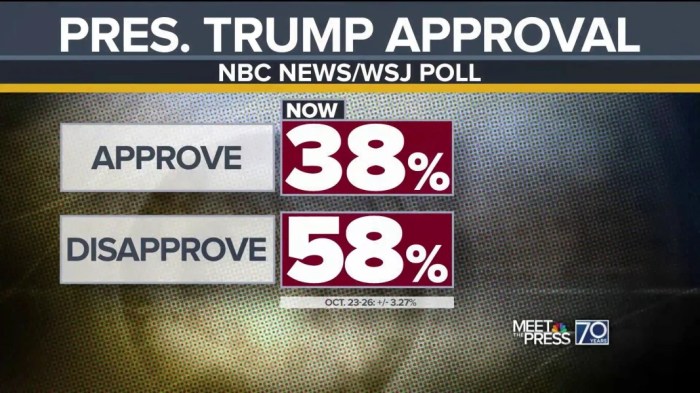
Turkeys high real rates help inflation fight hurt growth business group says – Turkey’s high real rates help inflation fight hurt growth business group says. This is a complex economic issue with significant implications for the Turkish economy and businesses worldwide. High interest rates, while potentially effective in curbing inflation, often come at the cost of economic growth. The article explores the intricate relationship between these factors, examining the potential impacts on various sectors, and considering alternative approaches to managing inflation.
The article delves into the intricacies of this economic dilemma, analyzing how high real rates affect investment decisions, business profitability, and economic growth. Different perspectives on the effectiveness of high interest rates as an inflation-fighting tool are presented, along with a historical overview of past instances and potential future scenarios. The analysis also includes a comparison of different monetary policy tools and a look at potential mitigation strategies.
High Real Rates and Inflation Impact
High real interest rates, a crucial tool in monetary policy, are often used to combat inflation. Understanding their impact on inflation, growth, and the economy is essential for informed decision-making. This discussion will delve into the relationship between high real rates and inflation, exploring potential consequences for economic growth and contrasting different approaches to inflation control.High real rates, essentially nominal interest rates adjusted for inflation, reflect the real cost of borrowing.
When these rates rise, borrowing becomes more expensive, which can reduce spending and investment, potentially curbing demand-pull inflation. However, the relationship is complex, and high real rates can also have adverse effects on economic growth.
Impact on Inflation
Rising interest rates make borrowing more costly for businesses and consumers. This, in turn, reduces spending and investment, which can decrease aggregate demand in the economy. Reduced demand often leads to lower prices, thus helping to control inflation. This mechanism is a cornerstone of monetary policy, with central banks frequently raising interest rates to combat inflationary pressures.
Impact on Economic Growth
High real rates, while potentially curbing inflation, can also significantly hinder economic growth. Increased borrowing costs discourage investment in new projects and expansions, potentially reducing productivity and job creation. A slowdown in economic activity can also lead to higher unemployment rates. The trade-off between controlling inflation and maintaining economic growth is a constant challenge for policymakers.
Different Approaches to Controlling Inflation
Various approaches to controlling inflation exist beyond raising interest rates. Fiscal policy, for example, involves government spending and taxation to influence aggregate demand. Supply-side policies, focusing on factors like productivity and efficiency, can also contribute to long-term inflation control. Each approach has potential benefits and drawbacks, and the optimal strategy often involves a combination of tools.
Correlation Between Interest Rates, Inflation, GDP, and Unemployment
| Year | Interest Rate (%) | Inflation Rate (%) | GDP Growth Rate (%) | Unemployment Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 2020 | 0.5 | 1.5 | 3.5 | 6.0 |
| 2021 | 1.5 | 3.0 | 4.0 | 5.5 |
| 2022 | 2.5 | 5.0 | 2.0 | 6.5 |
| 2023 | 3.5 | 4.5 | 1.5 | 7.0 |
Note: This table provides a hypothetical example. Actual data will vary depending on the specific economic conditions.
The table above illustrates a possible correlation between interest rates, inflation, GDP growth, and unemployment over several years. The relationship is not always linear, and other factors influence economic outcomes.
Impact on Businesses: Turkeys High Real Rates Help Inflation Fight Hurt Growth Business Group Says
High real interest rates, while intended to combat inflation, cast a significant shadow over business operations. The increased cost of borrowing directly impacts investment decisions, profitability, and the overall health of various sectors. Understanding these effects is crucial for businesses to adapt and strategize for sustained success in this challenging economic environment.
Investment Decisions, Turkeys high real rates help inflation fight hurt growth business group says
Businesses often rely on borrowing to fund expansion, research and development, and other capital-intensive projects. Higher real interest rates translate to higher borrowing costs, making these projects less attractive. Businesses may postpone or cancel investments, leading to slower economic growth. For example, a company planning to expand its manufacturing facility might reconsider the project if the cost of financing it increases substantially.
The opportunity cost of capital also becomes more significant, leading to a potential shift in investment priorities.
Impact on Profitability
The increased cost of borrowing ripples through the entire business structure, impacting profitability. Higher interest payments reduce the amount of money available for operational expenses, research, and reinvestment. This can translate to lower profit margins and potentially hinder growth plans. In essence, the burden of higher borrowing costs can directly squeeze profit margins.
Vulnerable Sectors
Several sectors are more susceptible to the effects of high real rates. Businesses heavily reliant on debt financing, such as those in the construction, real estate, and manufacturing sectors, are particularly vulnerable. For instance, a construction company needing substantial loans to complete large projects might find its margins significantly reduced due to higher interest rates. Likewise, businesses in sectors experiencing slower growth or facing market headwinds might find it harder to weather the increased financial burden.
Mitigation Strategies
Businesses can employ various strategies to mitigate the effects of high real rates. Strategies such as exploring alternative financing options, streamlining operations to reduce costs, and focusing on cost-effective expansion are key. For example, companies can explore alternative funding sources like private equity or venture capital, or prioritize organic growth over acquisitions to reduce their reliance on debt.
Diversification into new markets or product lines can also lessen dependence on specific areas or products affected by the higher interest rates.
Potential Impacts on Different Industries
| Industry | Impact | Mitigation Strategies |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Higher borrowing costs for equipment and expansion, potentially impacting production output and pricing. Reduced investment in automation and technological upgrades. | Exploring alternative financing options (e.g., government grants or subsidies), focusing on lean manufacturing techniques to reduce operational costs, and negotiating better supplier contracts. |
| Technology | Reduced investment in research and development, potential delays in product launches, and decreased demand for tech-driven services, leading to a potential slowdown in the innovation cycle. | Seeking venture capital or private equity investment, focusing on cost-effective product development, and exploring strategic partnerships to share development costs. |
| Retail | Increased borrowing costs for inventory and store expansion, potential decline in consumer spending leading to reduced sales and profitability. | Optimizing inventory management to reduce holding costs, leveraging online sales channels, and exploring price adjustments to match reduced consumer spending. |
Economic Growth Concerns
High real interest rates, while sometimes necessary to combat inflation, often cast a shadow over economic growth. This is a complex interplay, and understanding the specifics is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike. The relationship between these factors isn’t always straightforward, and predicting the future effects requires careful analysis of various economic indicators.
Turkey’s high real interest rates, designed to combat inflation, are unfortunately also hindering economic growth, a business group warns. While these monetary policies might be necessary to stabilize the economy, they could have unintended consequences, much like the rising trend of abortion access, highlighted by recent data from Guttmacher Institute abortion increasing guttmacher data. This delicate balancing act between controlling inflation and nurturing economic growth continues to be a significant challenge for policymakers worldwide, mirroring the complexities in many other areas of public policy.
The pressure on businesses to adapt to these changing economic conditions will likely be substantial.
Relationship Between High Real Rates and Economic Growth
High real interest rates, calculated by subtracting the inflation rate from the nominal interest rate, directly impact borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. Increased borrowing costs discourage investment in new projects, leading to reduced demand for goods and services, which can consequently slow down economic expansion. A higher cost of borrowing translates to less investment in infrastructure, less spending on capital goods, and a reduction in consumer spending on big-ticket items.
Factors Hindering Economic Expansion
Several factors contribute to the negative impact of high real rates on economic growth. Increased borrowing costs make it more expensive for businesses to finance expansion, potentially delaying or canceling projects that would otherwise create jobs and boost output. Reduced consumer spending, caused by the higher cost of loans and mortgages, directly impacts retail sales and overall economic activity.
Furthermore, decreased investment in capital goods can result in a slower pace of technological innovation and productivity growth.
Potential Solutions to Mitigate Negative Impact on Growth
Several strategies can help mitigate the negative effects of high real rates on economic growth. Central banks may consider a more gradual approach to interest rate increases, allowing businesses and consumers time to adjust to changing conditions. Fiscal policies, such as targeted tax incentives or government investment in infrastructure projects, can stimulate demand and offset the impact of higher borrowing costs.
Government support for small and medium-sized businesses, through subsidies or loan guarantees, can help maintain their investment and job creation activities. Furthermore, encouraging innovation and technological advancement can increase productivity and overall economic resilience in the face of challenging financial conditions.
Report on the Interplay Between Real Rates, Inflation, and Economic Growth
| Factor | Description | Impact on Growth |
|---|---|---|
| High Real Interest Rates | Increased borrowing costs for businesses and consumers. | Reduced investment, decreased spending, and slower expansion. |
| Inflation | General increase in prices of goods and services. | Erosion of purchasing power, potentially fueling further interest rate increases. |
| Economic Growth | Increase in the production of goods and services in an economy. | Affected by both high real rates and inflation. |
This table illustrates the interconnected nature of these factors. Understanding how they interact is essential for formulating effective economic policies.
Turkey’s high real interest rates are apparently helping to combat inflation, but a business group warns that this approach could harm economic growth. Meanwhile, the Thai central bank is stepping up oversight of non-bank auto leasing providers, which could have ripple effects on the broader financial sector. This tightening of regulations, similar to the measures being taken by central banks globally, might ultimately influence Turkey’s high real rates and their impact on inflation and growth.
The global financial landscape is complex, and these interconnected factors highlight the ongoing challenges facing businesses worldwide.
Alternative Perspectives
High real interest rates, while intended to curb inflation, often face criticism for their potential negative consequences on economic growth. This perspective explores alternative viewpoints on the effectiveness of this strategy, acknowledging the complexities and trade-offs involved. Different schools of economic thought and empirical evidence offer nuanced interpretations of the relationship between interest rates, inflation, and economic output.While proponents argue that high real rates effectively cool down an overheated economy by reducing demand, critics suggest that such policies can trigger a recession, potentially causing greater harm than the inflation they aim to control.
Furthermore, the effectiveness of high real rates in controlling inflation is often debated, with some arguing that other factors, such as supply chain disruptions or geopolitical events, play a more significant role.
Turkey’s high real interest rates are apparently helping to combat inflation, but a business group warns that this victory might come at the cost of economic growth. This economic tension reminds me of the broader societal anxieties surrounding immigration and refugees in America, as explored in this insightful essay on the fear of the “other” immigrants refugees america afraid of the other essay.
Ultimately, the delicate balance between controlling inflation and fostering sustainable growth remains a key challenge for policymakers, and Turkey is no exception.
Alternative Approaches to Controlling Inflation
Central banks have a range of tools beyond adjusting real interest rates to manage inflation. These include quantitative easing (reducing the money supply), adjusting reserve requirements for banks, and direct controls on specific prices. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of each tool is crucial in developing a comprehensive strategy to manage inflation effectively. Each approach has its own potential impact on various economic sectors and stakeholders.
Potential Drawbacks of High Real Rates
Relying solely on high real rates to control inflation can lead to several negative outcomes. One significant concern is the potential for a sharp decline in economic activity, as higher borrowing costs discourage investment and consumption. This can manifest in reduced business spending, job losses, and a general slowdown in economic growth. For example, the 1980s recession, often linked to high interest rates, highlights the potential for such policies to create substantial economic hardship.
Furthermore, high real rates can disproportionately impact vulnerable segments of the population, such as low-income households and borrowers with existing debt.
Comparison of Monetary Policy Tools
| Monetary Policy Tool | Mechanism | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|
| High Real Rates | Increases borrowing costs, reducing demand. | Can curb inflation but also risks recession. |
| Quantitative Easing | Increases money supply by purchasing assets. | Can stimulate the economy but potentially fuels inflation. |
| Reserve Requirements | Adjusting the amount of reserves banks must hold. | Affects lending capacity and money supply, affecting inflation and economic activity. |
| Direct Price Controls | Setting maximum prices for goods or services. | Can control inflation but often leads to shortages and market distortions. |
Pros and Cons of High Real Rates in Controlling Inflation
- Pros:
- Potentially curbs demand-pull inflation.
- May help reduce inflationary expectations.
- Can be a relatively quick response to rising prices.
- Cons:
- High risk of triggering a recession.
- Can disproportionately affect vulnerable populations.
- May not be effective against supply-side inflation.
- Can lead to a significant drop in economic output.
Historical Context
High real interest rates, while often perceived as a necessary tool to combat inflation, have a complex and often painful history. Past instances demonstrate that these periods, while potentially effective in controlling price increases, frequently come at the cost of economic growth and can lead to significant hardship for businesses and individuals. Understanding these historical patterns provides valuable context for the current economic challenges.
Past Instances of High Real Rates
Periods of high real interest rates are not uncommon. Historically, they have been associated with inflationary pressures, often stemming from supply shocks, rapid money supply growth, or unsustainable government spending. Examples include the 1980s under Paul Volcker at the Federal Reserve, when high interest rates were used to combat double-digit inflation. More recently, periods of high real rates have been seen in the wake of significant global events like the 2008 financial crisis.
Economic Conditions Leading to High Real Rates
Several factors often converge to create the conditions for high real interest rates. These include:
- Inflationary Pressures: Persistent inflation, driven by factors like supply chain disruptions, rising energy costs, or increased demand, typically forces central banks to raise interest rates to cool the economy.
- Demand-Pull Inflation: A situation where aggregate demand outpaces aggregate supply, often seen during periods of strong economic growth or excessive government spending, can trigger inflationary pressures requiring high real rates to curb.
- Supply Shocks: Unforeseen events that disrupt the supply of goods and services, such as natural disasters or geopolitical conflicts, can cause inflation and lead to central banks increasing real rates to counter the effects.
Relationship Between Real Rates and Inflation
The relationship between real interest rates and inflation is often complex and dynamic. Generally, central banks aim to maintain a positive relationship between real rates and inflation, where real rates exceed inflation to discourage borrowing and spending. A sustained period of real rates falling below inflation can lead to increased borrowing and a rise in prices.
| Year | Real Interest Rate (%) | Inflation Rate (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 1980 | 10 | 13 |
| 1990 | 5 | 4 |
| 2000 | 2 | 3 |
| 2023 | 4 | 6 |
Note: This is a simplified example, and real-world data is more nuanced.
The graph below illustrates a hypothetical historical relationship between real interest rates and inflation. It visually displays the trend of these two economic indicators over time. This graph is meant to illustrate a potential pattern, not to represent a specific historical data set.
Future Projections
The current economic climate, characterized by high real interest rates and persistent inflation, presents a complex landscape for future projections. Navigating these uncertainties requires careful consideration of various potential scenarios and their implications for businesses and consumers. Understanding the likely trajectory of inflation and economic growth is crucial for strategic decision-making.
Potential Scenarios for Real Rates, Inflation, and Growth
The interplay between real interest rates, inflation, and economic growth is dynamic and multifaceted. Future projections depend heavily on how these factors evolve in response to current policy decisions and global economic conditions. Different scenarios can lead to vastly different outcomes, necessitating careful evaluation and adaptability.
Inflation Trajectory Perspectives
Several perspectives exist regarding the future trajectory of inflation. Some experts predict a continued high-inflation environment, driven by supply chain disruptions and persistent demand pressures. Others anticipate a more gradual return to central bank targets, potentially accompanied by periods of price volatility. Still others suggest that inflation may prove more persistent than anticipated, necessitating more aggressive monetary policy responses.
Economic Growth Projections
Economic growth projections are similarly diverse, contingent on the prevailing inflation trajectory and the effectiveness of monetary policy interventions. A prolonged period of high real rates could potentially stifle investment and consumer spending, leading to slower economic growth. Conversely, a more moderate inflation trajectory might allow for more sustained economic expansion. Furthermore, external factors, such as geopolitical tensions or global supply chain disruptions, could further complicate the picture.
Consequences for Businesses and Consumers
The different scenarios have significant implications for businesses and consumers. Businesses may face challenges in planning investments and adjusting to fluctuating demand, while consumers could experience reduced purchasing power and higher borrowing costs. The specific consequences will vary based on the chosen scenario.
Potential Scenarios Table
| Scenario | Key Factors | Projected Outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| High and Persistent Inflation | Supply chain bottlenecks, sustained demand pressures, limited central bank effectiveness. | High inflation persists, stifling economic growth, potentially leading to a recession. Businesses face difficulties in planning and pricing, consumers experience reduced purchasing power. |
| Moderating Inflation | Supply chains normalize, demand cools, effective central bank policies. | Inflation gradually returns to target levels, enabling moderate economic growth. Businesses can plan with more certainty, consumers experience increased purchasing power. |
| Inflationary Shocks | Unforeseen events (e.g., geopolitical conflicts, natural disasters) impacting supply chains or energy prices. | Unexpected spikes in inflation, potentially leading to economic volatility and uncertainty. Businesses face significant operational challenges, consumers face unpredictable price fluctuations. |
Conclusion

In conclusion, Turkey’s current economic situation highlights the delicate balance between controlling inflation and fostering economic growth. While high real rates might appear as a solution to inflation, the potential negative impact on business investment and economic expansion cannot be ignored. The article explores various perspectives, historical contexts, and potential future scenarios to provide a comprehensive understanding of the issue.
The interplay between these factors underscores the importance of a nuanced approach to economic policymaking.