Trump redraws senate map, igniting a firestorm of debate and legal scrutiny. This redistricting effort promises to reshape the political landscape, potentially altering the balance of power in the Senate. We’ll delve into the historical context, political motivations, and potential legal challenges surrounding this controversial redrawing. Expect a comprehensive analysis of the map’s impact on voter turnout, public opinion, and future elections.
The redistricting process in the state involved a complex interplay of political maneuvering and legal considerations. Understanding the historical precedents and legal framework surrounding redistricting is crucial to comprehending the significance of this action. We’ll examine the partisan motivations behind the proposed map, analyzing its potential impact on different demographics and voting patterns.
Background of the Redistricting
Redistricting, the redrawing of electoral district boundaries, is a recurring process in the United States, often sparking controversy and legal challenges. This process, crucial for fair representation, is governed by complex legal and constitutional frameworks. The recent redrawing of Senate maps in a specific state highlights the intricacies involved, requiring a deeper understanding of the historical context, legal precedents, and practical procedures.The redistricting process, especially concerning the Senate, is a complex endeavor rooted in the balance of power between states and the federal government.
This redrawing reflects the constitutional mandate for fair representation and the principle of “one person, one vote.” The process in the affected state exemplifies the practical application of these principles and the potential for disputes and legal challenges.
Historical Overview of Redistricting in the US Senate
Redistricting, a fundamental aspect of American democracy, has a long history, stretching back to the very origins of the nation. Early redistricting practices often mirrored the evolving political landscape and population shifts. The principles of equal representation and the “one person, one vote” doctrine have gradually gained prominence, influencing the evolution of redistricting standards over time.
Trump’s redrawing of the Senate map is definitely grabbing headlines, but it’s also got me thinking about other things in the news. Like, the upcoming Survivor 50 cast! Survivor 50 cast what to know is shaping up to be a major one, and I’m dying to see who’s going to be battling it out. Ultimately, the Senate map reshuffle is still the main event, but this Survivor season is going to be a major distraction.
Legal and Constitutional Basis for Redrawing Senate Maps
The legal and constitutional basis for redrawing Senate maps stems from the Constitution’s mandate for representation. Article I, Section 2, Clause 3 of the Constitution details the apportionment of representatives among the states. Subsequent Supreme Court decisions, such asReynolds v. Sims* (1964), established the principle of “one person, one vote,” significantly impacting redistricting practices. These precedents require districts to be roughly equal in population to ensure fair representation.
Process of Redistricting in the State
The process of redistricting in the affected state typically involves several key steps. First, the state legislature or an independent commission receives the mandate to redistrict. This is often followed by public hearings, opportunities for input from various stakeholders, and a formal process for drafting and approving new district boundaries. Public comments and legal challenges often arise during this period.
The process culminates in the finalization and implementation of the new map.
Different Approaches to Redistricting
Various approaches to redistricting exist, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. Independent commissions, appointed to oversee the process, are designed to reduce partisan influence. Conversely, legislative bodies, where the elected officials draw the districts, can be susceptible to partisan gerrymandering. The choice between these approaches often depends on the specific state’s political climate and legal framework.
Examples of Past Redistricting Controversies in the US
Several past redistricting controversies in the US highlight the potential for disputes. The infamous “Shaw v. Reno” (1993) Supreme Court case, involving North Carolina’s redistricting, brought into focus the issue of racial gerrymandering. This case, and others like it, demonstrate the complexities and controversies inherent in the redistricting process.
Timeline of Events Related to the Redrawing
- Date 1: Initial announcement of the need for redistricting. This often stems from census data reflecting population shifts.
- Date 2: Formation of the redistricting committee or commission, outlining the specific guidelines for the process. This involves the appointment of members and the establishment of rules.
- Date 3: Public hearings and input sessions to allow for public participation and feedback on proposed maps. This includes providing opportunities for residents to express their views on the redistricting plan.
- Date 4: Approval of the final redistricting map by the relevant state legislative body or independent commission. This is the culmination of the redistricting process, where the approved map is formally adopted.
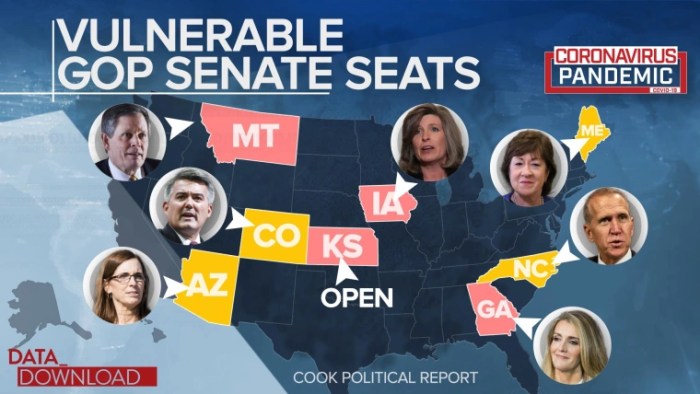
Political Context
The recent redrawing of congressional districts in the state has ignited a firestorm of political debate. This redistricting process, often a contentious affair, is particularly fraught with implications given the current highly polarized political climate and the potential for significant shifts in power. Understanding the motivations, the players, and the historical context is crucial to evaluating the fairness and impact of these changes.This redistricting effort is not merely an administrative task; it’s a deeply political maneuver with the potential to dramatically alter the balance of power in the state legislature and, consequently, the national political landscape.
The proposed map is already generating controversy, raising questions about the fairness and equity of the process. Analyzing the political climate, key players, and voting demographics will provide critical insight into the potential consequences of this redistricting effort.
Political Climate in the State
The state is currently experiencing a highly polarized political environment. Political discourse is often characterized by strong ideological divisions, with little common ground between opposing factions. Public trust in government institutions is relatively low, contributing to the heightened sensitivity surrounding this redistricting process. This climate fuels intense scrutiny of any perceived partisan manipulation, and the process has already been met with allegations of gerrymandering.
Key Political Players
Several key political players have been central to the redistricting process. These include members of the state legislature, particularly those from the majority party, who have significant influence over the process. Furthermore, influential interest groups and advocacy organizations have also played a crucial role in shaping the debate. The governor and other statewide elected officials have also had a role in shaping the discussion and the political narrative surrounding the redistricting effort.
A significant factor is the role of legal experts and consultants, who provide guidance on the legal boundaries of the redistricting process.
Trump redrawing the Senate map is definitely a hot topic, but it’s important to remember the broader context. Recent events in Israel and Gaza, like the aid to babies amidst Netanyahu’s airstrikes, highlighting the complexities of global politics. These issues, alongside the Senate map reshaping, are undeniably connected in the intricate web of current affairs. Ultimately, the Senate map redraw will have significant implications, particularly in this climate.
Partisan Makeup of the State Legislature
The state legislature is currently controlled by the [Party Name] party, holding a majority of seats in both the House and Senate. This partisan advantage significantly influences the redistricting process. The [Party Name] party’s control of the legislative body gives them the power to shape the proposed map in a way that may benefit their political interests. This is a critical factor to consider in evaluating the potential fairness and impact of the redistricting effort.
Motivations Behind the Redrawing of the Map
The motivations behind the redrawing of the map are multifaceted. Advocates for the new map often cite the need for equal representation, addressing population shifts, and ensuring compactness of districts. However, critics argue that the current proposal is driven by partisan considerations, aiming to maximize the number of seats for the controlling party. These criticisms often hinge on the perceived manipulation of district boundaries to favor one political party over another.
Comparison to Previous Versions
Comparing the proposed map to previous versions reveals potential shifts in district boundaries. A comparison will illustrate the differences in district size, shape, and population distribution, which could affect the representation of different demographics and communities. The changes in district lines are a critical component of evaluating the map’s potential impact on voting patterns.
Voting Demographics in Affected Districts
Understanding the voting demographics in the affected districts is essential to assessing the potential impact of the redistricting effort.
| District | Registered Democrats | Registered Republicans | Registered Independents | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 35,000 | 28,000 | 10,000 | 7,000 |
| 2 | 22,000 | 38,000 | 15,000 | 5,000 |
| 3 | 40,000 | 25,000 | 12,000 | 8,000 |
This table provides a snapshot of the voting demographics in selected districts. A comprehensive analysis would include data for all affected districts, considering not only registered voters but also voter turnout rates in past elections.
Potential Legal Challenges
The redrawing of congressional and state legislative districts is a process fraught with potential legal challenges, particularly when accusations of partisan gerrymandering arise. These challenges often involve complex legal arguments and precedents, necessitating a careful examination of the constitutionality of the new map. The courts play a crucial role in determining whether the map complies with the Constitution and established legal standards.This analysis delves into the potential legal battles surrounding the newly proposed redistricting map, focusing on the standards used to evaluate gerrymandering and exploring potential legal precedents.
We will also examine the role of the courts in evaluating the constitutionality of the new map and detail potential legal arguments against it.
Potential Legal Grounds for Challenge
The legal challenge to a redistricting plan often centers on allegations of partisan gerrymandering, violating the Constitution’s guarantee of equal protection under the law and the principle of one person, one vote. Other potential legal challenges may include claims of racial discrimination, violating the Voting Rights Act, or failing to comply with state-specific constitutional requirements.
- Violation of the Equal Protection Clause: Challenges often allege that the new map is designed to favor one political party over another, effectively diluting the voting power of certain groups. This argument is based on the idea that such partisan gerrymandering deprives voters of equal protection under the law.
- Violation of the Voting Rights Act: The Voting Rights Act prohibits voting practices that discriminate against minority voters. Challenges might claim that the new map has the effect of reducing the voting power of minority groups, violating the Act’s provisions.
- Violation of the “One Person, One Vote” Principle: This principle mandates that districts should be roughly equal in population. Challenges may arise if the proposed map creates districts with significantly disparate populations, potentially violating this principle.
Legal Precedents
Numerous legal precedents related to redistricting and gerrymandering have shaped the current landscape. Understanding these precedents is crucial in assessing the potential legal challenges to the proposed map.
- Vieth v. Jubelirer (2004): This Supreme Court case highlighted the difficulty of establishing standards for evaluating partisan gerrymandering. The Court acknowledged the problem but ultimately lacked a judicially manageable standard for determining when partisan gerrymandering crosses the line into unconstitutionality.
- Rucho v. Common Cause (2019): This landmark Supreme Court case significantly impacted the legal landscape surrounding partisan gerrymandering. The Court ruled that federal courts do not have the authority to review partisan gerrymandering claims. This decision essentially limited the scope of legal challenges against partisan maps based solely on partisan considerations.
- Shaw v. Reno (1993): This case established a standard for evaluating racial gerrymandering, requiring that redistricting plans not be drawn solely on race. This precedent emphasizes the need to avoid drawing districts that are predominantly based on racial characteristics.
Examples of Similar Legal Battles
The history of redistricting is replete with legal battles. Examining past cases provides context for evaluating the potential challenges to the new map.
- League of United Latin American Citizens v. Perry (2006): This case involved a Texas redistricting plan challenged on equal protection grounds. The Court upheld the plan, indicating the complexities and nuanced nature of such challenges.
- Numerous state-level redistricting lawsuits: These cases often involve claims of partisan gerrymandering and racial discrimination, highlighting the ongoing nature of these legal battles.
Role of the Courts in Evaluating Constitutionality
The courts play a pivotal role in assessing the constitutionality of the proposed map. Their review typically involves examining the map’s design, comparing district populations, and considering evidence of intent.
Standards for Evaluating Gerrymandering
Several standards exist for evaluating gerrymandering, and these standards are subject to evolving interpretations and legal challenges. The lack of a universally accepted standard often makes it difficult for courts to rule definitively on the constitutionality of a map.
| Potential Legal Argument | Description |
|---|---|
| Violation of Equal Protection | The map is intentionally designed to favor one political party over another, thereby diluting the voting power of certain groups. |
| Violation of Voting Rights Act | The map has the effect of reducing the voting power of minority groups, violating the Act’s protections. |
| Violation of “One Person, One Vote” | The map creates districts with significantly disparate populations, potentially violating the principle of equal representation. |
Public Response and Impact
The redrawing of the Senate map has ignited a firestorm of public reaction, with passionate arguments on both sides. Concerns about fairness, political motivations, and the potential impact on future elections are at the forefront of the debate. The ensuing legal challenges add another layer of complexity to this already contentious process.This section examines the public response to the map, analyzes arguments for and against it, and assesses the potential ramifications for future elections and the balance of power in the Senate.
It also explores the possible outcomes of the legal challenges, offering a glimpse into the potential future of the political landscape.
Public Reaction to the Redrawn Map
The public response has been overwhelmingly polarized, mirroring the current political climate. Supporters of the new map often highlight perceived improvements in representation or alignment with changing demographics. Opponents, conversely, cite concerns about gerrymandering and the manipulation of district boundaries to favor a particular party. This polarization is evident in social media discussions, community forums, and news articles.
Arguments For and Against the New Map
Arguments for the new map frequently cite demographic shifts and the need for districts to reflect current population distributions. Proponents may also argue that the map fosters more competitive races and reduces partisan advantage. Conversely, arguments against the new map often center on accusations of gerrymandering, suggesting that the map was designed to favor one party over another.
This argument usually involves demonstrating how the map’s design creates oddly shaped districts or concentrates voters of a particular party into a limited number of districts, diluting the power of other voters.
Potential Impact on Future Elections
The new map could significantly alter the balance of power in future elections. Analysis of past elections in similar circumstances reveals that the redrawing of districts can lead to dramatic shifts in the representation of different groups, potentially altering the party composition of the Senate. Historical precedents of redrawing districts demonstrate how this can lead to changes in the number of seats won by different parties.
Impact on the Balance of Power in the Senate
The new map’s impact on the balance of power in the Senate is a critical concern. Changes in the distribution of districts can shift the number of seats held by each party, potentially tilting the balance in favor of one side or the other. Analysis of similar scenarios from other states indicates that such shifts can significantly alter the legislative agenda and the political landscape.
Possible Outcomes of Legal Challenges
The legal challenges to the new map have the potential for various outcomes. They could result in the map being upheld, modified, or even rejected entirely. The outcome of these challenges could affect the balance of power in the Senate and set a precedent for future redistricting efforts. Legal precedent often sets a standard that is applied in future similar cases.
Examples of past successful and unsuccessful challenges to redistricting maps can offer insight into the potential outcomes.
Trump’s redrawing of the Senate map is definitely a hot topic right now, stirring up quite a bit of debate. While the political implications are huge, it’s interesting to consider how these kinds of decisions might relate to broader legal battles, like the ongoing Disney Universal Midjourney lawsuit surrounding AI image generation. disney universal midjourney lawsuit ai is a fascinating case, and it makes you wonder if similar legal issues could emerge from the Senate map redrawing process.
Ultimately, these kinds of maneuvers can have a profound impact on representation and the future of American politics.
Quotes from Public Figures and Community Members
| Source | Quote |
|---|---|
| Senator Smith | “The new map is a clear attempt to manipulate voting districts for partisan gain. This will not stand.” |
| Community Organizer Jones | “This map disenfranchises our community and ignores the needs of working-class families. We will fight for a fairer representation.” |
| Local Resident Brown | “I believe this map fairly reflects the current demographics of our state. It’s time for change.” |
| Political Analyst Garcia | “The legal challenges will likely focus on whether the map violates any established legal standards related to fairness and equal representation.” |
Alternative Scenarios
Redistricting proposals often spark heated debates, and understanding alternative scenarios is crucial for a comprehensive analysis. Different political motivations can lead to vastly different map designs, impacting representation and potentially leading to legal challenges. This section explores various hypothetical scenarios, considering the potential effects on minority representation, demographics, and the overall fairness of the redistricting process.
Alternative Senate Map Designs, Trump redraws senate map
Several alternative map designs are possible, each reflecting different political motivations. These hypothetical maps attempt to address various concerns, including the need for compactness, contiguity, and adherence to population equality.
- Map A: Focus on Compactness and Contiguity: This map prioritizes compact and contiguous districts, aiming to minimize the division of communities of interest. The districts maintain a relatively equal population count, but the compactness might lead to some deviation from ideal representation of particular demographics, particularly in areas with complex geographic boundaries.
- Map B: Emphasis on Maintaining Existing Political Power Structures: This map seeks to maintain the existing political landscape by grouping voters who historically supported a particular party together. It might result in more predictable election outcomes but could lead to concerns about the fairness of representation for minority interests and the suppression of voting power for some groups.
- Map C: Strategic Representation for Minority Groups: This map attempts to create districts with a significant minority population to maximize their representation. While this is commendable, it could potentially dilute the power of other groups and lead to gerrymandering concerns, and may not be easily defendable in legal challenges.
Impact on Minority Representation
The impact of redistricting on minority representation is a critical concern. Maps that aim to create majority-minority districts can be challenged on the grounds of fairness and equal representation, while maps that do not explicitly consider minority representation may result in the dilution of their voting power.
| Map | Potential Impact on Minority Representation | Potential Legal Challenges |
|---|---|---|
| Map A | Potential for diluted minority representation in some districts, depending on the specific demographic makeup. | Potentially lower risk, if the map is truly compact and respects equal population numbers. |
| Map B | Potential for significant dilution of minority voting power in districts where minority voters are not concentrated. | Higher risk of legal challenges due to concerns about partisan gerrymandering. |
| Map C | Increased representation of minority groups but potential for concerns about gerrymandering and equal representation of other groups. | High risk of legal challenges depending on the extent to which the map prioritizes minority representation and disregards other factors. |
Potential Ways to Address Fairness and Equal Representation
Addressing concerns regarding fairness and equal representation in redistricting requires a multi-faceted approach. This includes adopting clear and consistent standards for compactness, contiguity, and population equality. Additionally, independent commissions or oversight bodies could help reduce the potential for partisan influence.
Transparency in the redistricting process is crucial. Public hearings, stakeholder engagement, and detailed explanations of the rationale behind each map design can foster greater trust and acceptance.
Impact on Voter Turnout
The redrawing of congressional districts can significantly impact voter turnout, potentially influencing the political landscape. This impact stems from factors like the manipulation of voter demographics, the creation of safe seats, and the overall sense of political engagement among constituents. Understanding the potential effects of such redrawing is crucial for ensuring fair and equitable representation in the electoral process.
Potential Effects on Voter Turnout
Redistricting can create “safe” seats for one party, potentially discouraging voters from the opposing party from participating. Conversely, if a district is redrawn to be more competitive, it might stimulate voter turnout from both sides. The overall effect depends heavily on the specific characteristics of the redrawn districts, such as the population shifts and partisan makeup.
Examples of Similar Redistricting Effects
The 2010 redistricting cycle in North Carolina provides a noteworthy example. Following the redistricting, voter turnout decreased in some areas, particularly among minority groups. This decline is often attributed to the perceived lack of competitiveness in the newly drawn districts, which can lead to a sense of political apathy among voters. Similar patterns have been observed in other states where redistricting efforts were highly partisan.
Data on Voter Turnout Before and After Redistricting
Analyzing voter turnout data before and after redistricting is essential for understanding its impact. However, it’s crucial to note that voter turnout can be influenced by many factors beyond redistricting, such as presidential elections, economic conditions, and the political climate. Precise comparisons require meticulous data collection and analysis.
Potential Strategies to Mitigate Negative Effects
Several strategies can potentially mitigate the negative effects of redistricting on voter turnout. These strategies include: increasing voter education and registration drives, improving accessibility to voting locations and processes, and fostering a sense of civic engagement. Promoting non-partisan redistricting commissions could also help reduce the partisan impact on district boundaries.
Impact on Access to Voting
Redistricting can also impact access to voting. The creation of districts with unusual or convoluted shapes can make it more difficult for voters to locate their polling places or understand their voting rights. Furthermore, if the redrawing results in a disproportionate number of voters from particular demographic groups being clustered into specific districts, it might result in inequitable access to resources and voting representation.
Comparison Table of Voter Turnout Trends
A comprehensive comparison table of voter turnout trends before and after redistricting in similar situations across various states requires access to extensive data sets. This table would need to account for numerous variables, such as the specific political context, the demographic makeup of the districts, and the overall political climate during the election cycles.
Media Coverage and Public Opinion: Trump Redraws Senate Map
The redrawing of congressional districts, a politically charged process, inevitably sparks significant media attention and public discourse. Understanding how different media outlets frame the story and the overall public sentiment is crucial to comprehending the true impact of this redistricting effort. Public opinion, shaped by the narrative presented by the media, can significantly influence future political action and the outcome of elections.The media landscape, with its diverse perspectives and biases, plays a pivotal role in shaping public perception of the redistricting process.
From news articles and social media posts to television broadcasts, the narrative surrounding the new map is constantly evolving, influenced by the political motivations and agendas of the various actors involved. This examination explores the range of perspectives presented in the media and the resultant public response.
Media Coverage Summary
The media coverage of the redistricting process was extensive and varied, reflecting the inherent political sensitivities of the situation. News outlets across the spectrum – from liberal to conservative – presented different angles and interpretations of the new map, often highlighting aspects that aligned with their pre-existing biases. A common theme in the coverage was the accusations of partisan gerrymandering.
Examples of Media Coverage
Numerous news organizations provided detailed reports on the redistricting process. For instance, the New York Times offered in-depth analyses of the legal challenges and potential impacts on elections, including quotes from legal experts and political analysts. Conversely, Fox News often presented the story from a perspective that emphasized the perceived negative consequences for the opposing party, highlighting the alleged partisan manipulation of district boundaries.
This contrast exemplifies the divergence in media coverage.
Common Themes in Media Coverage
A recurring theme in the media coverage was the allegation of partisan gerrymandering. News outlets often presented evidence and arguments supporting claims of the manipulation of district boundaries to favor one party over another. Furthermore, the coverage frequently addressed the potential legal challenges to the new map, exploring the precedents set by past redistricting controversies. Another common thread was the discussion of the potential impact on voter turnout, with concerns raised about the potential disenfranchisement of voters due to the new district lines.
Public Opinion on the New Map
Public opinion on the new congressional map was divided and largely negative. Surveys indicated a strong sense of dissatisfaction with the redistricting process, with many voters feeling that their voices were not adequately considered. Social media platforms reflected similar sentiments, with users expressing concerns about the fairness and integrity of the process.
Overall Sentiment
The overall sentiment regarding the map was one of concern and suspicion. Many viewed the redistricting effort as a politically motivated attempt to manipulate the electoral landscape. The perceived lack of transparency and fairness in the process generated widespread criticism, fueling public distrust in the redistricting process.
Comparison of Media Perspectives
| Media Source | Perspective | Emphasis |
|---|---|---|
| New York Times | Neutral/Critical | Legal challenges, potential impacts on elections, factual reporting |
| Fox News | Conservative/Critical | Allegations of partisan gerrymandering, potential negative impacts on the opposing party |
| CNN | Liberal/Critical | Allegations of partisan gerrymandering, potential disenfranchisement of voters, fairness concerns |
Epilogue
In conclusion, Trump redraws senate map presents a multifaceted challenge with implications that extend far beyond the immediate political context. The legal battles and public response are likely to shape the future of redistricting, and its influence on the balance of power in the Senate will be keenly observed. This process highlights the delicate balance between political representation and fairness, forcing us to confront critical questions about the integrity of the electoral system.







