Medication abortion guttmacher data provides crucial insights into the landscape of this procedure. This exploration delves into the specifics of medication abortion procedures, examining various regimens, steps, and associated medications. The data reveals historical trends, geographical access patterns, and factors influencing availability. We’ll also discuss safety, effectiveness, potential complications, and public perceptions surrounding medication abortion policies.
The Guttmacher Institute’s data forms the backbone of this analysis, offering a comprehensive view of the topic. From historical usage to regional variations, we unpack the key statistics and present them in a clear and accessible manner. This allows for a deeper understanding of medication abortion’s role in reproductive healthcare, its impact on women’s health, and its comparison with surgical abortion.
Overview of Medication Abortion: Medication Abortion Guttmacher Data
Medication abortion, also known as medical abortion, is a safe and effective method for terminating a pregnancy early in its development. It involves using medications to induce the body’s natural process of miscarriage. This approach offers a non-surgical alternative, often preferred by individuals seeking a less invasive procedure.This method is generally used for pregnancies of 10 weeks or less, as the effectiveness decreases with gestational age.
The medications used work by blocking the hormone progesterone, which is essential for maintaining the pregnancy, and causing the uterus to contract and expel the pregnancy tissue.
Medication Abortion Regimens
Different medication abortion regimens exist, each utilizing a specific combination of medications. These variations ensure flexibility and tailoring to individual needs and circumstances.
- The most common regimen involves two medications: mifepristone and misoprostol.
- A second regimen, using only misoprostol, is also an option for some individuals.
Steps Involved in a Medication Abortion
The process typically involves two visits to a healthcare provider.
- First Visit: Mifepristone is administered orally, and this medication works by blocking the hormone progesterone, which is essential for the pregnancy to continue.
- Second Visit (usually within 24-48 hours later): Misoprostol is administered, either buccally (between the cheek and gum), vaginally, or sublingually (under the tongue). This medication induces uterine contractions, causing the expulsion of the pregnancy tissue.
Medications, Dosages, and Administration Schedules
The following table Artikels the various medications used, dosages, and administration schedules for a medication abortion:
| Medication | Dosage | Administration | Timing |
|---|---|---|---|
| Mifepristone | 200 mg orally | First visit | At the time of the first visit to the clinic or provider’s office. |
| Misoprostol | 800 mcg | Buccal, Vaginal, or Sublingual | Second visit, typically 24-48 hours after mifepristone. |
Note: Dosages and specific administration instructions may vary slightly depending on the individual’s circumstances and the healthcare provider’s recommendations. Always follow the provider’s instructions carefully.
Guttmacher Institute Data on Medication Abortion
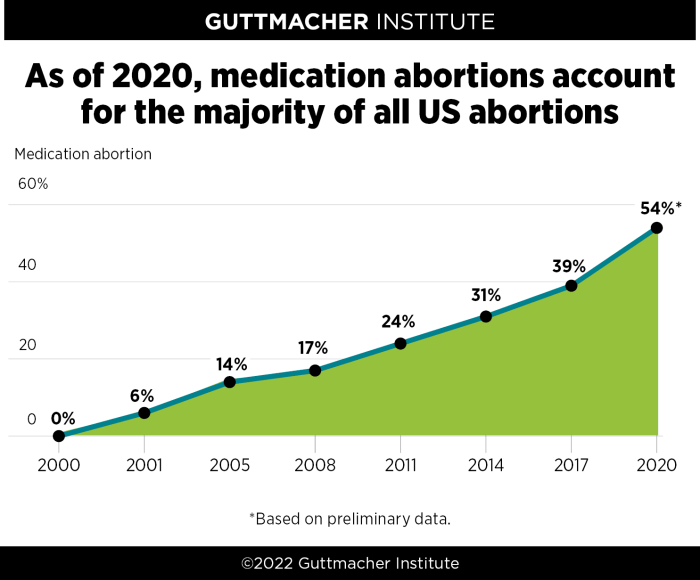
The Guttmacher Institute, a research organization dedicated to advancing reproductive rights and health, provides valuable insights into the use and accessibility of medication abortion. Their data offers a crucial perspective on the changing landscape of abortion care, revealing trends, challenges, and opportunities for improving access. This analysis will delve into historical trends, key statistics, and geographical distribution of medication abortion based on their reports.
Historical Trends in Medication Abortion Use
The use of medication abortion has seen significant growth since its introduction. Early adoption was often met with challenges related to access and provider availability. However, as medical understanding and acceptance have evolved, so too has the widespread adoption and refinement of medication abortion procedures. Data consistently demonstrates an increasing number of medication abortions performed annually, reflecting both the growing acceptance of the procedure and increased patient awareness.
Key Statistics on Medication Abortion Access and Utilization
Access to medication abortion varies greatly across the United States, influencing the utilization rate in different regions. The Guttmacher Institute data highlights key statistics, such as the number of medication abortion procedures performed annually, the percentage of abortions that are medication abortions, and the distribution of providers offering this service. These statistics are crucial for understanding the overall picture of access and use of medication abortion.
Factors like the availability of healthcare providers trained in the procedure and the policies impacting access are essential to consider.
Geographical Distribution of Medication Abortion Access
The distribution of medication abortion access across the US is highly uneven, reflecting both geographic factors and legislative influences. Examining this distribution provides a critical understanding of the varying levels of access available to women in different parts of the country. This is crucial to identify areas with limited access and develop targeted strategies to improve availability and affordability.
| State/Region | Medication Abortion Access (e.g., number of providers) | Notes |
|---|---|---|
| Northeast | High | Generally strong provider network and supportive policies. |
| Midwest | Moderate | Mixed availability, influenced by local factors. |
| South | Low | Significant legislative restrictions and fewer providers. |
| West | Variable | Access varies by state, with some having robust access and others with limitations. |
Comparison of Medication Abortion Rates in Different States/Regions Over Time
Analyzing medication abortion rates over time in various states or regions provides a dynamic view of how access has evolved and the disparities that persist. The Guttmacher Institute data helps visualize trends and identify factors influencing the rate of medication abortion procedures in different parts of the country. Changes in state laws, the availability of providers, and public awareness all contribute to variations in these rates.
This comparison allows for a deeper understanding of the ongoing impact of political and social influences on reproductive healthcare decisions. Comparing states with different levels of restrictions demonstrates how policies directly impact access to and use of medication abortion.
Access and Availability of Medication Abortion
Medication abortion, a safe and effective alternative to surgical abortion, is increasingly recognized for its accessibility and convenience. However, the availability of this procedure varies significantly across different regions and countries, influenced by a complex interplay of legal, logistical, and societal factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for ensuring equitable access to this important reproductive healthcare option.The factors influencing the availability of medication abortion services are multifaceted, encompassing legal restrictions, provider availability, and the broader social and political context.
Guttmacher Institute data on medication abortion shows a clear trend of increasing access. While that’s important, the current geopolitical climate, especially with the ongoing conflict in Ukraine and Russia’s aggression, highlights the complex global factors influencing healthcare access and policy. For a deeper dive into the recent strikes and the situation in Eastern Europe, check out this informative article on germany ukraine russia strikes explained.
Ultimately, understanding these global dynamics is crucial to contextualizing the evolving conversation around medication abortion access.
The Guttmacher Institute’s data highlights the significant role played by state-level regulations, which can vary dramatically, impacting both the ease and cost of obtaining this procedure. Access to medication abortion, therefore, is not uniform, and understanding these disparities is vital to advocating for equitable access.
Legal Landscape Surrounding Medication Abortion Access
The legal landscape surrounding medication abortion varies significantly across different jurisdictions. Guttmacher Institute data reveals a correlation between restrictive state laws and limited access to medication abortion. States with stricter regulations, often focused on gestational limits or mandatory waiting periods, frequently report lower rates of medication abortion provision. These restrictions frequently target the providers themselves, impacting their ability to offer the procedure, which in turn affects patients’ access to care.
Geographical Variations in Access to Medication Abortion
Geographic variations in access to medication abortion are considerable. The Guttmacher Institute’s data demonstrates substantial differences in access based on state policies. Areas with restrictive laws often face shortages of providers willing to offer medication abortion, resulting in limited availability for patients in those regions. This geographical disparity in access highlights the urgent need for policy changes that promote equitable access to reproductive healthcare across all communities.
The Guttmacher Institute’s data on medication abortion is really interesting, showing how safe and accessible it can be. While we’re on the topic of important health information, it’s also crucial to understand whooping cough, a potentially serious illness. Learning more about preventative measures and treatment options for whooping cough is key, and you can find some great resources on that topic here.
Ultimately, the Guttmacher data underscores the need for clear, evidence-based information on reproductive health options.
Role of Healthcare Providers in Facilitating Medication Abortion Access
Healthcare providers play a pivotal role in facilitating access to medication abortion. Guttmacher Institute data underscores the importance of providers who are knowledgeable, supportive, and well-equipped to address the unique needs of patients seeking this option. The availability of trained providers directly correlates with increased access to medication abortion services. Access to reliable, up-to-date information about the procedure and the overall support system around medication abortion can increase patient comfort and confidence.
Recent Guttmacher Institute data on medication abortion shows a clear trend, but it’s interesting to consider how this relates to current events. For example, the upcoming Canadian election, with its candidates like Pierre Poilievre and Justin Trudeau, and even some American political figures like Donald Trump, are all part of the larger political landscape that might influence healthcare policy.
To better understand these potential influences, check out this explainer on the Canada election Carney Poilievre Trump explainer. Ultimately, the Guttmacher data highlights the need for continued awareness and access to safe and legal abortion options.
A lack of such resources can severely hinder the procedure’s efficacy and safety.
Safety and Effectiveness of Medication Abortion
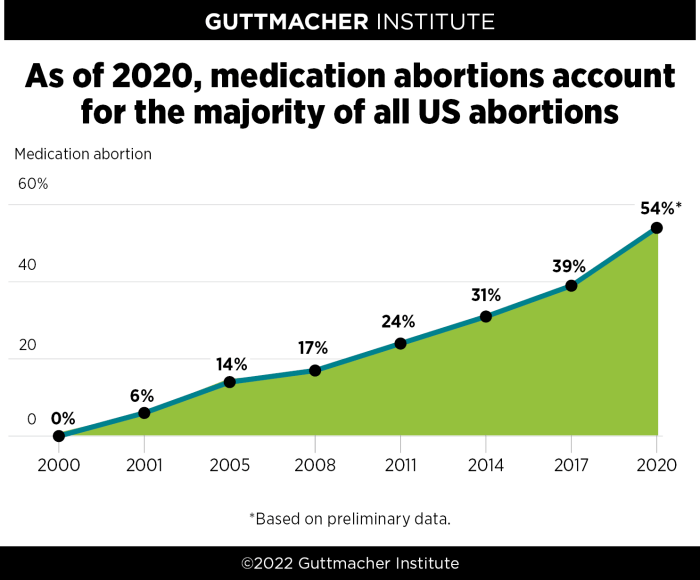
Medication abortion, often referred to as the abortion pill, is a safe and effective method of ending a pregnancy. It’s a significant advancement in reproductive healthcare, offering a non-surgical option for managing early pregnancies. This approach has been carefully studied and refined over time, with robust data supporting its safety and efficacy. The process typically involves two medications taken at different points in the process.
These medications work in concert to terminate the pregnancy, mimicking the effects of a natural miscarriage. It’s crucial to understand the nuances of this process and the associated risks and benefits for informed decision-making.
Safety Profile of Medication Abortion
Medication abortion has a very good safety profile, with serious complications being rare. Studies consistently demonstrate a low rate of major complications. The Guttmacher Institute’s research highlights the importance of close medical supervision during the process, ensuring patient well-being and prompt management of any potential issues.
Effectiveness of Medication Abortion
Medication abortion is highly effective, especially when administered early in pregnancy. The Guttmacher Institute’s data consistently demonstrates high success rates, often exceeding 95% in early pregnancies. This high degree of effectiveness underscores its value as a reliable option for managing unintended pregnancies. In situations where the procedure isn’t fully successful, follow-up care is available to address any remaining pregnancy tissue or potential complications.
Potential Complications of Medication Abortion
While rare, potential complications associated with medication abortion include incomplete abortion, infection, and excessive bleeding. The Guttmacher Institute’s research emphasizes the importance of post-abortion care and follow-up appointments to address any potential complications promptly. These are similar to the complications associated with a natural miscarriage.
Reported Adverse Effects and Frequencies
The table below summarizes the reported adverse effects of medication abortion, based on Guttmacher Institute data, and their relative frequencies. It’s important to remember that these are just general observations and individual experiences can vary.
| Adverse Effect | Frequency (estimated) |
|---|---|
| Incomplete Abortion | Low |
| Infection | Very Low |
| Heavy Bleeding | Low |
| Nausea | Common |
| Cramping | Common |
| Fever | Uncommon |
| Vomiting | Common |
Public Perception and Policy Debates Surrounding Medication Abortion
Navigating the complexities of medication abortion often involves navigating a landscape of differing opinions and perspectives. Public understanding and acceptance of this method of abortion are shaped by various factors, including religious beliefs, personal experiences, and the availability of accurate information. This exploration delves into the public perception of medication abortion and the multifaceted policy debates surrounding its access.Public opinion on medication abortion is a complex and often polarized issue.
Different demographics hold diverse views, with some expressing strong support for its availability and others opposing it on moral or religious grounds. The ongoing dialogue surrounding this issue highlights the need for accessible and unbiased information to inform the public and encourage respectful discourse.
Public Opinions on Medication Abortion
Public opinion on medication abortion is influenced by factors such as religious affiliation, political leanings, and perceived safety. Studies consistently reveal a correlation between those holding more conservative views and a greater degree of opposition to medication abortion. Conversely, individuals identifying as more liberal or progressive often demonstrate greater support for access. The degree of knowledge regarding the procedure also plays a significant role.
Those with greater understanding of the medical process, safety, and efficacy tend to be more supportive of access.
Policy Debates Surrounding Medication Abortion Access, Medication abortion guttmacher data
Policy debates regarding medication abortion access often center on the balance between a woman’s reproductive rights and potential ethical or moral concerns. These debates have manifested in varying regulations and restrictions imposed on the provision of this procedure, highlighting the political polarization surrounding the issue. The Guttmacher Institute’s data consistently illustrates the disparities in access across different states, with some jurisdictions enacting measures that significantly limit access.
Different Viewpoints on Medication Abortion Policy
Different viewpoints on medication abortion policy stem from differing interpretations of ethical and moral values, alongside varying levels of perceived medical safety. Those advocating for unrestricted access emphasize bodily autonomy and the right to choose. They often point to the procedure’s safety and efficacy as supported by extensive medical research. Conversely, those opposing unrestricted access frequently cite moral or religious objections to the procedure.
They may argue for the protection of fetal life and suggest alternatives such as adoption.
Contrasting Policy Approaches to Medication Abortion Across Jurisdictions
| Jurisdiction | Policy Approach | Supporting Data/Examples |
|---|---|---|
| States with few or no restrictions | Generally allow broad access to medication abortion, with minimal regulatory hurdles. | Examples include states with permissive regulations regarding telehealth consultations and mail-order medication. Guttmacher Institute data may highlight a correlation between these approaches and higher rates of access. |
| States with significant restrictions | Implement various measures to limit access to medication abortion, such as mandatory waiting periods, parental consent laws for minors, or requirements for in-person consultations. | Examples include states mandating specific types of counseling or requiring physicians to provide specific information that could be perceived as biased or misleading. Guttmacher Institute data may show lower rates of access in these states. |
| States with partial restrictions | These states have regulations that fall between the extremes, implementing some restrictions while still ensuring a degree of access. | Examples might include states that permit telehealth consultations but require in-person examinations at a later stage. Guttmacher Institute data could illustrate the varying levels of access in these jurisdictions. |
Medication Abortion and Women’s Health
Medication abortion, a safe and effective method for ending a pregnancy, raises concerns about its impact on women’s overall health. Understanding the potential effects, both immediate and long-term, is crucial for informed decision-making. This discussion will explore the effects of medication abortion on women’s health, highlighting the importance of comprehensive reproductive healthcare and post-abortion care.The overall safety profile of medication abortion is well-documented, and the vast majority of women experience minimal or no long-term health complications.
However, like any medical procedure, potential risks and benefits must be considered. Individual experiences can vary, and factors such as pre-existing conditions and the patient’s overall health play a significant role in the outcome.
Impact on Women’s Overall Health
Medication abortion typically involves taking two medications, mifepristone and misoprostol, within a specific timeframe. The process is generally well-tolerated, but some women may experience side effects like cramping, bleeding, nausea, or vomiting. These side effects are typically mild and temporary, resolving within a few days. However, some women may experience more severe side effects or complications. Careful monitoring and follow-up are essential to ensure the woman’s well-being.
Potential Long-Term Effects
While the majority of women experience no long-term complications, potential risks, though rare, should be acknowledged. Studies have indicated that the risk of future infertility is not significantly higher among women who have had a medication abortion compared to women who carry their pregnancies to term. However, individual circumstances and pre-existing conditions can influence the outcome. Comprehensive reproductive healthcare, including regular checkups, is important to identify and address any potential health concerns, whether related to medication abortion or other factors.
Importance of Comprehensive Reproductive Healthcare
Comprehensive reproductive healthcare services are crucial for women considering or undergoing medication abortion. These services should include counseling, pre-abortion assessments, and post-abortion follow-up care. The counseling aspect is vital to provide women with complete information, addressing their concerns and helping them make informed decisions. Pre-abortion assessments help identify any potential health risks or conditions that could affect the procedure’s outcome.
Post-abortion care, including regular check-ups, allows for monitoring of the woman’s recovery and addressing any concerns that may arise. Access to contraception and family planning resources is also critical for women’s reproductive health.
Importance of Post-abortion Care and Follow-up
Post-abortion care is essential for monitoring a woman’s recovery and addressing any potential complications. This care should include regular check-ups to ensure the woman is healing properly and to detect any signs of infection or other problems. Follow-up care also provides an opportunity to address any emotional or psychological concerns that may arise following the procedure. The role of mental health professionals in supporting women during this time is critical.
Comprehensive care, both physical and mental, is crucial for women’s well-being after a medication abortion. Medical providers should provide clear instructions for follow-up care, including when and how to contact them with concerns.
Comparison of Medication Abortion with Surgical Abortion
Choosing between medication and surgical abortion is a deeply personal decision. Both methods are safe and effective when performed by trained medical professionals. This comparison will explore the key differences in procedures, costs, recovery times, and potential risks and benefits to help individuals make informed choices.Understanding the nuances of each method can empower individuals to discuss their options with healthcare providers and make decisions that align with their individual circumstances.
This information should not be considered medical advice. Always consult with a qualified healthcare professional for personalized guidance.
Procedure Differences
Medication abortion involves taking specific medications to induce the abortion process. These medications are typically taken in a two-step process, with the first medication terminating the pregnancy and the second causing the expulsion of pregnancy tissue. Surgical abortion, on the other hand, is a minor surgical procedure performed in a clinical setting. A doctor uses instruments to remove the pregnancy tissue.
The procedure is generally faster than the medication abortion process.
Costs and Accessibility
The cost of medication abortion and surgical abortion varies depending on location, clinic, and insurance coverage. Medication abortion is often more affordable than surgical abortion, especially when considering potential travel costs and time off work for surgical procedures. Accessibility also varies; medication abortion can be obtained through telehealth or in-person consultations, which can be more convenient and accessible in certain regions.
Surgical abortions are usually performed in clinics or hospitals, and availability may depend on local healthcare infrastructure.
Recovery Time
Recovery times for both procedures differ significantly. Medication abortion generally involves minimal recovery time. Some women may experience cramping, bleeding, and other side effects, but these typically resolve within a few days. Surgical abortion, while a minor procedure, can have a slightly longer recovery period. Some women may experience cramping and light bleeding for a few days following the procedure.
However, recovery is typically relatively quick. The exact recovery time depends on individual factors.
Potential Risks and Benefits
Both medication and surgical abortion are generally safe procedures when performed by trained medical professionals. Medication abortion carries a lower risk of complications than surgical abortion. Potential risks for both include infection, allergic reactions, and incomplete abortion. The benefits of medication abortion include the convenience of home-based treatment in some cases and reduced risk of complications compared to surgical procedures.
Surgical abortion offers a more controlled and rapid procedure for removing pregnancy tissue.
| Characteristic | Medication Abortion | Surgical Abortion |
|---|---|---|
| Procedure | Taking medications | Surgical procedure |
| Cost | Generally more affordable | Often more expensive |
| Accessibility | Potentially higher accessibility in some areas | Typically performed in clinics or hospitals |
| Recovery Time | Minimal | Slightly longer |
| Risks | Lower risk of complications | Potential for complications, though rare |
| Benefits | Convenience, potentially lower cost | Faster procedure, more controlled removal |
Last Word
In conclusion, medication abortion guttmacher data paints a detailed picture of this procedure’s prevalence, accessibility, and impact. The data highlights both the safety and effectiveness of medication abortion, alongside potential complications and public perception. Ultimately, understanding these factors is critical for informed discussions about reproductive healthcare choices and policies. Further research is essential to fully grasp the nuanced complexities surrounding this sensitive issue.

