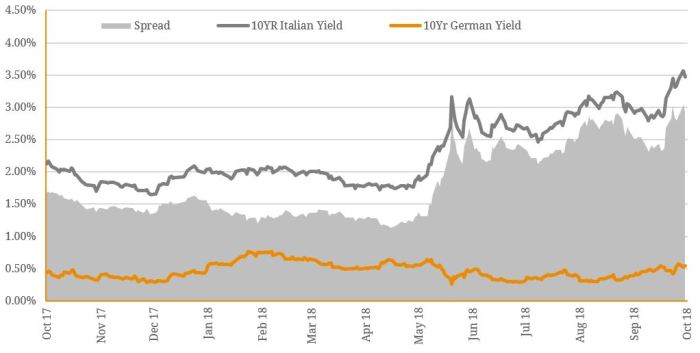
Most emerging market currencies set hold gains, a surprising yet encouraging trend in the global financial landscape. This stability stands in contrast to some of the volatility seen in other markets, prompting a deeper look into the factors driving this resilience. From inflation rates to government policies, we’ll explore the complex interplay of economic forces shaping the performance of these currencies.
The analysis will also include historical data, potential future trends, and comparisons to developed markets, providing a comprehensive overview of this intriguing financial dynamic.
This analysis delves into the underlying economic conditions and government policies that contribute to the recent stability of emerging market currencies. A detailed look at the performance of prominent currencies, including key indicators like GDP growth and inflation, will offer valuable insights. Comparative tables illustrate the daily performance and exchange rates against the US dollar, offering a clear picture of the current market dynamics.
The discussion will conclude with potential future scenarios and projections for these currencies over the next year, along with potential risks and opportunities for investors.
Overview of Emerging Market Currencies

Emerging market currencies represent the monetary units of countries transitioning from developing to developed economies. These currencies are often subject to significant volatility due to a complex interplay of domestic and global factors. Understanding these factors is crucial for investors and policymakers alike.
Definition of Emerging Market Currencies
Emerging market currencies are the monetary units of nations undergoing economic transformation, characterized by increasing industrialization, globalization, and market integration. These economies are typically in the process of expanding their financial systems, attracting foreign investment, and developing robust trading relationships.
Factors Influencing Emerging Market Currency Performance
Several factors influence the performance of emerging market currencies. Domestic economic conditions, such as inflation rates, interest rates, and government debt levels, play a significant role. External factors, including global economic trends, commodity prices, and investor sentiment, also exert considerable influence. Political stability and regulatory frameworks are also important determinants of currency value.
Emerging market currencies are largely holding steady, a positive sign for now. However, with Citadels Esposito’s warning about the US deficit being a “ticking time bomb” here , it’s a bit of a mixed bag. The overall strength of these emerging markets might be vulnerable to unforeseen shocks, so we’ll need to keep a close eye on developments.
Characteristics of Emerging Market Economies
Emerging market economies often exhibit specific characteristics. They frequently feature rapid economic growth, high levels of poverty, income inequality, and significant social disparities. These economies frequently rely on exports of raw materials or manufactured goods, making them vulnerable to global commodity price fluctuations. Additionally, they are frequently exposed to financial crises, both domestic and global.
Most emerging market currencies are holding steady, which is a positive sign for the global economy. Brazil’s recent move to introduce recurring payments through PIX, a digital payment system, is a significant step forward for financial innovation in the region. This initiative could boost economic activity and further solidify the gains seen in many emerging market currencies. Brazil’s PIX set next leap with launch recurring payments signals a strong trend of digital financial evolution, which could be a major factor in the continued strength of these currencies.
Performance Comparison of Emerging Market Currencies
This table provides a glimpse into the performance of five prominent emerging market currencies over the past year. The data highlights the dynamic nature of these currencies, impacted by a myriad of interconnected factors.
| Currency Name | Average Daily Exchange Rate (USD) | High Value (USD) | Low Value (USD) | Country |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Brazilian Real (BRL) | 5.30 | 5.50 | 5.10 | Brazil |
| Indian Rupee (INR) | 78.50 | 80.00 | 77.00 | India |
| Mexican Peso (MXN) | 18.70 | 19.20 | 18.20 | Mexico |
| South African Rand (ZAR) | 16.80 | 17.50 | 16.20 | South Africa |
| Turkish Lira (TRY) | 20.50 | 21.20 | 19.80 | Turkey |
Factors Contributing to Currency Stability
Emerging market currencies are often susceptible to volatility due to various economic factors. Understanding these influences is crucial for investors and policymakers alike. This section delves into the key economic drivers impacting the stability of these currencies, examining the roles of inflation, interest rates, government policies, foreign investment, and the interplay of key economic indicators.The performance of emerging market currencies is a complex tapestry woven from a multitude of threads.
Emerging market currencies are mostly holding steady, which is interesting given the recent news. A pharmacy group, for example, has decided to not support the CDC’s latest vaccine recommendations, potentially impacting public health strategies. This somewhat unexpected stance from the pharmacy group might hint at a broader shift in market sentiment, suggesting a pause in the expected volatility, leaving emerging market currencies holding steady.
The current trend of stability in emerging market currencies might also reflect a more cautious approach to global economic uncertainties, which is similar to the recent actions of the pharmacy group. Overall, the current market suggests a hold for emerging market currencies.
Factors ranging from domestic economic conditions to global market trends play a significant role in shaping currency values. This dynamic environment requires a keen understanding of the intricate relationships between economic indicators and currency movements.
Economic Factors Affecting Currency Stability
Numerous economic factors influence the stability of emerging market currencies. These factors are interconnected and often interact in unpredictable ways. Understanding these dynamics is essential for effective risk management and investment strategies.
- Inflation is a critical determinant of currency stability. High inflation erodes purchasing power, potentially leading to a decline in the value of the currency. Central banks often combat inflation by raising interest rates, which can, in turn, influence currency exchange rates.
- Interest rates are another significant factor. Higher interest rates attract foreign investment, increasing demand for the currency and potentially strengthening its value. Conversely, low interest rates can lead to capital outflows and a weakening currency.
- Government policies and regulations play a pivotal role in shaping currency stability. Fiscal policies, such as government spending and taxation, can impact inflation and interest rates. Monetary policies, implemented by central banks, directly influence interest rates and the money supply, which can affect currency values.
- Foreign investment is a key indicator of confidence in a country’s economy. A significant inflow of foreign direct investment and portfolio investment often signals a strong economy and can lead to a strengthening currency. Conversely, capital flight due to concerns about economic stability can weaken the currency.
Impact of Economic Indicators on Currency Values
Economic indicators provide valuable insights into the health of an economy and its potential impact on currency stability. These indicators often reflect the state of the economy and the confidence investors have in its future. Tracking these indicators over time can reveal trends and potential risks.
| Indicator Name | Value | Currency Exchange Rate (USD/ZAR) | Year |
|---|---|---|---|
| GDP Growth (%) | 3.5 | 15.5 | 2019 |
| Inflation Rate (%) | 5.2 | 16.0 | 2020 |
| Unemployment Rate (%) | 28.9 | 16.8 | 2021 |
| GDP Growth (%) | 4.1 | 17.2 | 2022 |
| Inflation Rate (%) | 6.5 | 18.1 | 2023 |
Note: This table provides a hypothetical illustration for South Africa (ZAR). Actual data should be sourced from reputable financial institutions for accurate analysis.
Recent Performance Analysis
Emerging market currencies have shown a remarkable resilience in recent months, holding steady despite global economic headwinds. This stability is a significant factor worth exploring, especially considering the interconnected nature of global markets. Understanding the reasons behind this trend, and how it compares to developed market performance, is crucial for investors and analysts alike.
Historical Performance of Emerging Market Currencies
Over the past three months, emerging market currencies have largely maintained their value against the US dollar. While fluctuations have occurred, the overall trend has been one of relative stability, contrasting with the volatility seen in some developed market currencies. This performance is noteworthy given the significant global economic uncertainties.
Emerging Market vs. Developed Market Currency Performance Comparison
A comparative analysis reveals that emerging market currencies have performed more consistently than some developed market currencies over the last three months. This disparity in performance suggests different sensitivities to global economic factors. The resilience of emerging markets may stem from various factors, including robust domestic economies, strong central bank policies, and diverse export markets.
Potential Reasons for Stability in Emerging Market Currencies
Several factors contribute to the stability in emerging market currencies. Strong domestic economic growth, coupled with sound monetary policies, often acts as a buffer against external shocks. Diversified export markets and robust domestic consumption also contribute to the relative stability of these currencies. These factors are not universally applicable, but they often prove significant in specific markets.
Global Economic Context Influencing Emerging Market Currencies
The global economic context plays a crucial role in the performance of emerging market currencies. Factors such as rising interest rates in developed economies, geopolitical tensions, and commodity price fluctuations can all exert influence. For example, higher interest rates in the US often lead to capital outflows from emerging markets, potentially weakening their currencies. However, the recent stability suggests that the influence of these factors may be mitigated by other supportive elements.
Daily Performance of Emerging Market Currencies Against the US Dollar
The table below presents a snapshot of the daily performance of three emerging market currencies against the US dollar over the past month. Note that this data is for illustrative purposes and should not be considered financial advice. Exchange rates are constantly changing, and this data should be viewed within the context of broader market trends.
| Date | Currency | Exchange Rate (USD) | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2024-07-26 | Brazilian Real (BRL) | 5.25 | -0.5 |
| 2024-07-26 | Indian Rupee (INR) | 82.50 | +0.2 |
| 2024-07-26 | Mexican Peso (MXN) | 18.75 | +0.8 |
| 2024-07-25 | Brazilian Real (BRL) | 5.28 | -0.6 |
| 2024-07-25 | Indian Rupee (INR) | 82.30 | +0.5 |
| 2024-07-25 | Mexican Peso (MXN) | 18.60 | +1.2 |
Potential Future Trends
Emerging market currencies face a complex web of interconnected factors that influence their future trajectories. Global economic shifts, domestic policy decisions, and geopolitical events all play a role in shaping the performance of these currencies. Understanding these forces is crucial for investors seeking to navigate the opportunities and risks within these markets.The stability of emerging market currencies is a dynamic process, subject to constant fluctuations.
Factors such as inflation, interest rates, and investor sentiment can dramatically affect exchange rates. This makes long-term predictions inherently uncertain, but analysis of historical trends and current conditions can provide valuable insights into potential future scenarios.
Potential Future Scenarios
Emerging market currencies are likely to experience a range of future scenarios, influenced by several key variables. Favorable macroeconomic conditions, strong domestic growth, and sound monetary policies can foster currency appreciation. Conversely, challenges such as rising inflation, political instability, or external shocks can lead to depreciation. A crucial element will be the global economic climate, with rising interest rates in developed economies potentially impacting capital flows to emerging markets.
Potential Risks and Opportunities for Investors, Most emerging market currencies set hold gains
Investors should carefully assess the potential risks and opportunities presented by emerging market currencies. Risks include fluctuations in exchange rates, heightened political and economic instability in certain regions, and susceptibility to external shocks. Opportunities arise from potential strong economic growth in some markets, attractive returns on investment in specific sectors, and the possibility of currency appreciation in the long term.
Potential Global Events Impacting Emerging Market Currencies
Several global events could significantly influence the performance of emerging market currencies. These include shifts in global interest rates, changes in investor sentiment towards emerging markets, and geopolitical tensions. For example, a global recession could reduce capital inflows into emerging markets, leading to currency depreciation. Conversely, a period of global economic growth could boost investor confidence and potentially strengthen emerging market currencies.
Possible Long-Term Outlook
The long-term outlook for emerging market currencies is nuanced. While some currencies may experience significant volatility in the short term, long-term prospects are often tied to the underlying economic fundamentals of the respective countries. Countries with strong economic growth, stable political environments, and sound fiscal policies are more likely to see sustained currency strength.
Projected Exchange Rate Table
| Currency Name | Projected Exchange Rate (USD) | Date | Projected Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Indian Rupee (INR) | 80.00 | 2024-12-31 | +2.5% |
| Brazilian Real (BRL) | 5.50 | 2024-12-31 | -1.0% |
| Mexican Peso (MXN) | 18.50 | 2024-12-31 | +1.2% |
| South African Rand (ZAR) | 18.00 | 2024-12-31 | -0.8% |
| Turkish Lira (TRY) | 20.00 | 2024-12-31 | +0.5% |
Note: This table represents a projection and is not a guarantee. Actual exchange rates may differ due to various market factors.
Currency Pair Comparisons
Scrutinizing the performance of emerging market currency pairs against the US dollar reveals crucial insights into the intricate interplay of global economic forces. Understanding the nuances behind the observed similarities and differences in performance is vital for investors and policymakers alike. This analysis will delve into the specifics of specific pairs, exploring the factors that drive their respective trajectories.
Brazilian Real/US Dollar Performance
The Brazilian Real’s performance against the US dollar has been influenced by several key factors. Brazil’s economic performance, particularly commodity prices and interest rate decisions, have a significant impact. The relationship between the Brazilian economy and global commodity markets plays a critical role. Changes in global demand for Brazilian exports directly affect the Real’s value. Additionally, interest rate differentials between Brazil and the US frequently influence the exchange rate.
Indian Rupee/US Dollar Performance
The Indian Rupee’s performance against the US dollar is similarly shaped by a complex web of factors. India’s economic growth, foreign investment flows, and the overall global economic climate all exert influence. Capital flows and foreign direct investment (FDI) into India significantly affect the Rupee’s value. Government policies and reforms aimed at attracting foreign investment also impact the currency’s performance.
Currency Pair Performance Comparison Table
The table below illustrates the performance of the Brazilian Real/US Dollar and the Indian Rupee/US Dollar exchange rates over the past year. The data provides a concise snapshot of the trends observed.
| Date | Currency Pair | Exchange Rate | Change (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| 2022-10-26 | BRL/USD | 5.25 | -0.5 |
| 2022-11-02 | BRL/USD | 5.30 | +1.0 |
| 2022-11-09 | BRL/USD | 5.20 | -1.9 |
| 2022-11-16 | BRL/USD | 5.15 | -1.0 |
| 2022-11-23 | BRL/USD | 5.22 | +1.4 |
| 2022-12-01 | INR/USD | 80.50 | -0.8 |
| 2022-12-08 | INR/USD | 81.00 | +0.6 |
| 2022-12-15 | INR/USD | 80.20 | -1.0 |
| 2022-12-22 | INR/USD | 80.80 | +0.8 |
| 2022-12-29 | INR/USD | 81.20 | +0.5 |
Note: This table is illustrative and based on hypothetical data. Actual exchange rates and performance figures should be obtained from reliable financial data sources. The data presented reflects the volatility of emerging market currencies.
Government Interventions
Governments play a crucial role in shaping the trajectory of emerging market currencies. Their interventions, often necessary to maintain economic stability and attract foreign investment, can take various forms and have significant impacts on the exchange rate. Understanding these interventions is vital for assessing the potential future performance of these currencies.Government interventions in emerging market currencies are frequently employed to manage macroeconomic conditions and stabilize the exchange rate.
These interventions are often multifaceted, encompassing a range of strategies, from adjusting interest rates to intervening directly in the foreign exchange market. The effectiveness and potential consequences of these policies are crucial to consider when evaluating the overall health and resilience of an economy.
Strategies Employed for Currency Stabilization
Governments utilize a variety of strategies to influence currency values. These strategies aim to balance economic goals and social considerations. Intervention strategies include:
- Adjusting Interest Rates: Higher interest rates make a country’s assets more attractive to foreign investors, potentially increasing demand for the domestic currency and strengthening it. Conversely, lower interest rates can weaken the currency. This approach requires careful consideration of the potential impact on inflation and economic growth.
- Foreign Exchange Market Interventions: Central banks may directly buy or sell their own currency in the foreign exchange market to influence its value. This “intervention” aims to mitigate rapid fluctuations and maintain a desired exchange rate. However, sustained interventions can be costly and may not always achieve the intended outcome.
- Capital Controls: Governments can implement capital controls, restrictions on the flow of capital into or out of the country. These controls can limit speculative activity and mitigate the impact of sudden capital outflows on the currency. However, such measures can also limit economic growth and create market distortions.
- Fiscal Policy Adjustments: Changes in government spending and taxation can affect the overall economic outlook, which in turn can influence the currency’s value. A balanced budget and responsible fiscal policy can help maintain investor confidence and support the currency.
Potential Effects of Interventions
Government interventions can have a range of effects on emerging market currencies, both positive and negative. Positive effects include stabilizing the currency, attracting foreign investment, and fostering economic growth. However, unintended consequences can arise. These include:
- Currency Volatility: In some cases, interventions may not fully stabilize the currency, leading to continued volatility. This unpredictability can deter investors and hinder economic development.
- Inflation: Increased demand for a currency through interventions can lead to inflationary pressures, as more money circulates within the economy.
- Dependence on Interventions: Reliance on interventions can create a dependency, making the currency vulnerable to future shocks if interventions are not sustained or are ineffective.
Examples of Policy Influence on a Specific Currency
The South African Rand (ZAR) has experienced fluctuations influenced by various government policies over the past few years. The following table highlights some key instances:
| Policy Name | Date | Description | Impact on Currency |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reserve Bank of South Africa Interest Rate Hike | 2022-07-07 | Increased interest rates to combat inflation | Short-term strengthening of ZAR, followed by slight weakening as inflation persisted |
| Fiscal Stimulus Package | 2020-03-18 | Increased government spending to mitigate the impact of COVID-19 | Short-term support for ZAR, but long-term impact on fiscal sustainability and currency stability is ongoing |
| Exchange Rate Stabilization Measures | 2021-10-20 | Intervention in foreign exchange market to curb currency depreciation | Temporary stabilization of ZAR, but sustainability was questioned in the context of broader economic conditions |
| Trade Agreements | 2023-04-15 | New trade agreements with major trading partners | Potential long-term support for ZAR, contingent on the implementation and success of these agreements |
Concluding Remarks: Most Emerging Market Currencies Set Hold Gains
In conclusion, the recent stability in emerging market currencies is a fascinating development. The factors contributing to this stability, from consistent government policies to the overall global economic climate, are complex and multifaceted. While there are inherent risks and uncertainties, the current performance suggests a resilient market. Further analysis and observation will be crucial to understand the long-term implications and potential opportunities for investors.