UK trade minister meet USTR Greer discuss implementing tariff deal. This high-level meeting signals a crucial moment in transatlantic trade relations, potentially shaping the future of economic partnerships between the UK and the US. With a complex history of agreements and disputes, this discussion holds significant weight, particularly given the current global political climate. The meeting between the UK Trade Minister and USTR Greer promises to be pivotal in determining the trajectory of bilateral trade, with the potential for significant benefits or challenges depending on the outcome.
This meeting delves into the potential ramifications of a tariff deal, exploring possible areas of agreement, the potential economic impacts on both countries, and the likely public and political responses. The discussion will analyze potential outcomes, considering both positive and negative consequences, and Artikel various scenarios, including alternative outcomes if a deal is not reached.
Background of the Trade Meeting
The UK and US, two global economic powerhouses, have a long and complex history of trade relations, marked by periods of cooperation and contention. Understanding this history is crucial to contextualizing the current discussions around implementing a tariff deal. This meeting, a crucial step in navigating these complexities, represents a pivotal moment for both nations.
Historical Overview of UK-US Trade Relations, Uk trade minister meet ustr greer discuss implementing tariff deal
A detailed examination of trade relations reveals a dynamic interplay of agreements and disputes. The historical trajectory demonstrates both periods of strong collaboration and instances of significant friction. These interactions have shaped the current landscape, influencing the current negotiation environment.
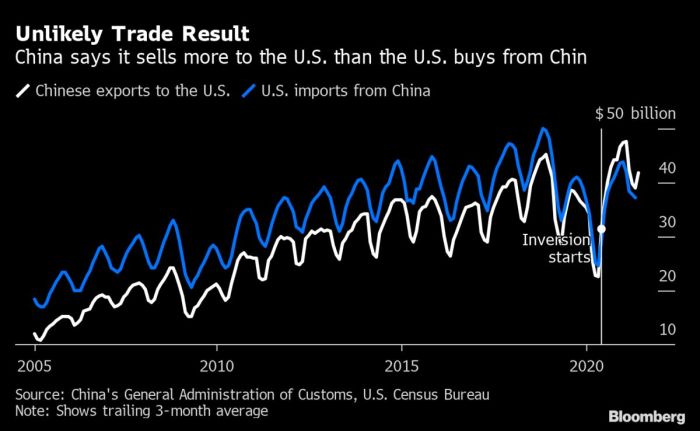
The UK trade minister meeting with the USTR’s Katherine Tai to discuss implementing the tariff deal is definitely interesting, especially given the recent news about China issuing rare earth licenses to suppliers for top 3 US automakers, as reported by this article. This could significantly impact the global auto industry and potentially influence the tariff negotiations. Ultimately, the UK trade minister’s discussions with the USTR are crucial for navigating these complex trade dynamics.
| Date | Event | Key Players | Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1948 | Establishment of the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trade (GATT) | Various nations, including the UK and US | Reduced trade barriers and fostered global economic growth. |
| 1994 | Creation of the World Trade Organization (WTO) | Various nations, including the UK and US | Further formalized global trade rules and mechanisms for dispute resolution. |
| 2000s-2010s | Rise of Bilateral Trade Agreements | UK and US, alongside other countries | Led to increased trade but also raised concerns about potential disruptions in global trade. |
| 2010s-2020s | Rise of Protectionist Tendencies | Various countries, including the UK and US | Led to trade disputes and challenges to established trade norms. |
| 2020-Present | Ongoing trade negotiations | UK Trade Minister and US Trade Representative | Ongoing, with the goal of implementing a tariff deal. |
Significant Trade Agreements and Disputes (Past Decade)
The past decade has witnessed a series of trade agreements and disputes impacting both the UK and US. These events have profoundly shaped the current negotiating climate. Notable instances include:
- The Transatlantic Trade and Investment Partnership (TTIP) negotiations: This proposed agreement aimed to reduce trade barriers between the EU and the US. However, it stalled due to various political and economic considerations. This highlights the challenges of large-scale trade agreements.
- The US-China trade war: This conflict involved significant tariffs imposed by the US on Chinese goods, impacting global trade flows and supply chains. This underscores the potential for significant disruptions when major economies engage in trade disputes.
- The UK’s departure from the European Union: This event significantly impacted the UK’s trade relations with its closest trading partner, necessitating a new trade strategy. This illustrates the impact of geopolitical events on trade relations.
Current Political Climate Impacting Trade Negotiations
The current political climate globally is characterized by various pressures, including differing political priorities and economic strategies. This environment significantly impacts trade negotiations.
- Geopolitical tensions: Global events, such as the war in Ukraine, can create uncertainty and instability in the global economy, influencing trade relations.
- Domestic policy priorities: Domestic political agendas and priorities can influence a nation’s approach to trade negotiations.
- Economic considerations: Fluctuations in economic conditions and global supply chain disruptions can impact trade negotiations.
Roles of the UK Trade Minister and the USTR
The UK Trade Minister and the USTR play crucial roles in shaping trade policy and conducting negotiations. Understanding their roles is essential for comprehending the context of the current meeting.
The UK trade minister meeting with the USTR’s Greer to discuss implementing the tariff deal is certainly interesting. It’s a fascinating parallel to the recent news about Trump revoking Harvard’s tax-exempt status, which raises some really intriguing questions about the future of tax policies. While the specifics of that situation are quite different, the underlying themes of power plays and policy shifts are undeniably present in both.
Ultimately, though, the focus remains on the potential impact of the UK trade deal.
- UK Trade Minister: The UK Trade Minister is responsible for developing and implementing the UK’s trade policy, including negotiating trade agreements. Their role involves representing the UK’s interests in international trade forums.
- USTR: The USTR is the principal advisor to the President of the United States on trade policy. Their role involves negotiating trade agreements and representing the US’s interests in trade relations with other countries.
Objectives and Goals of the Meeting
The upcoming meeting between the UK Trade Minister and the USTR Greer marks a crucial step in solidifying a tariff deal. Both sides bring distinct perspectives and priorities to the table, shaping the potential outcomes. Understanding these objectives is key to anticipating the success or challenges of the negotiations.
Potential Objectives of the UK Trade Minister
The UK Trade Minister likely seeks to finalize the tariff deal, securing favorable terms for UK exporters. A primary objective will be minimizing potential disruptions to UK businesses and maintaining a smooth transition for affected industries. Furthermore, the minister will likely emphasize the importance of ensuring the agreement benefits UK consumers by maintaining competitive pricing. The minister might also aim to address specific concerns raised by UK businesses regarding the deal’s implementation.
Likely Objectives of the USTR
The USTR, representing the US, is expected to prioritize reciprocal benefits for American businesses. A key objective will be ensuring the agreement promotes fair trade practices, protecting American industries from unfair competition. The USTR will likely also focus on enforcing provisions that guarantee American companies access to the UK market, potentially addressing any concerns about market access barriers.
Furthermore, the USTR will likely emphasize the importance of a transparent and effective implementation plan for the tariff deal.
Expected Outcomes of the Meeting
The meeting’s success hinges on the ability of both sides to find common ground. Potential benefits include a streamlined trade process, reduced trade barriers, and increased economic activity for both the UK and the US. This could lead to increased exports, job creation, and potentially lower consumer prices. However, challenges may arise from differing perspectives on specific provisions or the enforcement of the deal.
Disagreements could lead to delays or even a breakdown in negotiations.
Potential Benefits and Challenges for Both Sides
| Aspect | UK | US |
|---|---|---|
| Potential Benefits | Reduced trade barriers, increased exports, lower consumer prices, improved trade relations | Reciprocal access to the UK market, protection of American industries, streamlined trade process |
| Potential Challenges | Concerns about market access, potential disruptions to UK industries, enforcement difficulties | Differences in interpretation of provisions, enforcement of fair trade practices, concerns about market access for US businesses |
Potential Tariff Deal Details: Uk Trade Minister Meet Ustr Greer Discuss Implementing Tariff Deal
A potential tariff deal between the UK and the US presents a complex tapestry of opportunities and challenges. This agreement, if successfully negotiated, could significantly impact various sectors, from agriculture to manufacturing. Understanding the potential details of such a deal is crucial for businesses, consumers, and policymakers alike.This discussion delves into the potential areas for a tariff deal, examines possible terms and conditions, and assesses the likely impact on UK and US consumers.
The UK trade minister meeting with the USTR’s Katherine Tai to discuss implementing the tariff deal is significant. It’s a crucial step, but we need to consider the broader context of climate change impacts, like the devastating fires in Australia and the recent Los Angeles wildfires. Learning from these events, as detailed in fires australia lessons los angeles climate change adaptation , is essential for future adaptation strategies.
Ultimately, the trade deal discussions need to factor in these environmental realities for long-term sustainability.
Specific examples will be used to illustrate the potential benefits and drawbacks.
Potential Areas for a Tariff Deal
The potential areas for a tariff deal are diverse, ranging from specific agricultural products to certain manufactured goods. Areas ripe for discussion include:
- Agricultural Products: Negotiations could focus on tariffs on specific agricultural products like beef, poultry, and certain fruits. The UK and US are both major agricultural exporters, and a deal could reduce trade barriers, potentially increasing market access for both nations. Examples include tariff reductions on US beef exports to the UK and reciprocal tariff reductions on UK agricultural exports to the US.
- Manufactured Goods: Certain manufactured goods, such as automobiles and electronics, could be subject to tariff reductions. This could lead to increased trade volume and lower prices for consumers, although it could also affect domestic industries. For example, the UK could potentially reduce tariffs on US-made electronics, while the US could reduce tariffs on UK-made automobiles.
- Pharmaceuticals: Pharmaceutical products are another area where potential tariff reductions could be discussed. The UK and US are both major players in the pharmaceutical industry, and a reduction in tariffs could benefit consumers through lower prices and greater access to a wider range of medications.
Terms and Conditions of the Tariff Deal
The terms and conditions of a tariff deal are critical for its success. These include timelines, dispute resolution mechanisms, and potential safeguards for domestic industries.
- Timelines: A well-defined timeline for the implementation of the tariff deal is essential. This should consider the necessary time for businesses to adapt to the new trade environment. A realistic timeline, potentially spanning several months, would allow for a smooth transition.
- Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: A robust dispute resolution mechanism is crucial to address any disagreements that may arise during the implementation of the deal. This mechanism should be impartial and transparent, providing a clear process for resolving conflicts.
- Safeguards for Domestic Industries: Safeguards for domestic industries are crucial to mitigate potential negative impacts. These safeguards could involve temporary tariffs, quotas, or other measures to protect domestic producers.
Potential Tariffs and Their Impact
The following table Artikels potential tariffs and their impact on various industries. This table provides a snapshot, but the full impact will vary based on the specifics of the deal.
| Product Category | Potential Tariff (percent) | Impact on UK Industries | Impact on US Industries |
|---|---|---|---|
| Agricultural Products | 0-10% | Reduced input costs, increased exports | Increased market access, potential for greater production |
| Manufactured Goods | 5-15% | Potential job losses in some sectors | Increased market access, potential for expansion |
| Pharmaceuticals | 0-5% | Lower drug costs, increased competition | Increased market access, potential for increased exports |
Impact on Consumers
The likely impact of the deal on UK and US consumers will depend on the specifics of the tariff reductions. Generally, lower tariffs could lead to lower prices for consumers, as goods become more accessible and affordable.
- Lower Prices: Lower tariffs on imported goods often result in lower prices for consumers, as competition increases and costs decrease.
- Increased Choice: A tariff deal can lead to a greater variety of goods available to consumers, as trade barriers are reduced.
- Potential for Inflation: In some cases, tariffs on imported raw materials could potentially lead to higher prices for certain consumer goods.
Potential Implications of the Deal
This tariff deal, a delicate dance between economic interests and political considerations, promises significant shifts in the global trade landscape. Understanding the potential implications, both positive and negative, is crucial for businesses, policymakers, and individuals alike. The consequences extend far beyond the immediate parties involved, impacting global trade flows and potentially reshaping societal structures.
Economic Consequences for Both Countries
The economic ramifications of this tariff agreement will vary depending on the specifics of the deal. Positive outcomes could include increased trade volumes, reduced costs for consumers, and enhanced economic growth. Conversely, potential downsides include disruptions to existing supply chains, job losses in certain sectors, and inflationary pressures. The overall impact hinges on the specific sectors affected, the magnitude of tariff reductions, and the ability of industries to adapt.
Potential Impact on Global Trade Dynamics
This tariff deal could set a precedent for future trade agreements, either fostering multilateral cooperation or exacerbating existing trade tensions. If successful, it might inspire similar negotiations, potentially leading to a more integrated global economy. However, a failure could further fragment the international trading system, leading to protectionist measures and a more fractured global market. Past examples of similar agreements offer both optimistic and cautionary tales, highlighting the complexity of predicting the global impact of such deals.
Potential Societal Impacts of the Deal
The societal implications are multifaceted and could range from improved living standards to heightened social inequality. Increased access to goods and services at lower prices could boost consumer welfare. However, potential job losses in specific industries could exacerbate existing social inequalities. The distribution of benefits and burdens will be a key factor in determining the overall societal impact. The success of implementing social safety nets and retraining programs will be critical to mitigating negative societal consequences.
Potential Impacts on Specific Industries
The impact of the tariff deal will vary significantly across industries. A well-structured deal could lead to substantial gains in some sectors, while others might experience considerable disruption.
| Industry | Potential Positive Impacts | Potential Negative Impacts |
|---|---|---|
| Agriculture | Increased exports, lower input costs, expanded market access. | Disruption of existing supply chains, competition from subsidized imports, potential job losses in certain segments. |
| Manufacturing | Lower production costs, increased competitiveness in the global market, potentially attracting foreign investment. | Job losses in import-competing industries, potential relocation of factories, and increased reliance on foreign supply chains. |
| Technology | Increased trade in advanced technology products, potential for collaboration. | Disruption of established tech supply chains, increased scrutiny of data flows, potential for trade disputes over intellectual property. |
| Tourism | Increased tourism if tariffs are reduced, potentially boosting employment in the tourism sector. | Reduced tourism if tariffs are increased, negatively impacting employment in tourism-related industries. |
Public and Political Responses
The outcome of the UK trade minister’s meeting with the USTR Greer regarding tariff implementation will undoubtedly generate a diverse range of public and political reactions in both countries. Public sentiment is often shaped by economic factors, perceived benefits, and national interests. Political responses, on the other hand, will be heavily influenced by the deal’s potential impact on different constituencies and the prevailing political climate.Public and political reactions will be influenced by how the tariff deal affects different segments of society.
For instance, a deal that lowers the price of imported goods might be welcomed by consumers but could negatively impact domestic industries reliant on tariffs for protection. The perceived fairness and equity of the agreement will also be crucial in shaping public opinion.
Public Reactions in the UK
The UK public’s response to the tariff deal will depend heavily on how it impacts their everyday lives. Lower import costs could lead to lower prices on consumer goods, which would likely be seen positively. However, if the deal leads to job losses in specific sectors, such as manufacturing or agriculture, public dissatisfaction is likely. The extent of public support will depend on the transparency of the agreement and the government’s communication strategy.
Public Reactions in the US
Similar to the UK, public opinion in the US will be influenced by the deal’s impact on consumers and industries. If the agreement reduces consumer prices on certain goods, it will likely receive positive feedback. Conversely, if the deal results in job losses in sectors like agriculture or manufacturing, public opposition could arise. The perceived impact on national security and strategic interests will also play a crucial role in shaping public sentiment.
Political Responses
Political responses will be multifaceted, involving various interest groups with varying perspectives. Governments will need to address the concerns of affected sectors, industries, and political parties. The deal’s compatibility with existing trade agreements and domestic legislation will also be a significant factor in political considerations.
Legislative Processes
The implementation of the tariff deal will necessitate specific legislative processes in both the UK and the US. These processes will likely include the drafting and approval of new legislation, adjustments to existing trade regulations, and potential amendments to existing trade agreements. The timeline for these legislative processes will depend on the specifics of the deal and the political landscape.
Potential Political Responses from Interest Groups
| Interest Group | Potential Response | Rationale |
|---|---|---|
| Consumer groups | Positive if lower prices; negative if job losses | Consumer groups prioritize lower prices; job losses impact their livelihoods. |
| Manufacturing industries | Negative if import competition increases; positive if deal promotes exports | Increased competition from imports negatively impacts manufacturing; export opportunities can balance this. |
| Agricultural groups | Mixed; positive if fair compensation; negative if market disruption | Fair compensation for farmers crucial; market disruption negatively impacts farming communities. |
| Labor unions | Negative if job losses; positive if new job creation in related sectors | Job losses a primary concern; new jobs in supporting sectors could mitigate this. |
| Environmental groups | Mixed; positive if promotes sustainable practices; negative if harms environment | Promoting sustainability is a key concern; negative impacts on the environment are opposed. |
| Political parties | Opposition or support based on alignment with their platforms | Political alignment and their constituencies’ needs will shape their responses. |
Alternative Scenarios and Contingencies

The potential tariff deal between the UK and the USTR hinges on a delicate balance of interests. Failure to reach an agreement could have significant repercussions for both economies, impacting trade flows and investor confidence. Understanding alternative scenarios and contingencies is crucial for assessing the potential risks and opportunities.A successful tariff deal would provide clear benefits to both nations, but a failed negotiation necessitates exploring alternative pathways.
This involves evaluating the potential consequences of a breakdown, from trade disruptions to the need for revised strategies. It also demands a careful analysis of the potential long-term implications of these scenarios.
Potential Outcomes of a Failed Deal
A failed tariff deal could result in a range of negative consequences for both the UK and the USTR. These potential outcomes include:
- Increased Trade Barriers: Without a negotiated agreement, existing tariffs could remain in place, or new ones might be introduced, significantly impacting trade volumes and potentially leading to retaliatory measures.
- Disrupted Supply Chains: A lack of agreement could disrupt existing supply chains, potentially increasing costs for businesses and consumers. This could be exemplified by delays in import/export processes, shortages of specific goods, and price hikes.
- Reduced Investment Flows: Uncertainty surrounding trade relations can deter foreign investment in both countries. Investors may be hesitant to commit capital to projects if the trade environment is unpredictable or fraught with potential barriers.
- Impact on Consumer Prices: Increased tariffs and disrupted supply chains could lead to higher prices for consumers, making essential goods less affordable. The impact is often felt most severely on essential goods.
Alternative Trade Negotiation Strategies
If the current tariff negotiation fails, alternative strategies for future trade negotiations must be considered. These strategies should consider potential long-term implications.
- Re-evaluation of Trade Priorities: Both the UK and the USTR might need to re-evaluate their trade priorities and focus on areas where a mutually beneficial agreement is more achievable. This might involve focusing on different sectors or negotiating separate agreements.
- Enhanced Diplomatic Engagement: Increased diplomatic engagement between the UK and the USTR could lead to better communication and a more constructive negotiation environment. This includes higher-level discussions and direct communication channels.
- Exploring Dispute Resolution Mechanisms: Understanding the dispute resolution mechanisms available within existing trade agreements can be crucial in case of disagreements. The existence of robust dispute resolution processes can help manage potential conflicts.
- Developing Trade Diversification Strategies: Diversifying trade partners could lessen reliance on any single market. This would create more options for trading and importing goods, reducing the risk associated with a single trade relationship.
Contingency Planning for Both Sides
Both the UK and the USTR should prepare contingency plans for the possibility of a failed deal. This preparation involves anticipating potential issues and formulating strategies to mitigate their impact.
- Developing alternative supply chains: In the event of disruptions, both the UK and the USTR should prioritize developing alternative supply chains to minimize dependence on a single trading partner.
- Implementing buffer stocks: Building up buffer stocks of essential goods could help mitigate the effects of potential supply shortages.
- Strengthening domestic industries: Strengthening domestic industries and boosting local production can help reduce reliance on imports and make economies more resilient.
Visual Representation of Key Data
The upcoming trade deal between the UK and the US holds significant potential, but understanding its impact requires a clear visual representation of the existing relationship and the potential consequences. This section dives into key data visualizations to illustrate the trade relationship, potential tariff impacts, and supply chain effects, allowing for a more tangible grasp of the situation.
UK-US Trade Relationship Visualization
The UK and the US enjoy a robust trade relationship, with goods and services flowing in both directions. A Sankey diagram, a flow chart-style visualization, would effectively illustrate the trade flows. The diagram would show the volume of exports and imports between the UK and US for various product categories, such as automotive, technology, and agricultural goods. The width of the connecting lines would represent the magnitude of trade in each category.
A supplementary table could break down the data by specific product sectors for further analysis.
Impact of Tariff Deal on Specific Sectors
A series of bar charts, one for each sector, can visually display the potential impact of tariff reductions or increases. For example, a chart showing the projected change in US exports to the UK of certain agricultural products (e.g., soybeans) due to tariff reductions would clearly highlight the benefits for the relevant sectors. Similarly, a chart displaying the anticipated effect of tariffs on UK exports of high-tech components to the US would show the potential consequences for the technology sector.
Illustrative Examples of Tariff Effects on Supply Chains
Tariffs can disrupt supply chains. A flowchart could illustrate how a tariff on steel imported into the UK from the US might affect a UK car manufacturer. The flowchart would show the original supply chain, then highlight how the tariff would increase the price of steel, impacting the manufacturer’s costs and potentially affecting their ability to compete. Further, a map highlighting the geographic spread of UK-US supply chains would show the potential for wider disruptions.
Infographic of Trade Figures and Potential Tariff Rates
A comprehensive infographic would consolidate key trade figures and potential tariff rates. The infographic could present the total value of UK-US trade, the top five exported goods from the UK to the US, and the top five imported goods from the US to the UK. A segmented bar chart could show the potential tariff rates for different sectors, indicating the specific products or categories subject to potential changes.
The data presented would be clearly labeled and easily understood, providing a concise overview of the economic context.
Epilogue

The discussion between the UK Trade Minister and USTR Greer regarding a potential tariff deal promises to be a significant event, potentially shaping the future of UK-US trade relations. The meeting’s success will depend on finding common ground and addressing concerns from both sides. The potential economic and societal impacts of such a deal are substantial, requiring careful consideration of all perspectives.
The outcomes of this meeting will have implications not only for the UK and the US but also for the global trade landscape.