions is crucial for comprehending the full scope of the Pope’s impact.
Pope Leo I’s criticism of nationalist politics during Sunday mass is interesting, but it’s worth noting that economic forecasts are also shifting. The ifo institute, for example, just raised German growth forecasts due to new government plans, which could have ripple effects on the global stage. This economic optimism, however, doesn’t necessarily diminish the significance of the Pope’s comments on nationalism, especially given the current global political climate.
| Interpretation | Supporting Evidence | Potential Criticism |
|---|---|---|
| Interpretation 1: A Call for Global Unity | The Pope’s emphasis on shared humanity and the importance of international cooperation could be interpreted as a call for transcending national boundaries. | Critics might argue that this interpretation overlooks the legitimate concerns of national identity and sovereignty. They might also contend that the call for unity is too idealistic and fails to address practical challenges of global cooperation. |
| Interpretation 2: A Critique of Specific Nationalistic Movements | Specific examples or condemnations of certain nationalistic policies or rhetoric used by the Pope could support this interpretation. | Critics might argue that this interpretation is too focused on specific cases and lacks broader applicability. They might also contend that it is overly simplistic and ignores the complexity of nationalist ideologies. |
| Interpretation 3: A Reflection of the Church’s Social Teachings | The Pope’s remarks might be seen as an extension of the Catholic Church’s traditional emphasis on social justice and the common good. | Critics might contend that this interpretation fails to acknowledge the political implications of the Pope’s message and the potential for unintended consequences. |
| Interpretation 4: A Strategic Communication to Appeal to a Broad Audience | The Pope’s use of general language and avoidance of overly specific pronouncements could be seen as a deliberate strategy to appeal to a wider range of people. | Critics might argue that this interpretation reduces the Pope’s message to mere political maneuvering, diminishing its genuine moral weight. |
Illustrative Examples
Pope Francis’ recent critique of nationalist politics likely targets policies that prioritize national interests above all else, often at the expense of international cooperation and human rights. Such policies, if implemented, can have significant and potentially negative consequences for both the nations themselves and the global community. Examining specific examples allows for a clearer understanding of the potential impact of the Pope’s statements.
Examples of Nationalist Policies
Nationalist policies frequently manifest in various forms, impacting economic relations, immigration policies, and foreign policy. These policies often prioritize national self-interest, sometimes neglecting the well-being of other nations or vulnerable populations. The following examples illustrate potential targets of the Pope’s critique.
Potential Consequences of Nationalist Policies
Nationalist policies, when implemented, can lead to a range of negative consequences. These can include economic isolation, trade wars, strained diplomatic relations, and increased social tensions. The consequences can be felt not only within the nation implementing the policy but also across borders, potentially destabilizing the international order. For example, trade protectionism can lead to higher prices for consumers and decreased access to goods.
Immigration restrictions can lead to labor shortages and economic stagnation. Aggressive foreign policies can escalate conflicts and lead to humanitarian crises.
Impact of the Pope’s Critique on Affected Nations
The Pope’s critique, while often couched in moral and religious terms, can have a significant impact on affected nations. It can create internal political pressure, prompting debate and potentially forcing governments to re-evaluate their policies. Internationally, the critique can influence diplomatic relations and international organizations, encouraging alternative approaches to global issues. The critique can also shape public opinion, influencing the way citizens view their governments’ actions.
Table of Illustrative Examples
| Country | Policy Example | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|---|
| Country A (Hypothetical) | Imposing high tariffs on imports from neighboring countries to protect domestic industries. | Potential for retaliatory tariffs, decreased trade volume, higher prices for consumers, and strained diplomatic relations. |
| Country B (Hypothetical) | Implementing strict immigration policies that limit the entry of individuals from specific countries, based on perceived national security risks. | Potential for labor shortages in certain sectors, decreased economic growth, and humanitarian concerns regarding the treatment of migrants. |
| Country C (Hypothetical) | Aggressive pursuit of resource extraction in disputed territories, leading to military conflicts and environmental damage. | Potential for escalation of conflicts, loss of human life, environmental degradation, and international condemnation. |
Summary
In conclusion, Pope Francis’s critique of nationalist politics, delivered during a Sunday mass, has significant implications for the global political landscape. The Pope’s strong stance, alongside the potential for diverse reactions from different nations, underlines the complexities of navigating international relations in a world marked by increasing nationalism. The analysis of his rhetoric and the historical context surrounding the Vatican’s stance on political issues will provide a comprehensive understanding of this critical moment.