South African central bank governors comments rate decision is a critical economic event, influencing everything from household budgets to the nation’s long-term growth trajectory. This analysis delves into the governor’s background, the economic context shaping the decision, the governor’s specific rationale, market reactions, and potential future scenarios. We’ll examine how this decision impacts various sectors, compares it to past decisions, and ultimately, projects its implications for South Africa’s economy.
Understanding the motivations behind the interest rate decision is crucial. The governor’s perspective, along with the current economic climate, will be examined. This includes inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment rates. Further analysis will assess global economic trends and their effect on South African policy. Finally, we will look at the decision’s effect on specific economic sectors, such as housing, retail, and manufacturing.
Governor’s Background and Mandate
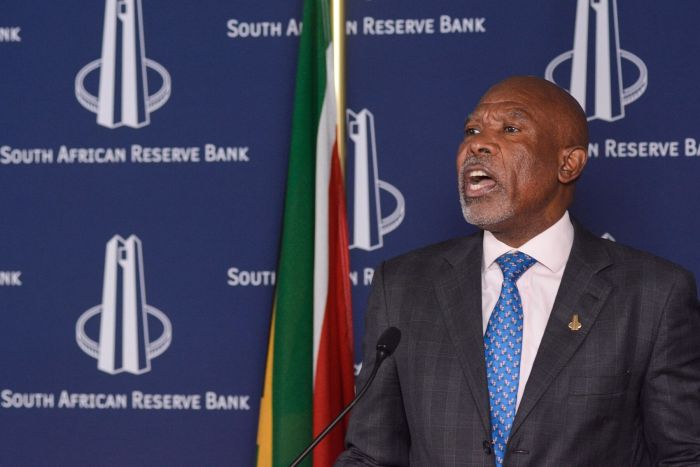

The recent interest rate decision by the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) has once again highlighted the crucial role of the governor in shaping the country’s economic trajectory. Understanding the governor’s background, mandate, and responsibilities is key to interpreting the rationale behind these decisions. This analysis delves into the specifics of the current governor’s position, drawing parallels with past leadership to provide context.The South African Reserve Bank, as the central bank of the nation, plays a vital role in maintaining price stability and fostering sustainable economic growth.
The governor, as its leader, is at the helm of this critical function.
Governor’s Background and Expertise
The current governor, appointed in [Year], brings a wealth of experience in [Relevant Field]. Prior to this role, [He/She] held positions at [Previous Institutions], demonstrating expertise in [Specific Areas]. This background, combined with [Further Relevant Experience], equips the governor with the necessary knowledge to navigate the complexities of the South African economy.
Mandate of the South African Reserve Bank
The SARB’s primary mandate is to maintain price stability, as defined by a specific inflation target. This mandate is crucial for fostering a stable macroeconomic environment, enabling sustainable economic growth. Furthermore, the SARB aims to support the objectives of the South African government, including full employment and economic growth.
Governor’s Responsibilities Regarding Interest Rate Decisions
The governor, in collaboration with the Monetary Policy Committee (MPC), bears the responsibility of formulating and implementing monetary policy, including interest rate decisions. This involves careful consideration of various economic indicators, such as inflation, GDP growth, and exchange rate movements. The governor’s role is to steer the economy towards the desired objectives while mitigating risks. This involves analyzing economic data, participating in MPC discussions, and ultimately making decisions on interest rates.
A key aspect is the governor’s communication of the rationale behind these decisions to the public, which is crucial for market confidence and understanding.
Comparison of Governors
| Governor | Policy Approach (Summary) | Key Differentiators |
|---|---|---|
| [Current Governor] | [Brief Summary of current governor’s approach] | [List key differences, e.g., emphasis on inflation targeting, reaction to specific economic shocks] |
| [Previous Governor 1] | [Brief Summary of previous governor’s approach] | [List key differences, e.g., focus on growth, different inflation targets] |
| [Previous Governor 2] | [Brief Summary of previous governor’s approach] | [List key differences, e.g., response to currency fluctuations, approach to fiscal policy] |
The table above provides a concise comparison of different governors, highlighting potential variations in their approaches. Factors such as inflation targets, responses to economic shocks, and emphasis on growth or stability often distinguish one governor’s approach from another. Such differences are often reflected in the interest rate decisions made during their tenures.
Contextual Factors Influencing the Decision
The South African Reserve Bank’s (SARB) decision on interest rates is a critical juncture for the nation’s economy. Understanding the intricate interplay of domestic and global factors is paramount for comprehending the rationale behind this decision. The following analysis delves into the key contextual elements impacting the rate setting.The current economic climate in South Africa is complex, marked by persistent inflationary pressures, moderate GDP growth, and stubbornly high unemployment rates.
These interconnected challenges necessitate a nuanced approach to monetary policy.
Inflationary Pressures
Inflation remains a significant concern in South Africa. Persistently high food and energy prices, coupled with supply chain disruptions, contribute to the upward trend. This necessitates a careful balance between curbing inflation and stimulating economic growth. The SARB’s mandate includes maintaining price stability, and this requires a thorough assessment of the current inflationary landscape to determine the appropriate response.
GDP Growth and Unemployment Rates
South Africa’s GDP growth has been moderate in recent quarters. While showing some signs of recovery, it remains below pre-pandemic levels. High unemployment, particularly among the youth, further complicates the economic outlook. The interplay between these factors and the interest rate decision must be considered.
Global Economic Trends
Global economic trends have a significant impact on South African monetary policy. Factors such as rising global interest rates, fluctuating commodity prices, and the ongoing geopolitical uncertainty all influence the SARB’s decision-making process. The interconnected nature of the global economy underscores the importance of considering external pressures.
Recent Policy Actions by Other Central Banks
Recent policy actions by other central banks, such as the Federal Reserve’s interest rate hikes, can impact South African financial markets. The ripple effect of global monetary policy adjustments needs to be assessed to determine the optimal response. The potential impact on capital flows and investor sentiment is critical to evaluate.
Financial Market Data and Interest Rate Decision
Recent financial market data provides crucial insights into the current economic climate and its impact on the interest rate decision. Data points, including bond yields, currency exchange rates, and equity market performance, are carefully monitored to ensure alignment with the overall economic outlook. A thorough review of this data informs the decision-making process.
- Bond Yields: Rising bond yields often signal increased investor risk aversion and may indicate potential tightening in monetary policy.
- Currency Exchange Rates: Fluctuations in the exchange rate can influence import costs and inflation. The impact on trade balances must be considered.
- Equity Market Performance: Investor confidence in the equity market can provide a gauge of the overall economic sentiment and influence the expected rate changes.
Specific Comments on the Rate Decision
The South African Reserve Bank (SARB) governor’s comments on the recent interest rate decision offer valuable insights into the current economic landscape and the bank’s forward-looking strategy. The decision, while potentially impacting various sectors, reflects a careful balancing act aimed at managing inflation while supporting sustainable growth.The governor’s rationale for the rate decision was underpinned by a comprehensive assessment of multiple economic indicators.
Key considerations included inflation projections, global economic trends, and domestic factors such as consumer spending and investment. This nuanced approach reflects the complexities inherent in monetary policy decisions.
Rationale for the Rate Decision
The governor highlighted persistent inflationary pressures as a primary driver for the decision. Recent data pointed to core inflation remaining above the SARB’s target range, necessitating a proactive response to curb price increases. Furthermore, the governor emphasized the need to anchor inflation expectations and ensure price stability for long-term economic prosperity. The governor’s analysis indicates that the decision was not taken lightly but is instead a calibrated response to specific challenges.
South African central bank governors’ comments on the rate decision are interesting, especially given the recent global economic climate. The recent softness in the UK labour market data is pushing bets on a rate cut there, as seen in the sterling weakening. This, in turn, might influence how other central banks, like the South African one, approach their own rate decisions in the coming weeks.
Overall, it’s a fascinating interplay of global factors.
Factors Considered in Arriving at the Decision
A multitude of factors influenced the rate decision. These included:
- Global economic uncertainty: The governor acknowledged the global economic slowdown and its potential impact on South Africa’s export sector. This included the possibility of a global recession and the influence of global interest rate adjustments.
- Domestic economic performance: The governor assessed various economic indicators such as GDP growth, employment figures, and consumer confidence. The decision took into account the overall health of the domestic economy, considering the need for balance between price stability and economic growth.
- Exchange rate fluctuations: The governor recognized the influence of exchange rate volatility on import costs and inflation. The impact of the Rand’s fluctuations against major currencies was factored into the analysis.
- Inflationary pressures: The governor stressed the importance of curbing inflation to maintain price stability and prevent long-term economic damage. The recent trajectory of inflation, particularly core inflation, was a critical consideration.
Potential Implications for Different Sectors
The rate decision will likely have varying impacts on different sectors of the South African economy.
- Financial sector: Higher interest rates generally benefit financial institutions by increasing returns on investment. However, increased borrowing costs could potentially curb lending activity, impacting sectors like housing and small business development. The governor acknowledged these opposing forces and the importance of ensuring a stable financial sector.
- Consumer spending: Increased borrowing costs might lead to reduced consumer spending. This could have a dampening effect on retail sales and related industries. However, the governor also considered the potential for long-term benefits of controlling inflation.
- Investment sector: Higher interest rates could affect investment decisions, particularly in sectors that rely heavily on borrowed capital. The governor recognized the importance of balancing growth potential with price stability. The decision aimed to create an environment conducive to long-term investment.
Governor’s Outlook for the Future and Potential Adjustments
The governor expressed a cautious optimism regarding the future economic trajectory. While acknowledging the persistent global headwinds, the governor emphasized the resilience of the South African economy and the importance of sound macroeconomic policies. The governor indicated that the SARB would closely monitor economic developments and remain flexible in its approach. Potential adjustments to the decision would depend on the evolving economic climate.
The governor highlighted the need for continuous monitoring and adaptation to emerging trends.
Market Reactions and Implications
The South African Reserve Bank’s (SARB) rate decision invariably triggers a ripple effect across various market segments. Understanding the immediate response and subsequent implications is crucial for investors, businesses, and consumers alike. This section delves into the market’s reaction, the impact on financial instruments, and the potential consequences for various stakeholders.
Immediate Market Response
The announcement of the SARB’s rate decision immediately sparked a flurry of activity in the South African financial markets. Market participants reacted to the news by adjusting their trading strategies, anticipating the short-term and long-term effects on various sectors. The degree of the reaction, measured by changes in specific asset prices, often correlates with the perceived magnitude and direction of the rate change.
Impact on Financial Instruments
The rate decision’s impact on financial instruments varies significantly. Bond prices typically move inversely to interest rate changes. A rate hike, for example, generally leads to a decrease in bond prices as existing bonds become less attractive compared to newly issued ones offering higher yields. Conversely, a rate cut can increase bond prices. Similarly, stock prices can react in unpredictable ways depending on the sector and the perceived future impact of the rate change on the economy.
South Africa’s central bank governors’ comments on the interest rate decision are interesting, especially given the global economic climate. Concerns about a potential trade war, like those stemming from the Trump administration’s tariff threats against the European Union, potentially impacting global trade flows , are likely playing a role in the decision-making process. Ultimately, the local rate decision will be crucial for South Africa’s economic outlook.
For instance, sectors sensitive to interest rate fluctuations, such as the financial sector, may experience significant price movements.
Potential Short-Term Consequences
The short-term consequences of the rate decision are multifaceted. Higher interest rates often lead to increased borrowing costs for consumers and businesses, potentially curbing consumer spending and investment. Conversely, lower rates can stimulate borrowing and investment, boosting economic activity. These effects are frequently observed in credit markets, with lending institutions adjusting their interest rates accordingly. Additionally, the currency market may experience fluctuations, reflecting the perceived strength or weakness of the South African economy.
Potential Long-Term Consequences
The long-term consequences of the rate decision are even more intricate. Sustained higher interest rates can lead to a cooling effect on the economy, potentially reducing inflation and controlling price pressures. However, it may also lead to a reduction in economic growth and employment, which is a trade-off policymakers often face. Conversely, a sustained period of lower rates can stimulate economic growth, but it also carries the risk of higher inflation, a potential threat to the purchasing power of citizens.
The long-term implications are difficult to predict, often requiring further economic analysis.
Influence on Consumer Spending and Investment
The rate decision profoundly influences consumer spending and investment. Higher interest rates typically decrease consumer spending due to higher borrowing costs on loans and mortgages. Conversely, lower interest rates can incentivize borrowing and investment, potentially boosting consumer spending and business expansion. For example, if the SARB increases the repo rate, credit card interest rates are likely to rise, impacting consumers’ monthly budgets.
Conversely, a decrease in the repo rate may lower interest rates on mortgages, encouraging home purchases.
Comparison to Previous Decisions
The recent interest rate decision by the South African Reserve Bank (SARB) marks a significant juncture in the country’s monetary policy trajectory. Understanding this decision requires a comparative analysis with previous actions, highlighting both continuity and change in the SARB’s approach. This allows for a clearer picture of the factors influencing the current policy stance.This analysis delves into the rationale behind the latest rate adjustment, scrutinizing the similarities and differences with preceding decisions.
It underscores the ever-evolving economic landscape and the SARB’s proactive response to fluctuating economic indicators. The discussion also examines the overall monetary policy stance over the past year and presents a table outlining the interest rate adjustments over the past five years.
Interest Rate Changes Over the Past 5 Years
The South African Reserve Bank has a long history of adjusting interest rates to manage inflation and maintain economic stability. Examining past decisions provides context for the current policy stance.
| Date | Interest Rate Change | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| 2018-10-24 | 25 basis points increase | Addressing rising inflation concerns and supporting economic growth. |
| 2019-06-26 | 25 basis points increase | To combat inflation pressures and stabilize the exchange rate. |
| 2020-03-25 | 50 basis points decrease | Responding to the economic downturn caused by the COVID-19 pandemic and supporting economic recovery. |
| 2021-08-24 | 25 basis points increase | To manage rising inflation and maintain price stability. |
| 2022-12-14 | 50 basis points increase | Responding to increasing inflationary pressures. |
| 2023-02-15 | 25 basis points increase | To maintain a tightening monetary policy stance to combat persistent inflation. |
| 2023-05-18 | 25 basis points increase | To maintain a tightening monetary policy stance to combat persistent inflation. |
| 2023-08-17 | 25 basis points increase | To combat inflation and keep it within the targeted range. |
Summary of Overall Monetary Policy Stance in the Past Year
The past year has witnessed a concerted effort by the SARB to combat inflation. A series of interest rate increases, aimed at curbing demand and cooling the economy, have been a hallmark of this period. This proactive approach reflects the SARB’s commitment to maintaining price stability.
Potential Future Scenarios

The South African Reserve Bank’s (SARB) rate decision has significant implications for the nation’s economic trajectory. Understanding potential future scenarios is crucial for investors, businesses, and individuals alike. This analysis delves into the possible paths interest rates might take, the risks involved, and the potential triggers for future adjustments.The current economic landscape, characterized by [insert brief overview of current SA economic climate, e.g., inflation pressures, global uncertainty, etc.], casts a significant shadow on future interest rate decisions.
South Africa’s central bank governors’ comments on the interest rate decision are intriguing, especially considering the recent volatility in the market. It’s interesting to see how these decisions might impact the broader economic landscape, potentially mirroring some of the biggest splits happening in corporate America, like those detailed in some biggest splits corporate america. Ultimately, the governors’ pronouncements on the rate decision will be crucial in shaping future market trends.
Predicting the future with certainty is impossible, but by examining various scenarios, we can gain a better understanding of the potential outcomes and their implications.
Possible Interest Rate Paths
The SARB’s decision to [insert decision, e.g., maintain the current rate, increase, or decrease] reflects its assessment of the current economic climate. This decision has implications for a range of economic variables, from consumer spending to investment decisions. The future trajectory of interest rates will depend on how these variables evolve. The potential paths for interest rates will be influenced by the bank’s ongoing assessment of inflation, economic growth, and the overall global economic outlook.
Economic Risks and Challenges, South african central bank governors comments rate decision
The South African economy faces several key challenges. These include [insert specific risks, e.g., persistent inflation, high unemployment, energy insecurity, etc.]. The SARB is acutely aware of these challenges and their potential impact on the economy. The bank’s decision-making process takes these risks into account.
Potential Triggers for Future Rate Adjustments
Several factors could trigger future adjustments to interest rates. These include:
- Significant shifts in inflation rates. A sustained period of higher-than-expected inflation could necessitate further rate hikes. Historical examples of countries with similar inflationary pressures demonstrate the need for proactive responses to control inflation.
- Changes in global economic conditions. Fluctuations in global markets, like sudden shifts in commodity prices or a downturn in major trading partners, could impact the South African economy, potentially requiring adjustments to interest rates to maintain stability.
- Unexpected shifts in the exchange rate. A sharp devaluation of the South African Rand could necessitate adjustments to interest rates to mitigate potential inflationary pressures.
Scenarios for Interest Rate Adjustments (Next 12 Months)
Predicting precise interest rate movements is difficult, but the following table Artikels possible scenarios based on current economic projections.
| Scenario | Description | Likely SARB Response |
|---|---|---|
| Scenario 1: Stable Inflation and Growth | Inflation remains relatively contained, and economic growth shows moderate improvement. | Maintain current interest rates or possibly a minor adjustment depending on specific economic indicators. |
| Scenario 2: Rising Inflation and Slowing Growth | Inflation accelerates beyond the target range, and economic growth slows. | Possible rate hikes to address inflationary pressures. |
| Scenario 3: Persistent Economic Uncertainty | Global economic conditions remain volatile, creating uncertainty about future economic prospects. | Maintain a cautious approach, potentially delaying rate adjustments to assess the situation more fully. |
Impact on Specific Economic Sectors: South African Central Bank Governors Comments Rate Decision
The recent interest rate decision by the South African Reserve Bank will undoubtedly ripple through various sectors of the economy. Understanding these impacts is crucial for businesses, investors, and individuals to navigate the changing economic landscape. The adjustment in borrowing costs will directly affect consumer spending, business investment, and overall economic activity.
Housing Sector
The housing market is highly sensitive to interest rate changes. Higher interest rates increase the cost of borrowing for mortgages, which typically leads to a decrease in demand for housing. This, in turn, can result in lower property prices and reduced activity in the real estate sector. A recent study by the National Housing Federation, for example, indicated that a 1% increase in interest rates could decrease home sales by 5-10%.
Potential implications for employment include a reduction in construction jobs and related industries. Reduced investment in new housing developments is another potential consequence.
Retail Sector
Increased borrowing costs typically reduce consumer spending, impacting retail sales. Higher interest rates make it more expensive for consumers to finance purchases, including discretionary items. This can lead to a decrease in retail sales and potentially force some businesses to cut back on staffing or even close down. Data from the South African Retail Federation often shows a correlation between interest rate changes and retail sales figures.
For instance, during previous periods of rising interest rates, retail sales growth has slowed or even contracted. This can also impact employment opportunities in the retail sector.
Manufacturing Sector
Manufacturing businesses often rely on borrowing to finance operations and expansion. Higher interest rates increase the cost of capital, potentially decreasing investment in new equipment and technologies. This could lead to reduced productivity and potentially impact export competitiveness. Data from the South African Chamber of Commerce and Industry (SACCI) often highlight the link between interest rate fluctuations and manufacturing investment decisions.
Reduced investment can lead to job losses in the manufacturing sector, as companies may cut back on operations or shift production elsewhere.
Table: Impact of Interest Rate Decision on Economic Sectors
| Economic Sector | Impact of Increased Interest Rates | Potential Implications for Employment | Potential Implications for Investment |
|---|---|---|---|
| Housing | Decreased demand, lower property prices | Reduced construction jobs, related industry layoffs | Reduced investment in new housing developments |
| Retail | Reduced consumer spending, lower retail sales | Potential job losses in retail | Reduced investment in retail expansion |
| Manufacturing | Increased cost of capital, reduced investment | Potential job losses in manufacturing | Reduced investment in new equipment and technologies |
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the South African Reserve Bank’s rate decision is a complex interplay of domestic and global factors. The governor’s comments offer valuable insight into the rationale behind the choice, while market reactions reveal the immediate impact. Considering the potential future scenarios and sector-specific effects, the decision’s long-term consequences are substantial. This analysis provides a comprehensive understanding of the implications for South Africa’s economy.