Trump european union tariff threat trade war concerns – Trump’s European Union tariff threat, sparking trade war concerns, casts a long shadow over global commerce. This complex issue delves into the historical US-EU trade relationship, exploring past disputes, Trump’s unique trade policies, and the potential impact on specific industries. The potential consequences of a trade war, including economic ramifications, political implications, and alternative dispute resolution methods, are also examined.
Understanding this situation requires a deep dive into the intricate web of economic interdependence between the US and EU, and a look at public opinion and potential negotiation scenarios.
The historical context reveals a complex relationship, marked by periods of cooperation and conflict. Trump’s approach to international trade, contrasting with previous administrations, is a key factor in understanding the current tensions. Analyzing the potential impacts on various sectors, from agriculture to automobiles, helps to visualize the potential consequences. Examining alternative dispute resolution mechanisms, including the roles of international organizations, offers a glimpse at possible solutions to this escalating trade conflict.
Historical Context of US-EU Trade Relations: Trump European Union Tariff Threat Trade War Concerns

The United States and the European Union, despite their political differences, have a long and complex history of trade interactions. This relationship has been defined by periods of cooperation and significant disputes, driven by shifting economic landscapes and evolving policy priorities. From early agreements to contemporary trade wars, understanding this history is crucial to appreciating the present dynamics and predicting potential future trajectories.The foundation of the US-EU trade relationship was laid in the post-World War II era.
The need for economic recovery and the desire to avoid future conflicts spurred the development of international trade organizations and agreements. This period saw the rise of multinational corporations and the growth of global supply chains, further intertwining the economies of the US and EU.
Evolution of Tariffs and Trade Disputes
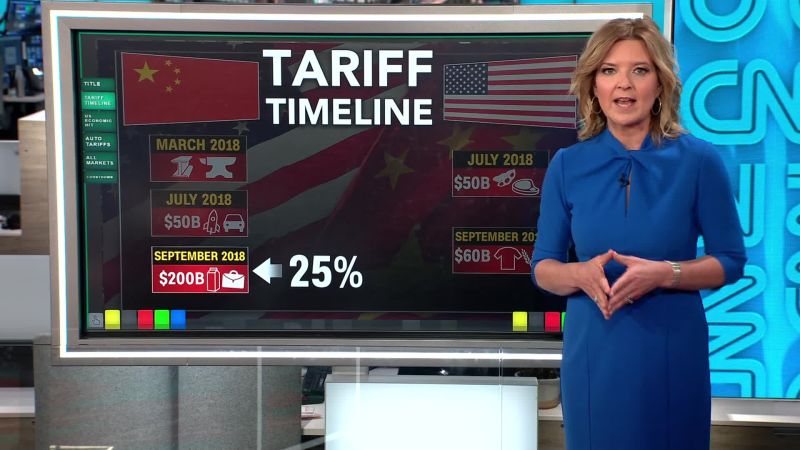
The evolution of tariffs and trade disputes between the US and EU has been marked by a series of agreements, negotiations, and disagreements. Early post-war agreements focused on reducing tariffs and fostering greater economic integration. However, disagreements over specific trade policies and practices have persisted throughout the years. The imposition of tariffs, often retaliatory, has been a recurring theme in the relationship.
These disputes highlight the challenges of balancing national interests with global economic interdependence.
Key Policy Differences and Potential Sources of Conflict
Key policy differences between the US and EU often stem from varying approaches to industrial support, environmental regulations, and labor standards. For example, the US has historically favored policies that encourage domestic production and sometimes take a more protectionist stance, while the EU tends to emphasize regulations aimed at protecting the environment and labor standards. These differences can create friction, particularly in areas like agricultural subsidies and industrial standards.
Impact of Past Trade Wars on the Global Economy
Past trade wars, including those involving the US and other nations, have demonstrated a demonstrably negative impact on global trade. The disruption of supply chains, uncertainty about future trade policies, and the rise in prices for consumers have been recurring consequences. The 1930 Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, which significantly increased tariffs on imported goods, is a historical example of the negative consequences of protectionist trade policies.
Economic Interdependence between the US and EU
The US and EU economies are highly interdependent. The EU is a significant market for US exports, and vice versa. A disruption in trade between the two could have significant repercussions for both economies. The EU is a major investor in the US, and US companies have extensive operations within the EU. This interconnectedness highlights the importance of maintaining stable and predictable trade relations.
The flow of goods, services, and capital between the two regions is a testament to the significant economic interdependence.
Trump’s Trade Policies and Stances Towards the EU
Donald Trump’s approach to international trade was characterized by a significant departure from previous US administrations. His policies, particularly those targeting the EU, were often framed by a belief in renegotiating existing trade agreements and imposing tariffs to protect American industries and jobs. This approach sparked considerable debate and resulted in trade tensions with key allies, including the EU.Trump’s trade policies were driven by a combination of economic nationalism and a belief in the power of bilateral negotiations.
He often argued that existing trade agreements were disadvantageous to the United States, and that tariffs were a necessary tool to address these imbalances. His rhetoric often emphasized the need for fairer trade deals and the importance of protecting American interests.
Trump’s Specific Policies Towards the EU
Trump’s administration implemented tariffs on various EU goods, including steel and aluminum. These tariffs were justified on national security grounds, though they were challenged in international forums. His administration also initiated renegotiation efforts for the Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) agreement.
Trump’s Rhetoric and Public Statements
Trump frequently criticized the EU’s trade practices, particularly its agricultural subsidies. His public statements often emphasized the need for the EU to reduce trade barriers and provide a level playing field for American businesses. He frequently used strong rhetoric, often threatening further tariffs or other trade actions. A prominent example was his repeated use of Twitter to express his stance on EU trade, often with forceful language and aggressive tone.
Key Reasons Behind Trump’s Actions
Several factors likely motivated Trump’s actions regarding EU trade. A key concern was perceived unfair trade practices by the EU, including agricultural subsidies. Furthermore, a desire to protect American industries and jobs was a recurring theme in his approach to trade. The belief that existing trade agreements were detrimental to the US economy was another important driving force.
Potential Motivations Behind Tariff Threats
Trump’s threats of tariffs on EU goods likely aimed to pressure the EU to make concessions in trade negotiations. The objective was likely to achieve better trade terms for the US, including reduced barriers to American exports and improved market access. These threats also served as a means of signaling the US administration’s determination to assert its interests in international trade.
The potential for retaliation from the EU was undoubtedly considered by the administration.
Comparison to Previous US Administrations
Trump’s approach to trade differed significantly from that of previous US administrations. Previous administrations generally favored multilateral trade agreements and a more cooperative approach to international trade relations. Trump’s emphasis on bilateral negotiations and the use of tariffs as a primary tool for achieving trade objectives marked a substantial departure from past practice. For example, the Obama administration’s focus on the Trans-Pacific Partnership (TPP) and other multilateral agreements stood in stark contrast to Trump’s approach.
Impact of Tariff Threats on Specific Industries
The potential for trade wars, particularly between the US and the EU, carries significant implications for various industries. Tariff threats disrupt established supply chains, increase costs for businesses, and ultimately affect consumers. The consequences can be far-reaching, impacting not only the directly targeted sectors but also related industries and global markets.
US Agricultural Industries
US agricultural exports to the EU face significant vulnerability to tariffs. Major agricultural products like soybeans, corn, and certain meats are significant components of the US agricultural economy. Tariffs imposed by the EU could dramatically reduce demand for these products, leading to lower prices and potential losses for farmers. The resulting economic impact could cascade to rural communities that rely on agricultural employment.
This scenario echoes past trade disputes where similar retaliatory actions have caused considerable distress within the affected sectors.
EU Manufacturing Industries
The EU’s manufacturing sector, particularly in automotive and machinery, is another critical area. Tariffs on US exports could lead to higher costs for European manufacturers sourcing components or finished products from the US. The potential for retaliatory tariffs by the US could result in similar consequences for EU companies operating in the US market. This is a classic case of a trade war’s negative ripple effect, highlighting how interconnectedness in the global economy amplifies the impact of trade disputes.
Automotive Sector
The automotive industry is highly susceptible to trade tensions. Tariffs on vehicle imports and components could lead to significant price increases for consumers. The industry’s complex global supply chains would likely experience disruptions, potentially impacting production capacity and employment. For example, a trade war in the 1930s had a devastating effect on the automotive industry globally. These disruptions often translate into job losses and factory closures.
Potential for Retaliatory Tariffs
The EU’s response to US tariff threats is likely to be a retaliatory tariff imposed on US goods. The specific goods targeted by the EU would likely be selected to maximize economic pressure on the US and minimize harm to the EU’s own industries. The EU’s response is not arbitrary; it is a strategic action aimed at leveling the playing field or protecting its own interests.
The potential for retaliatory tariffs demonstrates the cyclical nature of trade wars, where actions and reactions escalate tensions.
Ripple Effects on Other Global Markets
Trade disputes between major economies have wider implications for the global economy. Tariffs can impact global trade flows, leading to reduced investment, decreased economic growth, and increased uncertainty. This is a crucial aspect of international trade, where the actions of one country can have significant repercussions for others. For example, the 2008 financial crisis was partly fueled by global economic interconnectedness, demonstrating the vulnerability of global markets to localized events.
Impact Comparison Table
| Industry | Potential Impact of Tariffs | Potential for Retaliation | Economic Consequences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agriculture (US) | Reduced demand, lower prices, farm losses | EU tariffs on US agricultural imports | Rural community job losses, decreased farm income |
| Manufacturing (EU) | Increased costs for components/products | US tariffs on EU manufactured goods | Potential job losses, reduced profitability |
| Automotive | Increased prices for consumers, supply chain disruptions | US tariffs on EU vehicle imports | Job losses in factories, reduced production |
Potential Consequences of a Trade War
A trade war between the US and the EU, triggered by tariffs, carries significant risks. The potential repercussions extend far beyond the immediate economic impact, affecting global markets and international relations. This escalating conflict could lead to a domino effect, with other nations retaliating and potentially causing a global recession.
Economic Ramifications
A trade war between the US and the EU would likely result in a contraction of global trade. Businesses would face increased costs due to tariffs and potentially reduced consumer demand as prices rise. Supply chains would be disrupted, affecting the availability of goods and services, and hindering production processes. The automotive industry, for example, heavily reliant on cross-border parts and manufacturing, would experience significant setbacks.
Reduced investment in global markets is another likely consequence. The potential for decreased GDP growth in both regions is substantial.
Political Ramifications
Trade disputes often spill over into broader political tensions. A trade war could erode trust and cooperation between the US and the EU, potentially damaging the transatlantic relationship, which has been a cornerstone of global stability. The erosion of mutual trust could lead to a weakening of international institutions and agreements, hindering efforts to address shared challenges like climate change and security threats.
Historical precedents show that trade conflicts can have far-reaching political implications.
Effects on Global Trade and Investment
A trade war between the US and the EU would significantly disrupt global trade flows. Tariffs imposed on each other’s goods would lead to higher prices for consumers, reduced availability of products, and disruptions to global supply chains. Foreign direct investment (FDI) could decline as businesses become hesitant to operate in an uncertain and politically charged environment. This could have a particularly damaging impact on developing countries that rely on trade with both the US and the EU.
Effects on International Relations and Cooperation
International relations would likely suffer due to the trade war. The dispute could create friction and mistrust between the US and EU, potentially impacting their ability to work together on critical global issues. Reduced cooperation could weaken efforts to address global challenges, such as climate change, pandemics, and international security. The EU’s trade policies have traditionally been based on multilateral cooperation, and a trade war would challenge this approach.
Possible Scenarios and Outcomes
Several scenarios could unfold, each with varying degrees of severity. One scenario involves a protracted trade war with escalating tariffs and counter-tariffs. This could lead to significant economic damage and potentially a global recession. Another scenario involves a more limited trade war, focused on specific sectors. While less severe, it could still have significant consequences for those industries and potentially escalate.
A third scenario involves a negotiated resolution, where both sides agree to reduce or remove tariffs. This outcome would be the most favorable, minimizing the economic and political damage.
Table of Potential Consequences
| Category | Potential Consequences |
|---|---|
| Economic | Reduced global trade, higher prices, supply chain disruptions, reduced investment, decreased GDP growth. |
| Social | Job losses in affected industries, increased cost of living, reduced consumer choice. |
| Political | Erosion of trust between the US and EU, weakening of international institutions, reduced cooperation on global issues. |
Alternative Dispute Resolution Mechanisms
Navigating trade tensions between the US and the EU requires more than just threats and tariffs. Fortunately, a robust system of alternative dispute resolution exists, offering pathways to resolve trade disagreements peacefully and efficiently. These methods, often involving international organizations and established procedures, can be far more effective than escalating to a damaging trade war.
Dispute Settlement Mechanisms Under the WTO
The World Trade Organization (WTO) plays a crucial role in mediating international trade disputes. Its Dispute Settlement Body (DSB) provides a structured process for addressing grievances. This system, established under the WTO agreements, aims to resolve trade disagreements through consultations, panel rulings, and, ultimately, the possibility of authorizing retaliatory measures.
- Consultations: The initial stage typically involves bilateral consultations between the disputing parties. These informal discussions aim to find a mutually agreeable solution. The WTO Secretariat often assists in facilitating these talks. A successful consultation avoids the need for formal proceedings. A good example of this is the resolution of trade disputes between member countries over agricultural subsidies.
A key advantage is its speed and flexibility. However, these consultations can sometimes fail to reach an agreement, leading to more formal procedures.
- Panel Proceedings: If consultations fail, a panel of experts is established to examine the dispute. The panel’s findings are based on the WTO agreements and relevant evidence presented by both sides. The panel’s report is then submitted to the WTO DSB. A significant advantage of this process is its objectivity. However, the process can be lengthy and costly for both sides.
- Appeals: Parties can appeal the panel’s report to the WTO’s Appellate Body. The Appellate Body reviews the panel’s findings, focusing on points of law. This stage ensures a thorough review of the dispute and promotes consistency in the application of WTO rules. However, appeals can further prolong the process and potentially complicate the final outcome.
Role of International Organizations in Mediation
International organizations like the WTO and the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD) can actively facilitate dialogue and mediation between the US and EU. Their expertise in trade regulations, economics, and diplomacy can provide valuable support in finding common ground. The OECD, for instance, often hosts forums and workshops to promote dialogue on trade-related issues between countries.
These organizations offer a neutral platform for discussions, fostering trust and potentially leading to compromises.
Examples of Successful Dispute Resolution
Several instances exist where the WTO dispute settlement mechanism has successfully resolved trade disagreements between member nations. For example, cases involving trade barriers on agricultural products have been resolved through the system, leading to the reduction of tariffs and improved market access. Such outcomes highlight the potential for peaceful resolution of trade conflicts. A key example of the process’s efficacy is the dispute settlement over steel tariffs.
Comparison to a Trade War
A trade war, with its imposition of tariffs and retaliatory measures, creates significant economic uncertainty and can harm businesses and consumers on both sides. In contrast, alternative dispute resolution methods aim to resolve the issues through negotiation and compromise, minimizing the negative impacts on trade and fostering a more stable trading environment.
| Dispute Resolution Method | Steps | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| WTO Dispute Settlement | Consultations, Panel, Appeals | Structured, objective, international backing | Lengthy, costly, potential for deadlock |
| Bilateral Negotiations | Direct talks, compromises | Flexible, tailored to specific needs | Reliance on trust, potential for power imbalances |
Public Opinion and Political Implications
Public perception of trade policies plays a crucial role in shaping political outcomes, particularly in a potential trade war scenario. Public opinion, influenced by economic anxieties and political narratives, can significantly impact the actions of policymakers. Understanding the public sentiment in both the US and the EU is essential for analyzing the potential for political backlash and the likelihood of a trade war escalating.Public opinion often dictates the political climate surrounding trade disputes.
Political leaders, recognizing the importance of public sentiment, may adjust their strategies and tactics accordingly. The potential for political backlash from both sides necessitates a nuanced understanding of the social and economic concerns driving public opinion. The interplay between political leaders and public opinion is often complex, as leaders may try to shape public opinion while simultaneously responding to it.
Public Perception of Trade Policies in the US
US public opinion on trade policy is complex and often influenced by factors such as job security, economic anxieties, and perceptions of unfair trade practices by other countries. A significant portion of the US population may view trade policies as a tool to protect domestic industries and jobs. This perception can be driven by concerns about import competition and its potential impact on domestic employment.
Protectionist sentiments can be amplified by narratives emphasizing national interests and economic self-reliance. Conversely, some segments of the population might support free trade, emphasizing the benefits of global markets and economic interdependence.
Public Perception of Trade Policies in the EU
Public opinion in the EU regarding trade policies is similarly multifaceted. Public concern about fair trade practices, worker rights, and environmental protection can influence attitudes towards trade agreements. Public opinion often reflects the EU’s emphasis on multilateralism and international cooperation in trade. However, anxieties about the impact of imports on domestic industries and jobs may exist, especially in specific sectors.
Trump’s threats of tariffs on EU goods are raising trade war concerns, a complex issue. This economic tension is a reminder of the fragility of global trade relationships, especially when you consider the humanitarian crisis in Gaza, with the recent Israeli airstrikes and the vital aid needed for babies. The ongoing conflict, detailed in this article about Israel Gaza aid babies Netanyahu airstrikes , further complicates the global picture, highlighting the interconnectedness of political and economic issues.
These intertwined challenges create a very challenging backdrop for the potential trade war with the EU.
Concerns regarding the protection of European producers and consumers from unfair competition or practices are often a factor.
Political Ramifications of Potential Trade Conflicts
Potential trade conflicts can have significant domestic and international ramifications. Domestically, political leaders face pressure to respond to public concerns about job losses, economic hardship, and national security. Internationally, such conflicts can strain relationships with trading partners and create instability in global markets. The ripple effects of a trade war can be felt across various sectors, impacting consumers and businesses alike.
Political leaders need to balance the needs of their constituents with the necessity for maintaining a stable international trading environment.
Role of Political Leaders and Public Opinion
Political leaders play a crucial role in shaping trade policies, often responding to public opinion while simultaneously attempting to navigate the complex interplay of domestic and international pressures. Public opinion acts as a powerful force that can influence policy decisions, as demonstrated by past trade conflicts and political campaigns. The decisions of political leaders, in turn, shape public perception and can either mitigate or exacerbate the tensions surrounding trade disputes.
The interplay between public opinion and political leadership is critical in determining the course of trade relations.
Potential for Political Backlash
Political backlash from both the US and the EU is a significant possibility in the event of a trade war. Protectionist measures can lead to economic instability and create political challenges for policymakers. Public anger and disapproval may arise from perceived negative consequences, including job losses, higher prices, and diminished consumer choice. Political leaders need to anticipate and address potential backlash to maintain public support.
Summary of Public Opinion
| Region | General Sentiment | Key Concerns |
|---|---|---|
| US | Mixed, with protectionist sentiment present | Job security, import competition, national interests |
| EU | Concerned about fair trade practices and environmental protection | Impact on domestic industries, worker rights, and consumer protection |
Illustrative Scenarios of Trade Negotiations

Navigating the complexities of international trade often involves delicate negotiations. The potential for both fruitful agreements and damaging disputes is ever-present. Understanding these contrasting outcomes is crucial for anticipating the ramifications of various approaches. Successful trade negotiations can foster economic growth, while failed negotiations can lead to significant economic repercussions.
Successful Trade Agreement Scenario
A successful trade agreement between the US and the EU could involve reciprocal reductions in tariffs on key agricultural products and manufactured goods. Both sides might agree to eliminate certain non-tariff barriers, such as differing product labeling requirements, streamlining customs procedures, and fostering greater transparency in regulatory processes. This could lead to increased exports and imports, stimulating economic activity in both regions.
Trump’s threats of tariffs on EU goods sparked trade war anxieties, but the global economic landscape is more complex than that. The US-China rivalry extends beyond trade, now encompassing a crucial technological race, like the US-China robotics race , which is likely to further complicate international relations. Ultimately, these intertwined conflicts suggest a need for careful diplomacy and nuanced solutions to avoid further escalating trade tensions.
US companies could gain access to larger European markets, while European businesses could benefit from increased US market share. Reduced trade barriers could also encourage investment flows between the two economies.
“A successful US-EU trade agreement would entail reciprocal tariff reductions, streamlined customs procedures, and the elimination of non-tariff barriers, boosting economic growth and investment flows.”
Trade War Scenario, Trump european union tariff threat trade war concerns
A trade war between the US and the EU, triggered by escalating tariffs on various goods, could significantly harm both economies. The imposition of tariffs on key imports and exports would likely result in higher prices for consumers in both regions. This would hurt businesses that rely on imports and exports. Supply chains could be disrupted, leading to shortages of certain products and production delays.
Retaliatory measures by each side could spiral into a prolonged conflict with negative implications for global trade.
Trump’s threat of tariffs on the EU is raising trade war concerns, a pretty serious issue. While all that economic uncertainty is swirling, it got me thinking about the top 10 finest restaurants in the world according to AI. the top 10 finest restaurants in the world according to ai It’s fascinating how algorithms can evaluate culinary experiences.
Hopefully, cooler heads prevail, and these trade tensions don’t completely derail the global economy.
“A trade war initiated by escalating tariffs on US and EU goods would result in higher prices, supply chain disruptions, and potential damage to global trade.”
Factors Influencing Negotiation Success
Several factors influence the success or failure of trade negotiations. These include the political climate in both countries, the negotiating styles of the respective teams, the willingness to compromise, and the economic conditions of each nation. Domestic political pressures can significantly impact a nation’s ability to reach an agreement. A strong desire to protect domestic industries, for example, might make compromise more challenging.
Different Approaches to Trade Negotiations
Different approaches to trade negotiations can lead to varied outcomes. A confrontational approach, characterized by aggressive demands and a reluctance to compromise, is less likely to yield a successful outcome compared to a collaborative approach that emphasizes mutual gain and shared benefits. Understanding the nuances of different negotiating styles is essential for achieving positive results.
“The success of trade negotiations is dependent on various factors, including political climate, negotiating styles, willingness to compromise, and economic conditions. A collaborative approach emphasizing mutual gain is more likely to lead to a successful outcome.”
Illustrative Negotiation Approaches and Outcomes
| Negotiation Approach | Outcome |
|---|---|
| Confrontational | High likelihood of trade war, limited concessions, and potential economic damage. |
| Collaborative | Increased likelihood of a mutually beneficial agreement, leading to increased trade and economic growth. |
| Compromise-Oriented | Potential for a balanced agreement, acknowledging differing interests, and promoting economic stability. |
Visual Representation of Economic Interdependence
The US and EU are deeply intertwined economically, with significant trade flows and investment relationships. Understanding this interdependence is crucial for comprehending the potential ramifications of a trade war. A visual representation can help illustrate the complex web of economic ties, highlighting the potential losses for both sides if trade relations deteriorate.
Illustrative Flow of Goods and Services
The economic relationship between the US and the EU is characterized by a substantial two-way flow of goods, services, and investment. This complex web of transactions is crucial to the prosperity of both regions. A visual representation of this interdependence can be achieved through an infographic, displaying the major exports and imports between the two regions. This infographic could categorize flows by industry sector (e.g., automotive, pharmaceuticals, agricultural products) and by country of origin and destination.
This would highlight the significant volume of trade and investment between the two economies.
Impact on Specific Industries
A potential trade war would undoubtedly have a significant impact on specific industries in both the US and the EU. The infographic should include details on the most impacted sectors, showing the potential reduction in exports and the rise in costs for businesses in these sectors. The visual representation should demonstrate the interdependence by showcasing how supply chains are intertwined, with companies in one region reliant on inputs and components from the other.
Impact on Specific Countries
A map highlighting the countries most impacted by the potential trade conflict is vital. The map should show the volume of trade between US and EU countries, color-coded to illustrate the level of economic interdependence. Darker shades of color could indicate higher volumes of trade and investment, emphasizing the economic vulnerabilities of specific countries that rely heavily on trade with the US and EU.
The map should show a correlation between trade volumes and economic strength of countries, emphasizing that trade conflicts can have disproportionate impacts on smaller, more open economies.
Visualizing Interdependence
To effectively communicate the interconnectedness of the US and EU economies, an infographic is best. The infographic should use various visual elements, such as arrows, charts, and icons, to represent the flow of goods, services, and investment. The use of color-coding can highlight the importance of specific sectors or countries. For example, a chart illustrating the total value of trade between the US and EU countries over a period of time can effectively illustrate the scale of the economic relationship.
The visual should include key data points and labels for clarity.
Illustrative Example: The Automotive Industry
Consider the automotive industry. A significant portion of US and EU automakers depend on parts and components sourced from the other region. Disruptions in trade could result in shortages, production delays, and ultimately, higher prices for consumers. The infographic can show the intricate supply chains, emphasizing how the production of vehicles in both regions is deeply interwoven.
This could be visualized using a network diagram, showing the flow of parts from one country to another. This visualization would clearly demonstrate the impact a trade conflict would have on both the US and EU automotive industries.
Concluding Remarks
In conclusion, the looming threat of a trade war between the US and EU carries significant risks, with far-reaching consequences for global markets. The historical context, Trump’s policies, the potential impact on specific industries, and alternative solutions all contribute to a comprehensive understanding of the situation. The interdependence of the two economies, public opinion, and potential negotiation outcomes further complicate the picture.
Ultimately, navigating this complex issue requires a thorough analysis of the interconnected factors to predict the future of trade between these two giants.