Stablecoins step toward mainstream could shake up parts us treasury market, potentially disrupting traditional financial instruments and demanding a re-evaluation of the US Treasury’s operations. These digital tokens, designed to maintain a stable value pegged to fiat currencies, are rapidly gaining traction. Different types of stablecoins, backed by various assets, offer varying degrees of stability and security. This article delves into how these innovations might affect the US Treasury market, examining current practices, potential disruptions, and regulatory considerations.
The current US Treasury market, with its complex infrastructure and regulatory framework, faces a crucial juncture. The emergence of stablecoins brings both exciting opportunities and considerable challenges. This analysis will explore how stablecoins could revolutionize government transactions, from speed and cost to security. We’ll also investigate the global implications of this technological shift, considering international regulatory landscapes and potential competitive advantages or disadvantages for the US.
Introduction to Stablecoins and their Potential Impact
Stablecoins are cryptocurrencies designed to maintain a stable value pegged to a fiat currency, like the US dollar, or a commodity like gold. They function as digital representations of traditional money, enabling faster and potentially cheaper cross-border transactions. Their growing popularity stems from the desire for a more efficient and accessible financial system, challenging the status quo of traditional banking.The core function of stablecoins is to mitigate the volatility inherent in cryptocurrencies.
This stability attracts users who are uncomfortable with the price fluctuations of Bitcoin or Ethereum, allowing them to use digital assets without the risk of significant losses. This also opens doors for broader adoption and usage across diverse financial applications.
Types of Stablecoins and Their Underlying Assets
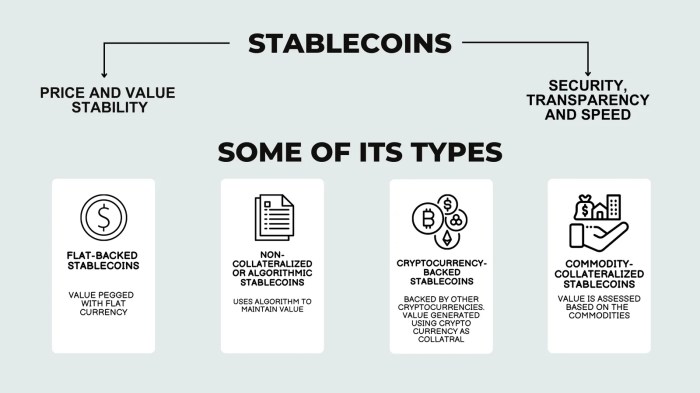
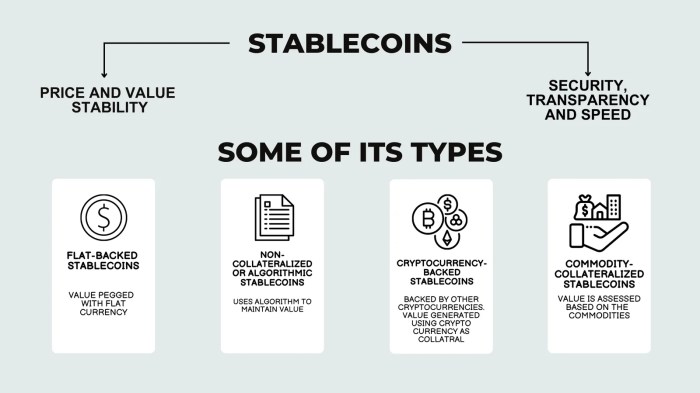
Stablecoins are categorized based on their backing mechanisms. Some stablecoins are fully backed by reserves of fiat currency held in bank accounts. Others are collateralized by other cryptocurrencies, or use a system of algorithmic mechanisms to maintain their value. Examples include:
- Fiat-backed stablecoins: These stablecoins are the most straightforward. They maintain their value by holding reserves of fiat currency, often in regulated bank accounts, mirroring traditional money. Examples include USDT and USDC.
- Crypto-collateralized stablecoins: These stablecoins are backed by a basket of other cryptocurrencies as collateral. The value of the collateral must exceed the value of the stablecoin. This approach can be more susceptible to volatility in the underlying crypto market.
- Algorithmic stablecoins: These stablecoins rely on complex algorithms to maintain their value. These algorithms often involve mechanisms to automatically adjust the supply of the stablecoin to match demand and maintain its peg to the target currency. An example is the TerraUSD (UST) stablecoin.
Potential Disruption of Traditional Financial Instruments
Stablecoins could potentially disrupt various traditional financial instruments. They could facilitate cheaper and faster cross-border payments, reducing transaction costs and time compared to traditional wire transfers. They could also enable new financial products and services that leverage the decentralized nature of blockchain technology, creating novel investment opportunities. Furthermore, they might lead to greater financial inclusion by providing access to financial services to unbanked populations.
Comparison of Traditional Payment Methods vs. Stablecoin Transactions
| Feature | Traditional Payment Methods | Stablecoin-Based Transactions |
|---|---|---|
| Speed | Variable, often days for international transfers | Potentially near-instantaneous |
| Cost | Significant fees, often based on transaction amount and location | Potentially lower fees, often based on network usage |
| Security | High, regulated by financial institutions | High, relying on cryptographic security, but potential risks exist |
The Current State of the US Treasury Market
The US Treasury market, a cornerstone of the global financial system, is a complex and vital arena for borrowing and lending. It underpins the US economy, providing funding for government operations and influencing interest rates across the world. Understanding its current state is crucial for comprehending the potential impact of new financial instruments like stablecoins.The market’s stability and efficiency are directly linked to the government’s ability to manage its debt effectively and to the confidence investors have in the US economy.
This, in turn, has a ripple effect on everything from consumer lending to international trade. This discussion delves into the key players, regulatory framework, infrastructure, and historical evolution of this critical market.
Key Players and Institutions
The US Treasury market is a vast network, involving numerous participants. The US Department of the Treasury acts as the central issuing authority for US Treasury securities, managing the national debt. Major commercial banks, investment banks, and broker-dealers facilitate the buying and selling of these securities. Hedge funds and institutional investors also play significant roles, often holding large portfolios of Treasury bonds.
Foreign central banks are also significant players, often holding substantial amounts of US Treasury securities as part of their reserves.
Regulatory Framework
The US Treasury market is governed by a complex regulatory framework, primarily established by the US Department of the Treasury itself, but also encompassing regulations from other agencies like the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC) and the Federal Reserve. These regulations aim to ensure market integrity, transparency, and investor protection. Specific regulations address the issuance, trading, and reporting of Treasury securities.
The regulatory landscape constantly evolves to adapt to changing market conditions and emerging risks.
Infrastructure and Processes
The US Treasury market boasts a sophisticated infrastructure, enabling efficient trading and settlement. Electronic trading platforms are widely used, facilitating real-time transactions among market participants. Clearinghouses play a crucial role in ensuring the smooth execution and settlement of trades. This infrastructure is vital to the market’s operational efficiency and its ability to handle massive volumes of transactions.
The processes involve rigorous verification procedures to maintain transparency and accountability.
Historical Overview
The US Treasury market has evolved significantly over time. Initially, it relied on more manual processes. The advent of electronic trading platforms and sophisticated financial instruments has streamlined operations and expanded market participation. Historically, events like the 2008 financial crisis have highlighted the importance of a robust regulatory framework and stable infrastructure in maintaining market resilience. The evolution reflects a continuous adaptation to technological advancements and changing economic landscapes.
Major Components of the US Treasury Market
| Component | Description |
|---|---|
| US Department of the Treasury | Issues Treasury securities, manages the national debt. |
| Commercial Banks | Facilitate trading and provide services to investors. |
| Investment Banks | Underwrite and trade securities, providing advisory services. |
| Broker-Dealers | Match buyers and sellers of Treasury securities. |
| Hedge Funds | Invest in Treasury securities, often as part of broader portfolios. |
| Institutional Investors | Hold significant portfolios of Treasury securities, like pension funds and mutual funds. |
| Foreign Central Banks | Hold substantial reserves in US Treasury securities. |
| Electronic Trading Platforms | Enable real-time trading and facilitate transactions. |
| Clearinghouses | Ensure the smooth execution and settlement of trades. |
Potential Disruptions and Opportunities
Stablecoins, with their promise of price stability, are poised to significantly impact the US Treasury market. Their potential to streamline transactions and reduce risks presents exciting opportunities, but also introduces complex challenges. Understanding these potential disruptions and opportunities is crucial for navigating the evolving financial landscape.The increasing adoption of stablecoins could revolutionize how the US Treasury manages its vast financial operations.
From facilitating faster payments to potentially lowering transaction costs, the implications are multifaceted and require careful consideration. This section explores the potential benefits, drawbacks, and risks associated with integrating stablecoins into the US Treasury’s infrastructure.
Potential Alterations in Treasury Market Operations
Stablecoins, by their nature, offer the potential for near-instantaneous and lower-cost transactions. This could impact the current Treasury market infrastructure, which relies on a network of banks and financial intermediaries. The speed and efficiency of stablecoin transactions could lead to more rapid settlements of government obligations and improved cash management. This could potentially lead to significant cost savings for the US government, as it reduces the time and resources required for traditional settlement processes.
Potential Benefits for the US Treasury
The introduction of stablecoins into Treasury operations could provide several advantages. Faster settlement times reduce the risk of liquidity shortages. Improved efficiency can lower transaction costs, freeing up resources for other government initiatives. The potential for greater transparency and traceability in transactions could enhance public trust in government operations. Furthermore, stablecoins could provide a more accessible payment mechanism for Treasury operations, reaching a wider range of stakeholders.
Potential Drawbacks and Risks
The integration of stablecoins also presents potential drawbacks and risks. The stability of the underlying asset backing the stablecoin is crucial. If the backing asset experiences a significant devaluation, it could undermine the stablecoin’s value and potentially destabilize the Treasury market. Regulatory uncertainty surrounding stablecoins remains a significant concern. Clear guidelines and oversight mechanisms are essential to mitigate the risks associated with their use.
Cybersecurity vulnerabilities are also a concern. The potential for malicious attacks on stablecoin networks could disrupt government transactions and compromise sensitive data.
The potential for stablecoins to become more mainstream is definitely intriguing, and it could shake up parts of the US treasury market. While that’s happening, it’s worth noting the exciting MLB roundup, where Eugenio Suárez and the D-backs absolutely dominated the Mariners. This impressive performance highlights the incredible athleticism in the sport, which is a welcome distraction from the complex financial considerations of stablecoins.
Ultimately, though, the widespread adoption of stablecoins still holds the potential to significantly reshape the treasury market.
Efficiency Comparison: Stablecoins vs. Traditional Methods
Traditional Treasury operations rely heavily on the banking system, which can introduce delays and costs. Stablecoins, in contrast, have the potential to streamline transactions, reducing settlement times and transaction fees. Real-time payments enabled by stablecoins could significantly improve the efficiency of government operations, allowing for quicker disbursement of funds and more timely responses to economic needs. This speed and efficiency, however, need to be carefully weighed against the potential risks.
Potential Impacts on Various Sectors within the US Treasury Market
| Sector | Potential Impact of Stablecoins |
|---|---|
| Payment Systems | Faster, cheaper, and potentially more accessible payments |
| Debt Management | Potentially faster and more efficient debt issuance and redemption |
| Cash Management | Reduced liquidity risk and potentially lower transaction costs |
| Government Operations | Improved efficiency and potentially greater transparency |
| Financial Intermediaries | Disruption of existing business models; need for adaptation and innovation |
Regulatory Landscape and Policy Implications
The burgeoning stablecoin market presents a complex regulatory challenge for the US Treasury. Current frameworks, primarily designed for traditional financial instruments, may not adequately address the unique characteristics of stablecoins, potentially leading to vulnerabilities in the financial system. Adapting existing regulations and potentially introducing new policies will be crucial to ensuring the safe and stable integration of stablecoins into the financial landscape.
Existing Regulatory Frameworks
Currently, stablecoins fall under the purview of various regulatory bodies, including the Federal Reserve, the Securities and Exchange Commission (SEC), and the Commodity Futures Trading Commission (CFTC). However, the regulatory treatment of stablecoins remains somewhat ambiguous. Some stablecoins are classified as securities, while others are considered commodities or even as a form of money, depending on their structure and functionalities.
This ambiguity creates uncertainty and potential regulatory arbitrage.
Adapting Existing Regulations
Existing regulations, designed for traditional financial instruments, need adjustments to encompass the unique features of stablecoins. This involves clearly defining the regulatory categorization of various stablecoin types and their associated risks. Furthermore, enhanced oversight mechanisms are needed to ensure transparency, prevent illicit activities, and maintain the stability of the financial system. Specific requirements may include enhanced reporting requirements for stablecoin issuers, stricter capital adequacy standards, and more rigorous stress testing protocols.
Potential for New Regulations
The need for new regulations is also evident. For instance, the establishment of specific licensing requirements for stablecoin issuers and the creation of a regulatory sandbox for innovative stablecoin technologies could be beneficial. Furthermore, specific regulations for stablecoin issuers’ reserves, focusing on the proportion and quality of assets held, might be necessary. This would aim to mitigate the risk of systemic instability.
Impact on Financial Policies
Stablecoin adoption could significantly impact existing financial policies. For example, the use of stablecoins for international payments could potentially challenge the dominance of traditional fiat currencies. The use of stablecoins for cross-border transactions could alter international trade patterns and necessitate the adaptation of existing international financial regulations. The integration of stablecoins into treasury operations, as mentioned earlier, would require careful consideration to ensure stability and security.
Potential Policy Adjustments
A well-structured regulatory framework is essential to ensure the safety and stability of the financial system in the face of stablecoin integration.
- Clearer Regulatory Classification: Establishing a clear regulatory framework for different types of stablecoins, including those pegged to fiat currencies, crypto assets, or other assets, is crucial to prevent regulatory arbitrage and ensure transparency.
- Enhanced Reserve Requirements: Imposing stricter reserve requirements for stablecoin issuers, mandating the holding of high-quality liquid assets, can significantly reduce the risk of runs and instability.
- Robust Oversight Mechanisms: Establishing robust oversight mechanisms for stablecoin issuers, including regular audits and reporting requirements, can promote transparency and accountability.
- International Collaboration: Promoting international collaboration and harmonization of regulations is vital to ensure a consistent and predictable regulatory environment for stablecoins in cross-border transactions.
- Consumer Protection Measures: Implementing robust consumer protection measures to safeguard users from potential risks associated with stablecoin use, such as fraud or scams, is paramount.
Technical and Infrastructure Considerations
Stablecoins, promising a more efficient and accessible financial system, require robust technical infrastructure. This includes the mechanisms for maintaining their pegged value to a fiat currency, the security protocols to prevent fraud and hacks, and the scalability to handle large transaction volumes. The seamless integration of these new technologies into existing financial systems, particularly the Treasury market, presents both opportunities and challenges.The technical underpinnings of stablecoins are multifaceted.
They rely on sophisticated algorithms, smart contracts, and secure communication channels to maintain their value and facilitate transactions. Understanding these intricate systems is crucial for assessing their potential impact on the Treasury market.
Stablecoin Transaction Mechanics
Stablecoins utilize various methods to maintain their peg to fiat currencies. Some rely on reserves held in stable assets like government bonds or cash, while others use algorithmic mechanisms to adjust supply and demand. These mechanisms are complex and require careful design to prevent instability. Examples of different stablecoin protocols highlight the variety of approaches.
Infrastructure Changes for Integration
The integration of stablecoins into existing Treasury platforms necessitates significant infrastructure upgrades. These platforms need to be capable of handling the unique characteristics of stablecoin transactions, including the potential for high-volume, near-instantaneous payments. This requires modifications to existing payment systems and potentially the development of new, specialized tools. Furthermore, the current infrastructure often lacks the necessary security measures to effectively protect stablecoin transactions.
This is a critical area requiring robust security measures.
Security Concerns in Stablecoin Transactions
Security is paramount in the stablecoin ecosystem. Hacking, fraud, and manipulation pose significant risks. Issues like liquidity risks, reserve mismanagement, and vulnerabilities in smart contracts can lead to substantial losses. These risks are not unique to stablecoins but represent significant concerns in the broader cryptocurrency landscape. Current and historical events in the cryptocurrency space illustrate the need for enhanced security protocols.
Solutions for Stablecoin Security
Robust security protocols are essential to mitigate risks. These include multi-signature wallets, advanced encryption techniques, and regular audits of smart contracts. Increased transparency and accountability in stablecoin operations are also critical to building trust and reducing vulnerabilities. Solutions often involve incorporating industry best practices and regulatory oversight.
Integrating Stablecoins into Treasury Platforms
Integrating stablecoins into Treasury platforms presents opportunities for efficiency and innovation. For example, treasury operations can leverage the speed and cost-effectiveness of stablecoin transactions for certain payments. Stablecoins can be used for settling international transactions, enabling quicker and more cost-effective cross-border payments. Implementing stablecoins could lead to significant improvements in Treasury operations.
Global Context and International Implications: Stablecoins Step Toward Mainstream Could Shake Up Parts Us Treasury Market
Stablecoins, with their promise of price stability and cross-border transactions, are rapidly gaining traction globally. This surge in adoption has significant implications for the US Treasury market, potentially altering its role in international finance and requiring a nuanced understanding of the global landscape. The US Treasury’s existing frameworks may need adaptation to remain relevant in this evolving financial environment.
Global Adoption of Stablecoins
Stablecoins are experiencing significant adoption across various jurisdictions. Their use cases extend beyond simple payments, potentially impacting cross-border trade, remittances, and even investment strategies. This widespread adoption highlights the growing need for a globally harmonized regulatory framework to ensure stability and prevent potential risks. The sheer volume of transactions facilitated by stablecoins could potentially challenge the existing dominance of traditional financial instruments.
Global Perspective on Stablecoin Regulation
A fragmented regulatory landscape across different countries presents a significant challenge to the global adoption of stablecoins. While some jurisdictions are proactively developing frameworks, others remain hesitant or lack clarity on their regulatory approach. This divergence in regulatory stances can lead to inconsistencies in the application of rules, making it challenging for stablecoin issuers to operate effectively across borders.
Different approaches to stablecoin regulation, from outright bans to permissive frameworks, underscore the need for international cooperation to ensure a stable and predictable global environment for stablecoins.
Potential Competitive Advantages or Disadvantages for the US Treasury Market
The US Treasury market, with its deep liquidity and established infrastructure, could potentially face competition from stablecoin-based systems. The ease of cross-border transactions facilitated by stablecoins could alter the dynamics of international capital flows, affecting the demand for traditional US Treasury securities. However, the US Treasury’s strong reputation and established market position could provide a competitive advantage. The ability to leverage existing infrastructure and adapt to the evolving landscape will be crucial.
Stablecoins’ move toward mainstream adoption could significantly impact parts of the US treasury market. Recent protests at Columbia University’s Butler Library, involving police arrests and political figures like former President Trump, as detailed in this explainer, highlighting the complexities of current events , offer a fascinating parallel. Ultimately, the changing landscape of stablecoins and their integration into financial systems could reshape how the treasury manages assets and liabilities.
Interplay Between Stablecoins and International Financial Systems
Stablecoins are increasingly integrated into international financial systems, enabling faster and cheaper cross-border payments. Their integration could potentially disrupt traditional remittance channels, potentially impacting the role of banks and other financial intermediaries in international transactions. The emergence of stablecoins necessitates a reassessment of existing international financial regulations and mechanisms to ensure their safe and effective integration.
The rise of stablecoins and their potential move into the mainstream could significantly disrupt certain parts of the US treasury market. This shift, while potentially shaking things up, is sadly overshadowed by the alarming news of death threats against Ecopetrol CEO, who bravely spoke out against discrimination. This is deeply concerning, and highlights the urgent need for acceptance and safety.
The situation with stablecoins still needs careful consideration, but this kind of societal progress is more important than any market fluctuation. Hopefully, this incident at Ecopetrol ( ecopetrol ceo denounces death threats over sexual orientation ) will bring needed attention to the dangers of prejudice and promote understanding. Ultimately, the stablecoin’s impact on the treasury market is still a complex issue that needs thorough analysis.
Comparative Analysis of Stablecoin Adoption
| Country | Regulatory Approach | Level of Adoption | Key Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Developing regulatory frameworks, primarily focused on security and consumer protection. | Growing adoption in fintech and payment sectors. | Balancing innovation with risk mitigation. |
| China | Generally restrictive, with a focus on regulatory control over cryptocurrencies. | Limited or controlled adoption. | Lack of clear guidelines for stablecoins. |
| European Union | Seeking to harmonize regulations across member states. | Growing interest, but still evolving. | Complexity in balancing innovation with consumer protection. |
| Japan | Generally supportive of innovation, with a focus on transparency and security. | Increasing interest and potential for adoption. | Potential for regulatory ambiguity. |
This table illustrates the varied approaches to stablecoin regulation across different countries. The regulatory environment plays a critical role in determining the level of stablecoin adoption. The differences in regulatory approaches highlight the importance of international cooperation to create a more consistent and predictable global framework for stablecoins.
Case Studies and Examples
Stablecoins, designed for their inherent stability, are rapidly gaining traction across various global markets. Their potential impact on the US Treasury market is substantial, and understanding how they function elsewhere offers valuable insights into possible future scenarios. Examining successful implementations, alongside potential pitfalls, provides a more comprehensive understanding of the implications for the US.
Stablecoin Usage in Other Markets
Stablecoins have already proven their utility in several markets, demonstrating both advantages and challenges. These examples range from facilitating cross-border payments to providing access to financial services in underserved communities.
Cross-Border Payments and Remittances
Stablecoins offer significant advantages in cross-border transactions. Reduced transaction fees and faster settlement times compared to traditional methods, are key factors in their growing appeal. For example, remittances sent via stablecoin platforms have shown potential for reducing costs and increasing efficiency. These lower costs could potentially impact how international trade is conducted in the future.
Financial Inclusion and Access to Capital, Stablecoins step toward mainstream could shake up parts us treasury market
Stablecoins can potentially enhance financial inclusion by providing access to capital markets for those previously excluded. This is particularly relevant in developing economies, where traditional banking systems may be limited. For instance, in certain emerging markets, stablecoins have been used to facilitate micro-lending, enabling individuals and small businesses to access credit more readily. This trend may lead to more efficient capital allocation.
Decentralized Finance (DeFi) Applications
The DeFi ecosystem utilizes stablecoins extensively. Stablecoins are crucial for maintaining value stability in various DeFi applications, such as lending and borrowing platforms. For instance, platforms using stablecoins allow users to access financial products and services in a transparent and often more accessible manner. This innovative approach to finance may encourage new financial products and services.
Examples of Stablecoin Transactions
Stablecoins have been used in diverse financial transactions. They have facilitated peer-to-peer (P2P) payments, enabling faster and more efficient transfers of value. Moreover, stablecoins are utilized in decentralized exchanges (DEXs), where trading occurs directly between users without intermediaries. This direct trading can disrupt existing financial intermediaries and potentially impact the US Treasury market.
Relationship to the US Treasury Market
The successful adoption of stablecoins in other markets suggests the potential for similar developments in the US. If stablecoins gain widespread acceptance, it could lead to changes in how the US Treasury manages its financial instruments, such as government bonds. Increased competition from stablecoin-based financial services may affect the demand for traditional financial instruments. This could influence government bond yields and interest rates.
Impact on Potential US Treasury Market Shifts
The adoption of stablecoins could result in a shift in the way the US Treasury market functions. Increased competition from stablecoin-based financial services may affect the demand for traditional financial instruments. This could influence government bond yields and interest rates. Lower transaction costs and faster settlement times may prompt a reevaluation of current Treasury market practices.
Key Takeaways for the US Treasury Market
- Stablecoin adoption in other markets demonstrates potential for disrupting traditional financial systems.
- Lower transaction costs and faster settlement times are key advantages of stablecoins.
- Stablecoins may offer enhanced financial inclusion and access to capital.
- The US Treasury market may need to adapt to maintain its relevance in a world with stablecoins.
- Potential changes in demand for government bonds and interest rates warrant consideration.
Closing Notes
In conclusion, the integration of stablecoins into the US Treasury market presents a significant opportunity for efficiency and innovation. However, it also brings forth potential risks and challenges that need careful consideration. The US Treasury must adapt its infrastructure, regulations, and policies to navigate this evolving landscape effectively. This article has explored the many facets of this transformation, highlighting the need for a proactive and well-informed approach to harnessing the potential of stablecoins while mitigating potential risks.

