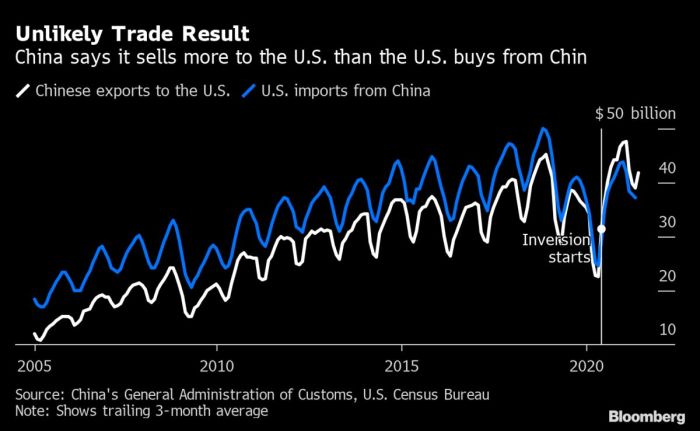
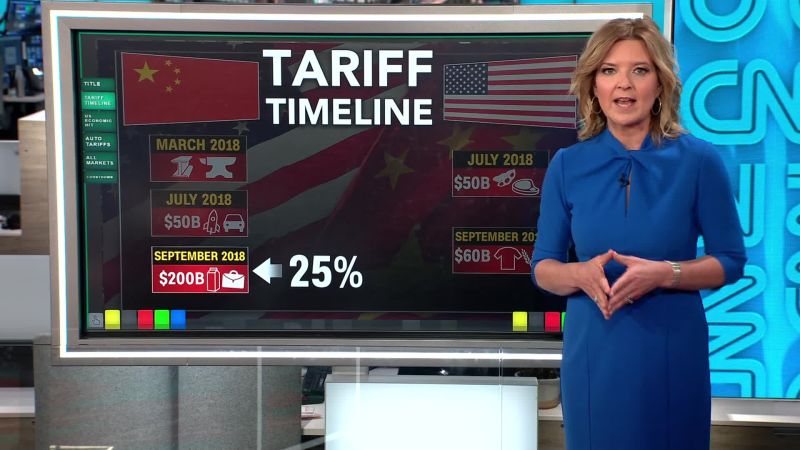
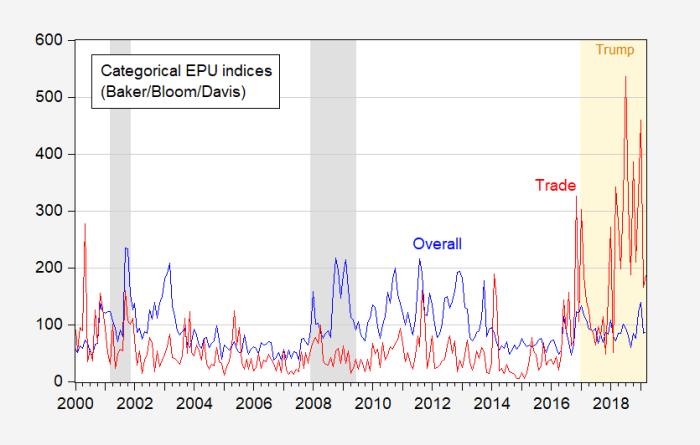
With world bank slashes global growth forecast trade tensions bite, the global economic outlook is darkening. The World Bank’s recent revision paints a concerning picture, suggesting a significant slowdown in global economic expansion. This downturn is largely attributed to escalating trade tensions, which are disrupting international trade flows and dampening investor confidence. The revised forecast predicts a considerable impact on various sectors, especially emerging markets, with potentially severe consequences for their development.
A detailed breakdown of projected growth rates, before and after the revision, for key countries will be presented, offering a clear comparison of the predicted economic performance.
Global Economic Impact
The World Bank’s recent downward revision of its global growth forecast underscores the growing challenges facing the world economy. Trade tensions, persistent inflation, and geopolitical uncertainties are all contributing factors to this concerning trend. This revision signals a potential slowdown in economic activity across various sectors and regions, with potentially significant consequences for emerging markets.
World Bank’s Revised Global Growth Forecast
The World Bank has lowered its global growth projection for 2024, citing a multitude of factors including the persistent impact of geopolitical events and the ongoing trade conflicts. This revised forecast reflects a more cautious outlook on the global economic landscape. The decrease in projected growth highlights the interconnectedness of global economies and the ripple effects of these uncertainties.
Impact on Different Sectors
The revised forecast is expected to have a discernible impact on various sectors of the global economy. Manufacturing, heavily reliant on international trade, is anticipated to experience a slowdown due to reduced demand and supply chain disruptions. The service sector, particularly in tourism and hospitality, could also see a decline in activity if consumer confidence and international travel decrease.
Furthermore, the agricultural sector might face challenges due to fluctuating commodity prices and potential disruptions in supply chains. These combined effects can potentially lead to reduced employment opportunities and a contraction in investment across various sectors.
Comparison with Previous Projections and Reasons for Revision
The current global growth forecast is lower than previous projections. The primary reasons for this downward revision include escalating trade tensions, increased interest rates implemented by central banks to combat inflation, and the persistent uncertainty surrounding geopolitical events. These factors have created a climate of economic anxiety, reducing consumer and investor confidence, and thereby impacting future investment and consumption.
For instance, the war in Ukraine continues to disrupt global energy markets and supply chains, impacting the overall global economic outlook.
Potential Consequences for Emerging Markets
Emerging markets are particularly vulnerable to a decrease in global growth. These economies often rely heavily on exports and foreign investment. A slowdown in global demand can lead to decreased export revenues and reduced foreign direct investment, potentially impacting their economic stability and development prospects. The impact of the revised forecast could be felt most acutely in developing countries that rely heavily on global trade for their economic progress.
Projected Growth Rates by Country (Pre-Revision vs. Post-Revision), World bank slashes global growth forecast trade tensions bite
| Country | Pre-Revision Growth Rate | Post-Revision Growth Rate | Reason for Revision |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | 2.5% | 2.0% | Rising interest rates and persistent inflation. |
| China | 5.2% | 4.8% | Geopolitical tensions and ongoing property sector challenges. |
| India | 6.5% | 6.0% | Global economic slowdown impacting exports and investment. |
| Brazil | 2.7% | 2.3% | Increased interest rates and high inflation. |
| Mexico | 2.9% | 2.5% | Reduced demand from major trading partners and high fuel prices. |
Note: These figures are illustrative examples and may not represent the exact figures from the World Bank report. Data and projections are subject to change.
Trade Tensions’ Role: World Bank Slashes Global Growth Forecast Trade Tensions Bite
Global economic anxieties are mounting, with the World Bank slashing its global growth forecast. A significant contributing factor is the escalating intensity of trade tensions between major economies. These tensions are disrupting supply chains, impacting investment decisions, and ultimately affecting the livelihoods of millions worldwide. Understanding the intricacies of these trade disputes is crucial to grasping the full picture of the current economic climate.
Impact on Global Growth
The World Bank’s revised forecast reflects the chilling effect of trade conflicts. Protectionist measures, tariffs, and trade wars create uncertainty in the global marketplace. Businesses hesitate to invest, consumers reduce spending, and overall economic activity slows down. This is often seen in reduced export volumes, decreased foreign direct investment, and decreased productivity.
Specific Trade Tensions
Trade disputes often involve accusations of unfair trade practices, intellectual property theft, and concerns about market access. Key examples include the US-China trade war, the EU-China trade tensions, and the trade disputes between the US and other countries like Japan and Mexico. These conflicts often involve complex issues beyond simple trade imbalances. The imposition of tariffs and quotas by one country often triggers retaliatory measures from other countries, creating a domino effect of trade restrictions.
The World Bank’s gloomy global growth forecast is a pretty big deal, highlighting the bite of trade tensions. It’s a worrying sign for the world economy. However, there’s a glimmer of hope, as Lutnick says US-China talks are progressing well and could wrap up by Wednesday , potentially mitigating some of the economic headwinds. Hopefully, these positive discussions will help to offset the negative impacts of the World Bank’s forecast.
Impact on International Trade Flows and Investment
Trade tensions significantly disrupt international trade flows. Tariffs increase the cost of imported goods, potentially impacting consumer prices and reducing the competitiveness of domestic industries. This can also result in decreased foreign direct investment as companies face greater uncertainty and higher costs associated with international trade. For example, a significant increase in steel tariffs may encourage the closure of steel plants in some countries and shift investment elsewhere.
Consequences of Trade Protectionism for Different Countries
Trade protectionism can have varied consequences for different countries. Developed nations with strong domestic industries may experience some short-term gains from protecting their industries, but can also face negative impacts like reduced consumer choice and higher prices. Developing countries often face a greater economic burden, as their exports may be targeted by trade restrictions, hindering their economic growth.
For example, agricultural exports from developing countries can be severely impacted by tariffs imposed by developed countries.
Examples of Trade Disputes Impacting Global Growth
The US-China trade war, initiated by the imposition of tariffs on Chinese goods, is a prime example. This dispute significantly affected global trade volumes and contributed to the slowdown in global growth. Other examples include the trade disputes between the EU and various countries, which have also had repercussions on international trade flows. The uncertainty created by these disputes has discouraged investment and negatively impacted consumer confidence, slowing down economic activity across the globe.
The World Bank’s recent slashing of the global growth forecast highlights the serious impact of trade tensions. Economic uncertainty is a major hurdle, especially for recent graduates looking for jobs. A great resource for understanding the challenges and opportunities in this area is this essay on sponsorship, mentorship, and job prospects for graduates sponsorship mentorship jobs graduates essay.
Ultimately, these global economic headwinds could significantly impact job markets and create hurdles for those seeking career advancement.
Policy Responses and Recommendations
The World Bank’s revised global growth forecast, signaling a potential downturn, necessitates proactive policy responses from governments and international organizations. Failure to address the underlying economic headwinds could lead to widespread repercussions, impacting vulnerable populations and hindering global progress. Swift and coordinated action is crucial to mitigating the negative effects and fostering resilience.Addressing the challenges requires a multi-faceted approach, considering the interconnectedness of global economies and the diverse nature of the crises impacting specific regions.
A focus on supporting vulnerable populations, fostering sustainable economic growth, and strengthening global trade partnerships will be key to navigating the current economic uncertainties.
Potential Policy Responses by Governments
Governments must implement policies that stimulate demand, foster innovation, and support vulnerable segments of the population. This includes targeted fiscal measures, such as infrastructure investments and social safety nets, to counter the negative impacts of the revised forecast.
- Targeted Fiscal Measures: Implementing well-defined fiscal stimulus packages focused on specific sectors experiencing the most significant downturns can be effective. For instance, increased funding for renewable energy projects can stimulate green technologies and create jobs, while investments in education and healthcare can build human capital for long-term economic growth. Examples include the stimulus packages implemented during the 2008 financial crisis, which, while not without criticism, demonstrated the potential of fiscal intervention.
- Investment in Infrastructure: Investing in infrastructure projects, such as transportation networks and digital connectivity, can boost productivity and economic activity. This creates jobs, improves logistics, and enhances the overall business environment. China’s extensive infrastructure investments in recent decades have served as a model for other countries, illustrating the positive impact of strategic infrastructure development.
- Social Safety Nets: Protecting vulnerable populations through enhanced social safety nets, such as unemployment benefits and food assistance programs, is crucial. These measures provide a crucial lifeline during economic downturns, preventing social unrest and maintaining social stability. Successful examples include the expansion of social safety nets in various developed countries during periods of economic recession.
Actions by International Organizations
International organizations, like the World Trade Organization (WTO) and the International Monetary Fund (IMF), play a critical role in coordinating global responses. They can provide technical assistance, financial support, and promote policy harmonization.
- Enhanced Trade Facilitation: International organizations can actively promote policies that reduce trade barriers and enhance trade flows. This can include streamlining customs procedures, reducing tariffs, and fostering greater transparency in trade regulations. Examples include initiatives by the WTO to facilitate cross-border trade and reduce trade barriers.
- Financial Support to Developing Economies: Providing financial support and technical assistance to developing economies is vital to ensure they can withstand the impacts of global economic headwinds. The IMF has a crucial role to play in this, as it has done during past crises, providing financial and technical support to struggling economies.
- Promoting Global Cooperation: International cooperation is crucial in fostering a stable and predictable global economic environment. This includes coordinating policies, sharing best practices, and engaging in dialogue to address common challenges. The G20 summits, for example, serve as forums for global cooperation and dialogue on economic matters.
Strategies to Bolster Global Trade and Investment
Enhancing global trade and investment is essential for economic growth and stability. This involves addressing trade tensions, promoting transparency, and reducing barriers to entry for foreign investment.
- Reducing Trade Barriers: Addressing trade tensions and reducing tariffs and non-tariff barriers can significantly boost global trade. This fosters a more predictable and stable environment for businesses and encourages investment. The elimination of trade barriers between member states in the European Union has facilitated significant economic growth and integration.
- Promoting Transparency and Predictability: Greater transparency and predictability in trade and investment regulations are crucial for attracting foreign investment. Clear and consistent rules reduce uncertainty and encourage long-term commitments. Countries that have consistently implemented transparent and predictable policies have seen higher levels of foreign direct investment.
- Encouraging Foreign Direct Investment: Creating an attractive environment for foreign direct investment can stimulate economic growth and job creation. This involves streamlining regulatory processes, improving infrastructure, and protecting intellectual property rights. Examples of countries that have successfully attracted foreign investment often highlight the importance of stability and predictable policies.
Policy Options Table
| Policy Option | Description | Potential Impact (positive/negative) |
|---|---|---|
| Targeted Fiscal Stimulus | Implementing fiscal stimulus packages focused on specific sectors. | Positive: Increased demand, job creation; Negative: Potential inflation, increased debt. |
| Infrastructure Investment | Investing in infrastructure projects (e.g., transportation, energy). | Positive: Increased productivity, job creation, economic activity; Negative: Potential for cost overruns, corruption. |
| Enhanced Social Safety Nets | Expanding unemployment benefits and social assistance programs. | Positive: Reduced poverty, social stability; Negative: Increased government spending. |
Illustrative Scenarios
The escalating trade tensions, as predicted by the World Bank’s revised growth forecast, pose significant risks to the global economy. These uncertainties demand a nuanced understanding of potential outcomes and their ramifications. The ripple effects of trade conflicts extend far beyond mere economic figures, affecting employment, living standards, and even geopolitical stability.
Impact of Continued Trade Tensions on Global GDP
Continued trade disputes can trigger a domino effect, reducing global trade volumes, impacting supply chains, and ultimately dampening economic activity. A decline in international commerce leads to lower export revenues for many countries, which can translate into slower GDP growth. For example, the 2008-2009 global financial crisis, partially triggered by trade disputes and credit market instability, saw a significant contraction in global GDP.
The severity of this impact depends on the duration and intensity of the trade conflict, as well as the retaliatory measures implemented. Countries heavily reliant on exports are particularly vulnerable.
Effects on Specific Industries
Trade tensions disproportionately affect specific industries. The manufacturing sector, heavily reliant on global supply chains, faces disruptions as tariffs and trade barriers increase production costs and limit market access. Agriculture, a vital sector for many developing countries, also experiences significant hardship due to reduced export opportunities and volatility in global commodity prices. For instance, tariffs on agricultural products can reduce farmer incomes and impact food security, especially in vulnerable regions.
Effects on Employment and Living Standards
The impact of trade tensions extends to employment and living standards. Job losses in export-oriented industries can lead to higher unemployment rates, especially in regions heavily reliant on these sectors. Reduced export revenues can translate into lower incomes for households and a decline in living standards, particularly for those in lower-income brackets. The 1930 Smoot-Hawley Tariff Act, a prime example of protectionist trade policies, is linked to a significant increase in unemployment and a decline in living standards globally.
The World Bank’s gloomy global growth forecast, citing trade tensions, is a pretty concerning sign. It’s a complex picture, though, and the recent US-Ukraine minerals deal, a case against potential supply chain disruptions, is worth considering. This deal could potentially mitigate some of the negative impacts, but the overall picture remains one of cautious optimism regarding the World Bank’s predictions, given the still-present trade friction.
Potential for a Global Recession
Escalating trade tensions significantly increase the risk of a global recession. The interconnected nature of the global economy means that disruptions in one sector quickly propagate to others, potentially triggering a cascade of negative impacts. Reduced consumer confidence, decreased investment, and diminished trade activity all contribute to a downturn in economic activity. The 2008 financial crisis provides a cautionary tale of how economic shocks can rapidly spread across borders and trigger a global recession.
Overview of Illustrated Scenarios
- Scenario 1: Impact of Escalating Tariffs on Global GDP: A scenario where significant tariffs are imposed across various sectors leads to a noticeable contraction in global GDP, with developing economies experiencing a disproportionate impact due to their dependence on exports.
- Scenario 2: Impact of Trade Disputes on Specific Industries: This scenario highlights the sector-specific consequences of trade tensions. For example, the automotive industry, reliant on global supply chains, faces higher production costs and reduced market access, potentially leading to factory closures and job losses.
- Scenario 3: Impact on Employment and Living Standards in Developing Economies: Trade disputes can negatively impact employment rates and living standards in developing countries heavily reliant on exports, potentially leading to social unrest and instability.
- Scenario 4: Potential for a Global Recession: Escalating trade tensions, combined with other global economic factors, could trigger a global recession characterized by reduced investment, decreased consumer confidence, and diminished trade activity.
Historical Context
The current global economic slowdown, fueled by trade tensions and a World Bank growth downgrade, echoes historical patterns of global economic downturns. Understanding these past events provides valuable context for analyzing the present situation and formulating effective responses. A deeper look into the factors contributing to previous crises reveals key similarities and differences with the current climate, offering lessons for navigating the challenges ahead.
Historical Overview of Global Economic Downturns
Several historical events, marked by significant global economic downturns, offer valuable insights into the complexities of global economic cycles. The Great Depression of the 1930s, the 1970s oil crisis, and the 2008 financial crisis are prime examples. Each event was triggered by a confluence of factors, impacting global trade, investment, and consumer confidence. Understanding these triggers is crucial to anticipating potential consequences of similar events.
Factors Contributing to Historical Events
Various factors contributed to these past economic downturns. Political instability, wars, and natural disasters were often major triggers. Furthermore, unsustainable economic policies, such as excessive debt or asset bubbles, frequently played a crucial role. Supply chain disruptions, technological advancements, and shifts in global power dynamics also contributed significantly.
Comparison and Contrast with the Current Situation
Comparing the current situation with past events reveals both similarities and differences. While trade tensions and geopolitical uncertainties echo historical challenges, the current context is unique in its complexity. Technological advancements, globalization, and interconnectedness amplify the potential impact of any disruption. The current environment also differs from the past due to the presence of sophisticated financial instruments and a globalized financial system.
Key Similarities and Differences
| Aspect | Similarities | Differences |
|---|---|---|
| Geopolitical Tensions | Trade wars, protectionist policies, and political instability have historically led to economic downturns. | Globalization and interconnectedness amplify the impact of current geopolitical uncertainties, making them more widespread. |
| Economic Policies | Unsustainable fiscal and monetary policies have contributed to past crises. | The current global financial system, with its interconnectedness, is more vulnerable to disruptions stemming from various sources. |
| Technological Advancements | Technological shifts have historically led to periods of both prosperity and disruption. | The speed and scale of technological change today are unprecedented, creating both opportunities and challenges for economies. |
Timeline of Key Events Leading to the Current Outlook
- 2018-2019: Escalating trade tensions between major economies created uncertainty and disrupted global supply chains.
- 2020: The COVID-19 pandemic caused widespread lockdowns, disrupting global supply chains and triggering a sharp recession.
- 2022: The Russian invasion of Ukraine triggered a global energy crisis, impacting commodity prices and inflationary pressures.
- Present: Persisting trade tensions, ongoing geopolitical conflicts, and inflationary pressures are creating a challenging economic environment.
Alternative Perspectives
The World Bank’s recent global growth forecast, tempered by trade tensions, has naturally sparked diverse opinions among economists and analysts. While the Bank’s assessment provides a valuable framework, alternative perspectives offer contrasting viewpoints, highlighting potential blind spots and unexpected developments. These divergent opinions are crucial in forming a comprehensive understanding of the complex global economic landscape.The World Bank’s assessment, while influential, is just one piece of the puzzle.
Alternative viewpoints can offer crucial insights into the potential for unexpected positive or negative outcomes. By considering these diverse perspectives, a more nuanced and comprehensive understanding of the current economic climate can be developed.
Alternative Economic Forecasts
Different economic institutions and independent analysts often present varying growth projections. These differences stem from diverse methodologies, assumptions about future policy decisions, and varying interpretations of existing economic data. For instance, some institutions might emphasize the resilience of certain sectors, leading to more optimistic projections, while others might highlight vulnerabilities in global supply chains, potentially leading to more pessimistic forecasts.
Counterarguments to the World Bank’s Assessment
Some economists argue that the World Bank’s forecast underestimates the potential for innovation and technological advancements to drive economic growth. They point to the rapid adoption of new technologies in various sectors, potentially fostering productivity gains and offsetting some of the negative impacts of trade tensions. Furthermore, the potential for regional trade agreements to mitigate the impact of global trade conflicts is also considered a potential counterargument.
Potential for Unexpected Positive Developments in Global Trade
While trade tensions remain a significant concern, the possibility of unexpected positive developments shouldn’t be discounted. Regional trade agreements and innovative solutions to supply chain disruptions could emerge, fostering new opportunities for growth and mitigating the negative impact of global trade conflicts. Recent examples of successful regional trade agreements, despite global uncertainty, demonstrate the potential for positive outcomes in international trade.
Different Expert Opinions Summarized
“Perspective 1: The World Bank’s forecast is overly pessimistic, failing to account for the resilience of the global economy and the potential for technological innovation to drive growth. The impact of trade tensions is likely to be less severe than predicted, with regional trade agreements and alternative supply chains potentially mitigating the effects.”
“Perspective 2: The World Bank’s assessment accurately reflects the current global climate of uncertainty. Trade tensions and geopolitical instability are creating substantial headwinds for global economic growth, and the forecast appropriately acknowledges the potential for negative outcomes, even with potential mitigating factors.”
“Perspective 3: While trade tensions pose a significant threat, the forecast underestimates the potential for unexpected positive developments in global trade.Innovation and adaptation could lead to unforeseen opportunities, potentially offsetting some of the negative impacts of the current challenges.”
Last Recap

In conclusion, the World Bank’s revised global growth forecast, significantly impacted by trade tensions, underscores the urgent need for proactive policy responses. The potential consequences, including the risk of a global recession, demand immediate attention from governments and international organizations. This analysis explores potential policy options, illustrative scenarios, and historical context to offer a comprehensive understanding of the challenges and potential solutions.
Alternative perspectives, from leading economists, are also included to provide a more nuanced view of the situation.