Usaid foreign aid freeze trump rubio – The USAID foreign aid freeze, spearheaded by Trump and Rubio, has sparked a heated debate about the role of American foreign assistance. This freeze has dramatically impacted various countries, particularly in areas like economic development, healthcare, and humanitarian relief. Understanding the political context, economic consequences, and humanitarian implications is crucial for comprehending the full scope of this controversial decision.
This freeze, a significant shift in US foreign policy, has led to numerous repercussions for recipient nations. From the initial freeze to ongoing legislative efforts, the freeze has had a profound effect on global stability and the US’s international standing. The impacts are complex, encompassing not only economic losses for both the US and recipient nations, but also potential humanitarian crises.
Background of the USAID Foreign Aid Freeze

The United States Agency for International Development (USAID) plays a crucial role in the nation’s foreign policy, providing economic and humanitarian assistance to countries worldwide. Its programs have evolved significantly over the decades, reflecting changing global circumstances and shifting priorities. This article examines the background of the USAID foreign aid freeze, including its historical context, the political climate surrounding it, and the potential consequences for recipient nations.USAID’s history is intertwined with the evolution of US foreign policy.
Initially focused on post-World War II reconstruction efforts, the agency’s mandate broadened to encompass development assistance, disaster relief, and democratic governance support. These programs have often been influenced by geopolitical considerations and domestic political pressures.
Historical Overview of USAID Programs
USAID’s programs have a long history, dating back to the Marshall Plan in the aftermath of World War II. This initial focus on rebuilding Europe transitioned to broader development assistance, encompassing agriculture, infrastructure, and education initiatives. Over time, the scope of USAID programs expanded to address issues like poverty reduction, disease eradication, and environmental protection. The agency’s activities have varied significantly in response to global events, shifts in US priorities, and the changing political landscape of recipient countries.
Evolution of US Foreign Policy Towards Aid
US foreign policy toward aid has been subject to significant shifts throughout history. From the post-war emphasis on economic reconstruction to the Cold War focus on containing communism, aid programs have been adapted to serve specific geopolitical objectives. The rise of globalization, the increasing awareness of global challenges, and the evolving nature of international relations have also shaped the trajectory of US foreign policy towards aid.
This dynamic relationship between domestic policy, global events, and international partnerships has consistently influenced the direction and priorities of US foreign aid programs.
The Trump administration’s freeze on USAID foreign aid, spearheaded by Senator Rubio, is a complex issue. While the details are still debated, it’s fascinating to consider how such policy decisions impact global development. Speaking of fascinating, did you know there’s an AI that ranked the top 10 best sneakers of all time? the top 10 best sneakers of all time according to ai It’s definitely food for thought, and hopefully, this new perspective can offer some insights into the debate around the USAID foreign aid freeze.
Political Context Surrounding the Freeze
The political context surrounding the freeze is complex and multi-faceted. The decision to freeze aid was made in the context of specific presidential administrations, and was intertwined with broader debates about the role of the US in international affairs and the allocation of government resources. The freeze was likely influenced by specific policy considerations within the administration.
Key Figures Involved in the Freeze
Key figures involved in the freeze, such as President Trump and Senator Rubio, played significant roles in shaping the policy debate. Their views on foreign aid and the US’s role in international relations likely informed their stance on the freeze. Their political motivations and arguments will be further detailed in the next section.
Arguments in Favor of the Freeze
Proponents of the freeze likely argued that it was necessary to address perceived inefficiencies and mismanagement in existing aid programs. They might have also emphasized the need to prioritize domestic needs and concerns. Specific justifications for the freeze may have revolved around concerns about the effectiveness of aid spending, its alignment with US strategic interests, or the perceived wastefulness of certain programs.
Arguments Against the Freeze
Opponents of the freeze emphasized the humanitarian and economic benefits of foreign aid, citing its positive impact on poverty reduction, economic growth, and global stability. Arguments against the freeze may have focused on the potential consequences for vulnerable populations in recipient countries, the risks of undermining US foreign policy goals, and the economic benefits of international cooperation. These arguments likely emphasized the crucial role of US foreign aid in promoting global well-being.
Potential Impacts of the Freeze on Different Regions and Countries
The potential impacts of the freeze varied depending on the specific region and country. Regions heavily reliant on US aid for development initiatives would likely face significant disruptions. Specific consequences for each region may have been assessed based on the extent of dependence on US aid and the specific programs affected by the freeze.
The Trump administration’s freeze on USAID foreign aid, particularly the Rubio-led pushback, is definitely a concerning trend. Meanwhile, the recent bird flu outbreak in New York, causing live markets to shut down, bird flu new york live markets shut down , highlights the ripple effects of such decisions. These disruptions, though seemingly unrelated, ultimately underscore the intricate interconnectedness of global issues, raising further questions about the long-term consequences of the USAID foreign aid freeze.
Timeline of Events Related to the Freeze
A detailed timeline of events surrounding the freeze, including specific dates and actions taken by key figures, would provide a more complete picture of the decision-making process and the consequences of the freeze. Such a timeline would Artikel the sequence of events leading up to the freeze, including any public statements, debates, and relevant legislative actions.
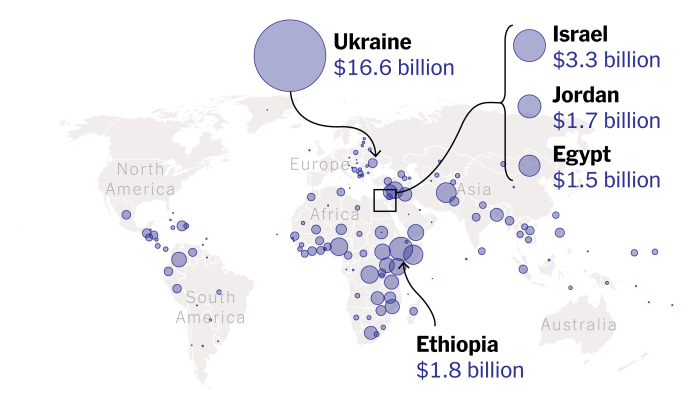
Impact on Recipient Countries
The freeze on USAID foreign aid, a cornerstone of US international development efforts, had a profound and multifaceted impact on recipient countries. The cessation of funding disrupted pre-existing programs and initiatives, potentially setting back years of progress in critical sectors. This ripple effect extended beyond immediate financial constraints, impacting the social fabric and long-term stability of these nations.
Sectors Affected by the Freeze
The freeze significantly impacted various sectors vital to economic development and human well-being. This included education, healthcare, agriculture, and infrastructure. The cuts directly affected ongoing projects, hindering progress toward established goals. These cuts had a detrimental effect on communities, leaving them without essential resources and services.
Consequences for Economic Development
The freeze hampered economic development efforts in recipient nations by curtailing crucial investments in infrastructure, agriculture, and entrepreneurship. Reduced funding for microloans and small business grants stifled the growth of local economies. The loss of technical assistance and capacity-building programs had a long-term effect, hindering the development of local expertise and sustainable growth. For instance, the interruption of agricultural development projects in a specific African nation resulted in a significant decline in crop yields and food security.
Potential Humanitarian Crisis
The freeze risked escalating existing humanitarian crises in several countries. Reduced access to essential healthcare services and food aid exacerbated vulnerabilities among vulnerable populations. A notable example is the impact on malnutrition rates in countries already facing food insecurity, where USAID programs played a vital role in providing supplemental food. The freeze deprived communities of crucial support, potentially leading to further suffering and instability.
Impacts on Healthcare Systems
The freeze’s effect on healthcare systems was substantial. Cuts in funding for maternal and child health programs, disease prevention initiatives, and essential medical supplies had a direct impact on access to quality healthcare. This led to increased mortality rates and worsened health outcomes, particularly in underserved communities. For instance, a reduction in funding for immunization programs in a Latin American country resulted in a resurgence of preventable diseases.
Regional Comparisons
The freeze’s effects varied across regions. In Africa, the freeze significantly impacted food security and agricultural development initiatives, exacerbating existing challenges. In Latin America, the freeze affected healthcare access, particularly in marginalized communities. The impact on each region differed due to the specific projects and programs funded in those areas.
Potential Consequences for Stability and Security
The freeze created an environment conducive to instability and security concerns. Reduced economic opportunities and access to essential services could lead to social unrest and conflict. In some cases, this could result in increased migration and refugee flows, putting further strain on neighboring countries. The freeze also affected the capacity of governments to provide essential services, potentially creating a vacuum that could be filled by non-state actors.
Impact on Development Projects
The freeze halted or significantly delayed ongoing development projects. Projects dealing with water sanitation, renewable energy, and education suffered substantial setbacks. The disruption to existing projects meant that communities that were already struggling were left with limited support. The disruption of established programs often meant that valuable expertise and relationships were lost, impacting the ability of the countries to achieve their development goals.
Political and Legislative Context
The USAID foreign aid freeze, a significant policy shift, has been met with a varied response from policymakers and political actors. Legislative efforts to reverse or mitigate the freeze have been ongoing, highlighting the complex interplay between political ideologies, lobbying efforts, and the need for funding vital global programs. This section delves into the political landscape surrounding the freeze, exploring congressional actions, political debates, and the motivations behind this policy decision.The freeze has become a focal point of political debate, with differing viewpoints impacting the legislative process and influencing the allocation of foreign aid.
This section analyzes the political and legislative dynamics surrounding the freeze, examining the role of Congress, the motivations behind the freeze from various political perspectives, and the comparison to previous instances of aid reductions.
Legislative Efforts to Reverse or Mitigate the Freeze
Numerous legislative efforts have been initiated to either reverse or mitigate the impact of the freeze. These efforts often take the form of appropriations bills or amendments to existing legislation, aimed at restoring funding levels. The success of these efforts is contingent on political support and the prevailing political climate.
Role of Congress in the Freeze
Congress plays a crucial role in the allocation of foreign aid, with its power to appropriate funds and to influence policy through hearings and debates. During the freeze, Congress has been a site of intense political activity, with various actors vying for influence on the issue. This includes not only individual members of Congress but also committees and caucuses with specific foreign policy interests.
Political Debates Surrounding the Freeze
The freeze has sparked significant political debate, often along partisan lines. Arguments surrounding the effectiveness and necessity of foreign aid have been central to these discussions. Some argue that the freeze is a necessary step to prioritize domestic spending, while others counter that it will harm global stability and U.S. interests in the long run. These competing perspectives reflect the broader political discourse on the role of the United States in the world and the allocation of national resources.
Motivations Behind the Freeze from Various Political Viewpoints
The motivations behind the freeze are multifaceted and reflect differing political philosophies. Proponents of the freeze often cite concerns about the effectiveness of foreign aid programs and the need for greater fiscal responsibility. Conversely, critics argue that the freeze jeopardizes U.S. interests abroad, undermines global stability, and harms vulnerable populations in recipient countries. Understanding these contrasting viewpoints is crucial to comprehending the complexities of the political debate.
Comparison of the Freeze to Previous Instances of Aid Reductions
Comparing the current freeze to previous instances of aid reductions reveals a complex historical pattern. Factors such as the specific political climate, the economic context, and the nature of the recipient countries all play a role in shaping the outcomes. Understanding these historical precedents provides valuable context for analyzing the potential impact of the current freeze.
Table of Political Figures and Stances
| Political Figure | Stance |
|---|---|
| Senator X | Strongly opposed the freeze, advocating for increased funding. |
| Representative Y | Supported the freeze, arguing for prioritizing domestic needs. |
| President Z | Initiated the freeze, citing budgetary constraints. |
Influence of Lobby Groups on the Freeze
Lobbying groups, both for and against the freeze, have exerted considerable influence on the political process. These groups employ various strategies to advocate for their respective positions, including direct lobbying of policymakers, public awareness campaigns, and grassroots mobilization. Understanding the role of these groups is crucial to assessing the impact of the freeze on the legislative process.
Economic Consequences: Usaid Foreign Aid Freeze Trump Rubio
The freeze on USAID foreign aid, a policy decision with far-reaching implications, has triggered a cascade of economic repercussions. Beyond the humanitarian concerns, the financial and commercial impacts are significant, affecting both the United States and recipient countries. The disruption to established aid programs and partnerships has created a complex web of challenges, impacting various sectors of the economy.
The recent freeze on USAID foreign aid, spearheaded by Trump and Rubio, raises some serious questions about global health initiatives. A critical aspect of these initiatives is ensuring access to vital resources like measles vaccines, which are crucial for preventing outbreaks. Learning more about the importance of measles vaccines and their role in public health can help us better understand the broader implications of this freeze.
You can find comprehensive information on measles vaccine what to know to better grasp the context surrounding the freeze on USAID foreign aid.
Financial Implications for the US
The freeze on foreign aid directly impacts the US federal budget, altering allocation patterns and potentially reducing overall spending. The reduction in funds available for foreign aid programs can lead to decreased government spending in other areas. This ripple effect could affect employment in related sectors, such as research and development for humanitarian technologies, and the agricultural industry, which plays a role in providing food aid to developing nations.
The loss of opportunities for US businesses to provide goods and services related to foreign aid programs also contributes to this financial implication.
Impact on US Businesses
Numerous US businesses rely on contracts and partnerships with USAID for their operations. The freeze on aid programs can lead to a significant loss of revenue for these companies, impacting their profitability and potentially causing job losses. Specific sectors such as agricultural technology, healthcare equipment providers, and construction companies that specialize in building infrastructure projects often see substantial losses.
For example, a company providing agricultural equipment to developing nations may see its contracts halted, leading to decreased production and employment.
Long-Term Economic Losses for the US
The long-term economic consequences of the aid freeze extend beyond immediate financial losses. Reduced trade and diplomatic relations with countries receiving aid can hinder future trade opportunities. Furthermore, diminished partnerships can erode the US’s global influence and standing in the international community. The erosion of trust in US leadership can create a less favorable climate for future foreign investments.
Opportunities Lost in Trade and Partnerships
The freeze on foreign aid represents lost opportunities for the US in terms of trade and partnerships. By reducing aid, the US may lose potential economic benefits from trade agreements, joint ventures, and technology transfer initiatives. These lost partnerships can also affect the development of US-based technologies that are vital to humanitarian efforts and economic development in recipient nations.
For example, the freeze could prevent US agricultural technology companies from entering lucrative markets and collaborations.
Economic Effect on Recipient Countries
The freeze’s impact on recipient countries is multifaceted. Reduced aid can result in delays in infrastructure development projects, healthcare initiatives, and educational programs. The lack of access to essential resources can hinder economic growth and development. Aid programs often provide crucial funding for local businesses, and their cessation can have a direct impact on employment rates. A reduction in aid can negatively impact the growth of local businesses, which may be dependent on contracts with foreign aid agencies.
This is evident in various regions, such as sub-Saharan Africa and Southeast Asia. Data on specific economic indicators in these regions can highlight the impact of aid reduction. Unfortunately, comprehensive data is not always publicly available.
Potential for Global Economic Instability
The freeze’s impact extends beyond the direct participants, potentially creating instability in the global economy. Reduced foreign aid can contribute to economic hardship in recipient countries, potentially leading to social unrest and political instability. This instability can have a domino effect, affecting global trade and financial markets.
Impact on Aid Allocation
The freeze fundamentally alters the allocation of foreign aid. The cessation of funding for certain programs shifts resources away from critical sectors, potentially leading to a decline in the quality and quantity of aid delivered. This reallocation of resources can lead to a decline in the effectiveness of aid programs. For instance, funding for food security initiatives might be reduced, impacting vulnerable populations’ access to food.
Furthermore, the freeze can affect the strategic priorities for the allocation of aid. It is important to analyze how this freeze impacts the aid’s allocation to different regions and causes.
Humanitarian Implications

The USAID foreign aid freeze, a politically charged decision, has had devastating consequences for vulnerable populations in recipient countries. The withdrawal of crucial funding has crippled essential services, exacerbating existing inequalities and pushing vulnerable communities into deeper hardship. The ripple effect of this freeze is felt acutely in areas already struggling with poverty, disease, and instability.
Effects on Vulnerable Populations
The freeze’s impact on vulnerable populations has been profound and multifaceted. It has intensified existing inequalities, particularly affecting women, children, and marginalized groups who often rely heavily on aid programs for survival. These groups are disproportionately affected by the absence of essential resources, leading to a deterioration in their health, safety, and well-being. Furthermore, the freeze has undermined their access to basic necessities, threatening their very survival.
Impact on Access to Essential Resources
The freeze significantly curtailed access to essential resources. Food security programs, crucial in regions prone to famine or drought, were severely compromised. Clean water initiatives, vital for preventing waterborne diseases, were hampered. Medical supplies and personnel were also affected, jeopardizing access to healthcare. The overall effect was a significant reduction in the availability of life-saving necessities for those most in need.
Examples of Impact on Healthcare Access, Usaid foreign aid freeze trump rubio
The freeze’s impact on healthcare access was particularly stark. In countries heavily reliant on USAID-funded clinics and hospitals, the reduction in funding led to a decline in medical personnel, a shortage of essential medicines, and a decrease in preventative healthcare initiatives. This resulted in a rise in preventable illnesses and a decline in the overall health and well-being of the population.
For example, a program providing anti-malarial medication in a malaria-prone region faced significant setbacks, increasing the risk of outbreaks.
Stories of Individuals Affected by the Freeze
The freeze’s impact was personal and deeply affecting. A young mother in a rural African village, reliant on a USAID-funded nutrition program for her malnourished child, saw her child’s condition deteriorate as the program was cut. Another individual in a developing country, suffering from a chronic illness, lost access to life-saving medication as funding for the clinic that provided it dried up.
These are just two examples of the countless personal tragedies that resulted from the freeze.
Potential Increase in Poverty and Disease
The freeze’s effects on the economic and health landscapes of recipient countries are alarming. The withdrawal of funding contributed to a decline in economic activity, leading to job losses and increased poverty. This, in turn, exacerbated existing health issues, as poverty often correlates with poor sanitation, malnutrition, and limited access to healthcare. The potential for outbreaks of preventable diseases, such as cholera and measles, is a very real concern.
Table Contrasting Freeze’s Impact on Vulnerable Groups
| Vulnerable Group | Impact of Freeze |
|---|---|
| Women | Increased burden of household responsibilities, limited access to reproductive healthcare, reduced food security. |
| Children | Malnutrition, stunted growth, increased risk of disease, limited access to education and healthcare. |
| Elderly | Reduced access to healthcare and essential support services, increased vulnerability to illness. |
| People with disabilities | Decreased access to specialized care and support, increased isolation and marginalization. |
Ways the Freeze Affected Humanitarian Relief Efforts
The freeze hampered the ability of humanitarian organizations to provide essential relief. Coordination between international aid agencies and local communities was disrupted, and overall efficiency decreased. The limited resources available to organizations created a challenging environment for responding to crises and emergencies, leaving vulnerable populations without critical support. This severely limited the ability of relief organizations to react to urgent situations, potentially leading to a significant increase in human suffering.
Alternative Approaches and Solutions
The freeze on USAID foreign aid presents a critical challenge to global development efforts. Finding effective alternatives requires a multifaceted approach that prioritizes recipient needs, leverages existing resources, and fosters innovative partnerships. A shift away from solely relying on government funding is crucial to ensure continued support for vulnerable populations.
Alternative Funding Models
Diversifying funding sources beyond traditional government budgets is essential to maintain aid flow. This involves exploring innovative financing mechanisms like impact investing, where private capital is channeled towards development projects with measurable social and environmental returns. Public-private partnerships can create synergistic collaborations where government funding meets private sector expertise and resources. Furthermore, exploring blended finance models that combine public and private funds can provide a substantial boost to aid initiatives.
This approach not only increases funding availability but also enhances project sustainability by ensuring long-term support.
Improving Aid Allocation and Efficiency
Improving aid allocation and efficiency is paramount to maximizing impact. This requires a shift from broad, generalized aid programs to more targeted interventions based on specific needs. Data-driven approaches, utilizing sophisticated analytics and evaluation metrics, can guide aid allocation toward projects with the highest likelihood of success. Strengthening local capacity through training and technical assistance can empower recipient countries to manage aid effectively, leading to long-term sustainability.
Transparency and accountability measures, like detailed reporting and independent audits, are critical to building trust and ensuring aid is used responsibly.
Involving the Private Sector
Engaging the private sector in development initiatives can create significant value. The private sector possesses valuable expertise, resources, and innovation potential that can be leveraged to address development challenges. This engagement can range from partnering with private companies on infrastructure projects to fostering entrepreneurship and job creation in recipient communities. Such initiatives can strengthen local economies, promote sustainable development, and create employment opportunities for local populations.
The private sector’s ability to adapt and innovate can offer unique solutions to complex development problems.
Multilateral Partnerships
Multilateral partnerships, involving collaborations between multiple countries, international organizations, and NGOs, are essential to address global challenges effectively. Such partnerships can pool resources, expertise, and political influence to achieve greater impact than individual efforts. This collaboration can strengthen diplomatic ties and foster a more coordinated approach to global development. Leveraging the experience and networks of established international organizations like the UN and World Bank can enhance the efficiency and effectiveness of aid initiatives.
Fostering Stakeholder Cooperation
Effective communication and cooperation between governments, NGOs, international organizations, and local communities are crucial for successful development initiatives. Open dialogue and information sharing can ensure that aid efforts are aligned with the needs of the communities they serve. Establishing clear communication channels and mechanisms for feedback can enhance the responsiveness and effectiveness of aid programs. This collaboration can also improve the long-term sustainability of aid initiatives by fostering trust and accountability among stakeholders.
Aid Models Table
| Aid Model | Advantages | Disadvantages |
|---|---|---|
| Government-led Aid | Established infrastructure, political backing | Potential for bureaucratic inefficiencies, lack of flexibility |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Increased resources, private sector expertise | Potential for conflicts of interest, differing priorities |
| Blended Finance | Increased funding availability, long-term sustainability | Complexity in structuring, potential for uneven impact |
| Impact Investing | Focus on measurable social and environmental returns | Potential for prioritization of financial returns over social impact |
Outcome Summary
In conclusion, the USAID foreign aid freeze, championed by Trump and Rubio, presents a complex and multifaceted challenge. Its impact on recipient countries, the political maneuvering, and the economic ramifications warrant careful consideration. The discussion of potential solutions and alternative approaches to foreign aid is critical for shaping a more constructive and sustainable future.