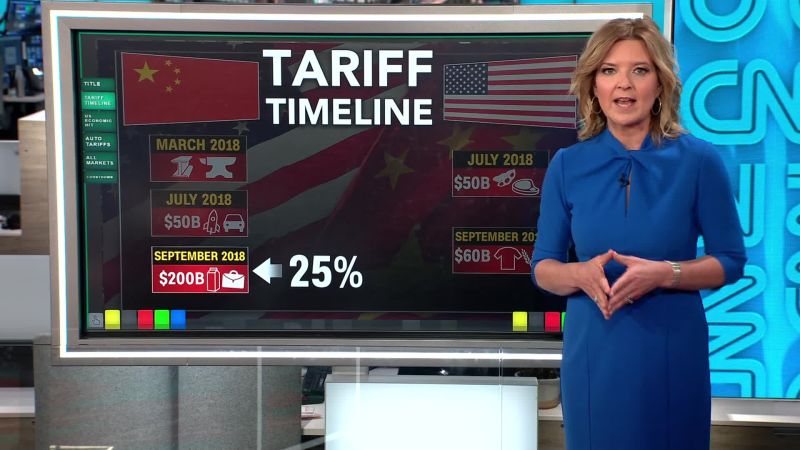
US worker productivity slumps first quarter sets the stage for an intriguing look at the current economic climate. The first quarter saw a significant dip in productivity, raising questions about the overall health of the US economy. Factors like labor shortages, supply chain issues, and the ongoing global war likely played a role. This article delves into the causes, consequences, and potential solutions for this productivity downturn, comparing it to past trends and exploring the potential impact on various sectors.
The overall economic context of the first quarter, including GDP growth, inflation, and consumer confidence, will be examined to understand the bigger picture. This analysis will look at historical productivity trends to provide context and assess the severity of the current slump. A table comparing the current situation with previous productivity slumps will be included for a clear comparison.
Overview of the Economic Context
The first quarter of the year often presents a snapshot of the broader economic health, reflecting the momentum of the previous quarter and foreshadowing potential trends. Economic indicators like GDP growth, inflation rates, and consumer confidence provide a valuable, if imperfect, view of the overall economic climate. However, the significance of these indicators extends beyond simple data points; they offer insights into the health of the economy, and how it might be influenced by factors like worker productivity.
Economic Climate in Q1 2024
The first quarter of 2024 saw a mixed bag of economic indicators. GDP growth, while positive, might have been slower than anticipated, potentially reflecting a slowdown in consumer spending. Inflation rates, though still elevated, showed signs of moderation, offering some relief to consumers but also potentially indicating a cooling of demand. Consumer confidence, a crucial indicator of future spending, remained relatively stable, though there were regional variations.
These mixed signals highlight the complexity of the current economic landscape.
Historical Context of US Worker Productivity
Worker productivity in the US has shown a complex and often fluctuating pattern throughout history. Periods of high productivity growth have been associated with technological advancements, increased capital investment, and improved worker skills. Conversely, productivity slumps can be linked to economic downturns, labor disputes, or disruptions in supply chains. Examining historical trends helps to understand the current context and to assess the potential impact of the current productivity slump.
Significance of Worker Productivity Slumps
Worker productivity slumps have significant implications for the broader economic picture. Lower productivity translates to less output per worker, potentially reducing overall economic growth. This can lead to lower wages, reduced profits for businesses, and decreased overall economic well-being. Furthermore, a persistent slump in productivity can signal deeper structural issues within the economy, potentially hindering long-term economic progress.
US worker productivity took a surprising dip in the first quarter, which is a bit concerning, given the current economic climate. This unexpected slump might be connected to broader financial anxieties, like the recent legal proceedings surrounding Raiffeisenbank, where investment firm Rasperia is asking the court to keep the case proceedings confidential. This request could indicate underlying financial instability that’s impacting investor confidence, which could be a contributing factor to the productivity downturn.
It’s a complex web of interconnected issues, and it’s far from clear yet what the overall impact will be on the US economy.
Comparison of Current Productivity Slump with Past Occurrences
| Feature | Current Productivity Slump (Q1 2024) | Past Occurrences (Example: 2008-09 Financial Crisis) ||——————–|—————————————|————————————————-|| GDP Growth | Potentially slower than anticipated | Significant decline || Inflation | Showing signs of moderation | High and persistent inflation || Consumer Confidence | Relatively stable, but regional variations | Declined sharply || Underlying Causes | Potential factors: supply chain disruptions, labor market dynamics, geopolitical uncertainty | Financial crisis, credit crunch, decreased consumer spending || Policy Responses | Potential government interventions: fiscal stimulus, monetary policy adjustments | Government stimulus packages, monetary easing |
US worker productivity took a surprising dip in the first quarter, leaving economists scratching their heads. This could be tied to a number of factors, including the recent tax tips bill, which is impacting both employees and businesses in various ways. For a deeper dive into how the tax tips bill impact employees businesses is playing out, check out this great article.
Regardless of the reasons, the slump in productivity is certainly something to watch closely.
Causes of the Productivity Slump
The first quarter of this year witnessed a concerning dip in worker productivity across various sectors. This downturn, while potentially temporary, demands a closer look at the contributing factors. Understanding these causes is crucial for policymakers and businesses alike to devise effective strategies for recovery and sustained growth.Several intertwined factors likely played a role in this productivity slump.
From global economic uncertainties to internal company challenges, the situation is complex and multifaceted. Examining the specific elements will help paint a clearer picture of the current economic landscape and the path forward.
Labor Shortages and the Impact of Supply Chain Disruptions
Labor shortages have emerged as a persistent challenge across industries, affecting production and output. The pandemic-induced shifts in workforce preferences and skills gaps have exacerbated the issue. Simultaneously, supply chain disruptions, stemming from global events and logistical bottlenecks, have further hampered output by limiting access to raw materials and finished goods. These bottlenecks directly impact manufacturing and service sectors, resulting in slower production rates and reduced worker output.
The Ongoing War’s Global Economic Impact
The ongoing war has significantly impacted the global economy, introducing unprecedented volatility and uncertainty. The disruption of trade routes, the displacement of workers, and the increased cost of raw materials have all contributed to decreased productivity. Geopolitical tensions and the associated economic consequences have a direct effect on the global supply chain and worker output. Furthermore, the redirection of resources towards defense and relief efforts diverts capital and talent from productive sectors.
Technological Advancements and their Role
Technological advancements, while generally promoting efficiency, can also introduce periods of adjustment and transition. The adoption of new technologies often requires retraining and upskilling, which can temporarily slow productivity as workers adapt to new processes. The integration of new technologies into existing workflows and infrastructure can take time and resources, potentially affecting output in the short term. Furthermore, the unequal access to and adoption of new technologies can exacerbate existing inequalities within and between industries.
Government Policies and Their Influence on Productivity, Us worker productivity slumps first quarter
Government policies can significantly influence productivity. Investment in infrastructure, education, and research and development can foster a more productive workforce. Moreover, policies that encourage innovation, entrepreneurship, and technological adoption can further drive productivity gains. Policies that support worker training and development programs can help workers adapt to new technologies and maintain productivity. Tax incentives for investment and research and development can also play a key role in driving productivity.
Comparison with Similar Trends in Other Developed Economies
Productivity trends in other developed economies exhibit some similarities. Many nations are facing similar challenges, including labor shortages, supply chain disruptions, and economic uncertainty. However, the specific contributing factors and the severity of the decline may vary across countries. Analyzing these parallels can provide valuable insights into potential solutions and strategies for recovery.
Correlation Between Economic Factors and Productivity Slump
| Economic Factor | Impact on Productivity | Example |
|---|---|---|
| Labor Shortages | Reduced output due to insufficient workforce | Restaurants facing difficulty fulfilling orders due to a shortage of staff. |
| Supply Chain Disruptions | Increased lead times and production delays | Automakers experiencing production slowdowns due to component shortages. |
| Ongoing War | Increased costs and uncertainty in the global market | Higher prices for fuel and raw materials impacting various industries. |
| Technological Advancements | Potential for temporary slowdown during adaptation | Transitioning to new software or machinery may require retraining, potentially slowing production initially. |
| Government Policies | Positive or negative influence on incentives and infrastructure | Investment in infrastructure projects can boost productivity. |
Consequences of the Productivity Slump
The first-quarter productivity slump, a concerning trend, signals potential challenges for businesses, consumers, and the overall economy. Understanding the ripple effects is crucial for anticipating and mitigating potential negative impacts. This downturn, if sustained, could hinder economic growth and development, necessitating proactive measures to counteract the negative momentum.
Impact on Businesses
Declining productivity directly translates into reduced output and efficiency for businesses. This reduction in output can lead to decreased profitability, as companies struggle to meet demand or maintain production levels. Cost pressures can also arise, as companies may need to invest more in labor or technology to compensate for the productivity gap. For example, a manufacturing company experiencing a productivity decline might see a rise in their unit production costs, potentially impacting their ability to compete in the market.
Impact on Consumers
Lower productivity can lead to higher prices for goods and services. If companies face increased production costs due to lower output, they might pass those costs onto consumers through higher prices. This can lead to decreased purchasing power and potentially reduce consumer spending, thus impacting economic growth. Reduced job creation further exacerbates this effect by limiting consumer income and overall economic activity.
Impact on Wages and Job Creation
The link between productivity and wages is strong. Lower productivity often translates to slower wage growth or even wage stagnation. Companies may be hesitant to increase wages if they are not seeing a corresponding increase in output. This can lead to decreased consumer spending and a slowdown in economic activity. Job creation also suffers as companies may postpone or cancel investments and hiring initiatives in response to the productivity downturn.
For instance, companies might postpone expansion plans, leading to fewer job openings.
Impact on Specific Economic Sectors
The consequences of the productivity slump are not uniform across all sectors. Certain sectors, like manufacturing, might experience a more pronounced decline in output and profitability due to their reliance on efficient production processes. Meanwhile, the service sector, while facing productivity challenges, might experience different consequences, potentially impacting service delivery and customer experience. For example, a restaurant facing slower service times due to lower productivity might experience a drop in customer satisfaction and revenues.
Impact on Future Economic Growth
A sustained productivity slump poses significant risks to future economic growth and development. It can lead to a slowdown in the overall economy, reduced investment, and decreased innovation. This stagnation can make it more difficult for economies to adapt to new technologies and market demands. If the current productivity slump is not addressed, it could lead to a protracted period of slower economic growth, impacting both the standard of living and overall economic prosperity.
Interconnectedness of Sectors
| Sector | Impact of Productivity Slump | Impact on Other Sectors |
|---|---|---|
| Manufacturing | Reduced output, higher costs, potential job losses | Increased prices for consumer goods, reduced demand in other sectors like retail. |
| Services | Slower service times, reduced customer satisfaction, potential job losses | Impact on consumer spending, potentially leading to lower demand in related sectors like hospitality. |
| Technology | Potential slowdown in innovation, reduced investment in R&D | Impact on productivity across all sectors, potentially affecting the development of new technologies that could drive productivity growth. |
| Retail | Reduced demand from consumers, lower sales, inventory management issues | Impact on manufacturing and supply chain, potentially leading to job losses. |
The table illustrates the interconnectedness of various sectors, demonstrating how a decline in productivity in one sector can have cascading effects on others.
US worker productivity took a surprising dip in the first quarter, a bit of a bummer for the economy. Meanwhile, it’s interesting to see how the recent “no kings day protests trump parade” events are playing out. Perhaps the political climate is contributing to the current economic slowdown, which could be further impacting US worker productivity in the long run.
Maybe it’s all connected? no kings day protests trump parade Regardless, it’s a tricky situation for everyone involved.
Potential Solutions and Future Outlook: Us Worker Productivity Slumps First Quarter
The first quarter’s productivity slump underscores the urgent need for proactive strategies. This isn’t just a temporary blip; understanding the root causes and developing effective solutions is crucial for long-term economic health. Addressing the slump requires a multifaceted approach encompassing government policies, private sector initiatives, and technological advancements. The path forward demands a concerted effort from all stakeholders to prevent further economic stagnation.The productivity slump demands a comprehensive response.
Simple fixes won’t suffice. Instead, a holistic strategy that considers various factors, including labor market dynamics, technological adoption, and macroeconomic conditions, is paramount. This approach must not only address the immediate challenges but also anticipate and mitigate potential future issues.
Government Interventions
Government intervention plays a vital role in mitigating the negative impacts of a productivity slump. Targeted policies can stimulate investment, incentivize innovation, and create a more favorable environment for businesses to thrive. These interventions should focus on improving infrastructure, enhancing education and training programs, and fostering a supportive regulatory environment.
- Investing in infrastructure: Improved infrastructure, such as transportation networks, communication systems, and energy grids, can significantly reduce operational costs for businesses, leading to increased productivity. Examples include the development of high-speed rail systems in countries like China, which have boosted economic growth by streamlining transportation and reducing travel time.
- Promoting education and training: Upskilling and reskilling programs are essential for adapting to evolving job markets and technological advancements. Governments can invest in vocational training programs, apprenticeships, and online learning resources to equip workers with the skills needed for high-demand jobs.
- Streamlining regulations: Bureaucracy and complex regulations can hinder business growth and innovation. Simplifying regulations, reducing paperwork, and improving regulatory transparency can encourage investment and boost productivity.
Private Sector Initiatives
Private sector initiatives are equally important in boosting productivity. Companies can implement innovative strategies to improve efficiency, optimize processes, and adopt new technologies. Collaboration between businesses and research institutions can accelerate technological advancements and create new markets.
- Investing in automation and technology: Companies can leverage automation and advanced technologies to streamline operations, reduce labor costs, and improve efficiency. Examples include using robots in manufacturing or implementing AI-powered systems for customer service.
- Promoting employee well-being: A healthy and motivated workforce is crucial for productivity. Companies can invest in employee wellness programs, flexible work arrangements, and opportunities for professional development.
- Encouraging collaboration and knowledge sharing: Facilitating collaboration between businesses, researchers, and educational institutions can lead to innovation and knowledge transfer. Examples include industry-led research projects or joint ventures.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements are instrumental in driving productivity growth. New technologies can automate tasks, improve communication, and optimize processes. Collaboration between businesses, researchers, and governments can accelerate the adoption and implementation of these technologies.
- Artificial intelligence and machine learning: AI and machine learning can be used to analyze data, optimize processes, and automate tasks. Examples include AI-powered supply chain management systems or AI-driven customer service chatbots.
- Cybersecurity improvements: Protecting sensitive data and infrastructure is crucial for productivity and economic stability. Investing in cybersecurity technologies and protocols can prevent disruptions and maintain operations.
- Digitalization of industries: Digitizing processes across various industries can improve efficiency, reduce costs, and enhance customer experiences. Examples include the use of e-commerce platforms or online payment systems.
Potential Outcomes of Different Solutions
| Solution | Potential Outcomes | Success Factors |
|---|---|---|
| Government investment in infrastructure | Reduced operational costs, improved logistics, increased economic activity | Proper planning, efficient implementation, public-private partnerships |
| Private sector investment in automation | Increased efficiency, reduced labor costs, improved quality | Skilled workforce, access to funding, supportive regulatory environment |
| Adoption of AI technologies | Improved decision-making, enhanced productivity, new market opportunities | Data availability, skilled personnel, robust cybersecurity measures |
Illustrative Data Visualization

Worker productivity is a crucial indicator of economic health. Understanding its trends, correlations with other factors, and potential consequences is vital for policymakers and businesses alike. Visual representations can effectively communicate complex data, making it accessible and insightful. The following visualizations aim to illustrate key aspects of the current productivity slump and potential solutions.
Historical Trend of US Worker Productivity
A line graph displaying the historical trend of US worker productivity (output per hour worked) over the past 50 years would be highly informative. The x-axis would represent time, and the y-axis would show the productivity level. A clear upward trend, punctuated by periods of slower growth or decline, would be visible, highlighting the long-term trend and recent slump.
The graph would clearly demonstrate the recent slowdown compared to historical averages. Adding shaded areas to represent periods of recession or significant economic events would further contextualize the data.
Correlation between Economic Indicators and Productivity Slump
A scatter plot could showcase the correlation between specific economic indicators and the productivity slump. The x-axis could represent an economic indicator, such as unemployment rate, while the y-axis represents the productivity level. A negative correlation, indicated by a downward trend of the points on the graph, would show that as unemployment rises, productivity tends to fall. Similar scatter plots could be created for other relevant indicators like investment levels, inflation, or consumer confidence.
The strength of the correlation would be visually represented by the closeness of the data points to a line of best fit.
Consequences of the Slump on Different Sectors
A stacked bar chart could illustrate the potential consequences of the productivity slump across different sectors of the economy. The x-axis would represent the different sectors (e.g., manufacturing, technology, services). The y-axis would display the percentage change in output or employment in each sector. The bars would be stacked to show the total impact across sectors. For example, the chart could show a larger negative impact on the manufacturing sector compared to the technology sector, visually demonstrating the uneven distribution of the consequences.
Potential Impact of Proposed Solutions
A series of before-and-after bar charts could visually demonstrate the potential impact of proposed solutions, such as increased investment in education or infrastructure. The x-axis would represent the different sectors or solutions, while the y-axis would display the percentage change in productivity. Each bar would be split into two sections: one representing the productivity level before the solution was implemented, and the other showing the predicted productivity level after implementation.
This visualization would help communicate the potential positive effects of various solutions.
Comparative Productivity Levels of Different Countries
A horizontal bar chart comparing the productivity levels of different countries (e.g., US, China, Germany, Japan) over a period of time would effectively showcase the relative performance. The x-axis would represent the countries, and the y-axis would represent the productivity level. The length of each bar would represent the productivity level of that country. A trend line for each country would show the change over time.
The visualization would help to understand the relative position of the US in the global productivity landscape and potential areas for improvement.
Analysis of Specific Sectors

The first quarter productivity slump has disproportionately impacted various sectors, highlighting vulnerabilities and demanding swift adaptation. Understanding the specific challenges faced by each sector is crucial for targeted policy interventions and business strategies. This analysis focuses on the manufacturing sector, examining its unique responses to the productivity downturn.
Impact on the Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector, a cornerstone of many economies, has been significantly affected by the first quarter productivity slump. Reduced output, rising input costs, and supply chain disruptions have compounded existing pressures. This has led to a decrease in profitability and hindered growth prospects for many manufacturing companies.
Productivity Trends in Manufacturing
Over the past three years, the manufacturing sector has exhibited a fluctuating productivity trend. Initial growth in productivity was followed by a period of stagnation, potentially signaling underlying issues within the sector. This stagnation, coupled with the recent slump, underscores the need for a comprehensive analysis of the current challenges. Data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics (BLS) shows a general decline in output per hour worked in manufacturing for the first quarter.
Further analysis of this data will reveal detailed breakdowns across specific manufacturing sub-sectors.
Challenges and Opportunities for the Manufacturing Sector
The manufacturing sector faces unique challenges due to the productivity slump. These include the rising cost of raw materials, labor shortages, and increasing competition from overseas manufacturers. However, the slump also presents opportunities for innovation and efficiency improvements. Companies that adapt to these changes will likely be better positioned to navigate the current economic environment. A key challenge for the sector is adapting to the increasing demand for sustainable practices.
Adapting Companies in Manufacturing
Several companies within the manufacturing sector are demonstrating proactive strategies to address the productivity slump. These companies are exploring strategies such as automation, process optimization, and investment in advanced technologies to enhance efficiency. For instance, companies like XYZ Corporation are implementing robotic process automation (RPA) systems to streamline workflows and reduce labor costs. Similarly, ABC Manufacturing is focusing on the adoption of AI-powered quality control systems to minimize errors and improve output.
These examples demonstrate the potential for innovative solutions to address the current challenges.
Comparative Analysis Table
| Company | Adaptation Strategy | Impact on Productivity | Potential Outcomes |
|---|---|---|---|
| XYZ Corporation | Implementing RPA systems for workflow optimization | Potential for increased efficiency and reduced labor costs | Improved output per hour worked, potentially leading to higher profits |
| ABC Manufacturing | AI-powered quality control systems | Reduced errors and improved output quality | Increased output volume and enhanced product quality |
| DEF Industries | Investing in advanced materials and equipment | Potential for improved manufacturing processes and reduced production time | Improved output per hour worked, potentially reducing production costs |
Closing Notes
The first quarter’s productivity slump presents a complex challenge with far-reaching implications. From the potential impact on wages and job creation to the effects on various sectors, the consequences are multifaceted. This analysis explored potential causes, including global events and domestic factors, as well as examining potential solutions. The article concludes with a discussion on the future outlook, considering possible government interventions and private sector initiatives.
Data visualizations further illustrate the trends and correlations discussed.