
Advanced nuclear companies others urge senate keep energy tax credits – Advanced nuclear companies, along with others, are urging the Senate to keep energy tax credits. This push highlights the critical role these credits play in fostering innovation and investment in cutting-edge nuclear technologies. The debate surrounding these credits touches upon the future of clean energy, the potential for job creation, and the economic benefits of supporting a nascent but promising industry.
Existing tax credits for renewable energy sources will be compared to those for advanced nuclear, showcasing the specific provisions related to nuclear power. Different reactor designs and their respective strengths and weaknesses will be examined, along with the current tax credit structure for various energy sources. The arguments for and against these credits will be presented, including their potential impacts on job creation and the overall energy sector.
This push for continued support underscores the significant potential of advanced nuclear energy. The discussion delves into the specific benefits of these technologies, their place within the current energy landscape, and the arguments for maintaining supportive policies.
Background on Advanced Nuclear Companies
Advanced nuclear energy technologies represent a significant leap forward in the quest for sustainable and reliable energy sources. These innovations build upon decades of nuclear research and development, promising improved safety, efficiency, and environmental performance compared to traditional nuclear power plants. This evolving field presents both exciting opportunities and complex challenges.The pursuit of advanced nuclear reactors stems from the desire to mitigate the risks and limitations of existing designs while harnessing the substantial energy potential of nuclear fission.
Concerns about nuclear waste disposal, reactor safety, and the economics of large-scale power generation have driven the development of innovative reactor designs, pushing the boundaries of engineering and materials science.
History of Advanced Nuclear Technology Development
The concept of nuclear energy dates back to the early 20th century, with significant breakthroughs in the mid-20th century. Early research focused on understanding nuclear fission and its potential applications, culminating in the development of the first nuclear reactors. Over the years, various designs emerged, including pressurized water reactors (PWRs) and boiling water reactors (BWRs), which form the basis of most current nuclear power plants.
However, these designs have inherent limitations that advanced reactor technologies aim to overcome.
Current Landscape of Advanced Nuclear Companies
Numerous companies are actively developing and commercializing advanced nuclear reactor designs. These companies are driven by the potential for significant economic and environmental benefits. The landscape is diverse, encompassing a range of reactor types and technological approaches. Some companies are focusing on small modular reactors (SMRs), while others are developing innovative reactor designs that improve upon existing technologies.
The industry is witnessing rapid growth, driven by supportive government policies and a growing awareness of the importance of decarbonizing the energy sector.
Examples of Advanced Nuclear Reactor Designs
Several innovative reactor designs are under development. One prominent example is the molten salt reactor (MSR), which uses a molten salt as a coolant and fuel. Another type is the high-temperature gas-cooled reactor (HTGR), which utilizes a gas coolant. These designs offer advantages in terms of safety, efficiency, and waste management compared to traditional reactors. Other designs are focused on specific niche applications, like naval propulsion.
The development of these designs is constantly evolving, and new ideas are continuously emerging.
Key Technological Advancements
Advanced nuclear companies are making strides in several key areas. These include:
- Advanced materials: New materials with enhanced heat resistance and corrosion resistance are being developed to improve reactor performance and safety. These advancements are crucial for ensuring long-term operation and reliability.
- Passive safety systems: Design principles are being implemented to reduce reliance on active safety systems. This minimizes the risk of accidents and improves the inherent safety of the reactors. The shift toward passive systems is a crucial aspect of enhancing safety in the nuclear sector.
- Improved fuel cycles: Research is focused on fuel cycles that minimize nuclear waste and maximize fuel utilization. This contributes to a more sustainable and environmentally friendly approach to nuclear power generation.
Comparison of Advanced Nuclear Reactor Types
| Reactor Type | Strengths | Weaknesses | Current Status |
|---|---|---|---|
| Molten Salt Reactor (MSR) | High safety potential, inherent safety features, potential for higher efficiency, reduced waste volume | Materials compatibility challenges, complexity in design, need for further testing | Several companies are actively developing MSR designs, with pilot projects underway |
| Small Modular Reactor (SMR) | Scalability, reduced construction time and cost, potential for deployment in remote areas, enhanced safety features | Smaller power output compared to large reactors, need for specialized infrastructure, regulatory hurdles | Several SMR designs are in various stages of development and testing, with some approaching commercialization |
| High-Temperature Gas-Cooled Reactor (HTGR) | High thermal efficiency, potential for process heat applications, inherent safety features | Material challenges at high temperatures, complexity in design, need for further development of fuel cycles | Some research and development projects ongoing, but commercial deployment remains a challenge |
Senate Energy Tax Credits
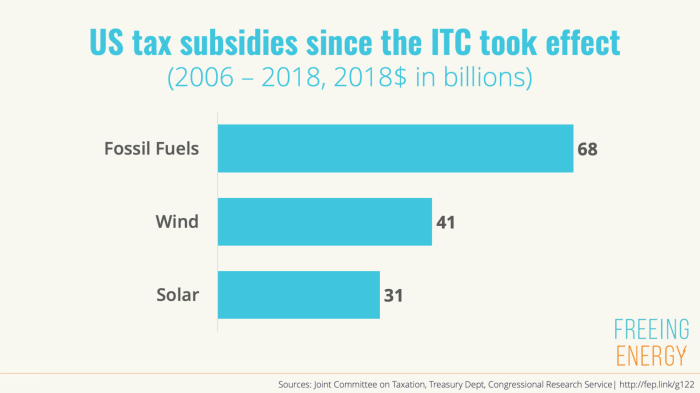
The ongoing debate surrounding energy tax credits highlights their crucial role in fostering innovation and investment in clean energy technologies. These incentives, often crucial for startups and established companies alike, can significantly impact the trajectory of energy development. Understanding the specifics of these credits, particularly for advanced nuclear energy, is essential for evaluating their potential and impact.
Existing Renewable Energy Tax Credits
Current tax credits for renewable energy sources are diverse and multifaceted, encompassing various technologies and stages of development. Solar, wind, and biofuels frequently receive substantial support through production tax credits (PTC), investment tax credits (ITC), and other mechanisms designed to stimulate investment and accelerate deployment. These credits often target specific technologies and project sizes, reflecting an understanding of the unique challenges and opportunities presented by each.
Their effectiveness is often measured by the increased deployment rates of the corresponding energy sources.
Nuclear Energy Tax Credits: Specific Provisions
While nuclear energy has traditionally received less direct financial support compared to other renewables, some provisions within existing tax codes offer indirect incentives. These typically focus on research and development (R&D) activities, advanced reactor technologies, and potentially, the decommissioning of existing facilities. The lack of a dedicated, large-scale tax credit specifically for advanced nuclear power is a significant difference compared to some other energy sectors.
Advanced nuclear companies and others are urging the Senate to maintain energy tax credits, a crucial step for innovation in this sector. While these credits are vital for bolstering the industry, it’s also worth considering the broader literary landscape, particularly the works of Percival Everett, whose exploration of identity and narrative structure in his literary canon offers a unique lens through which to view societal shifts.
Ultimately, supporting these credits is essential for driving progress in clean energy technologies.
Importance of Credits for Attracting Investment
Investment in advanced nuclear power, like any nascent industry, is inherently risky. The need for substantial upfront capital for research, development, and construction, coupled with potential regulatory hurdles, necessitates a robust incentive structure. Tax credits act as a powerful catalyst, reducing the financial burden on developers and increasing the attractiveness of nuclear energy as a viable investment option.
This can translate to faster project development and greater market penetration. Successful deployments of similar incentive programs in other sectors provide a valuable precedent.
Comparison with Credits for Other Energy Sources
A direct comparison of tax credits across different energy sources reveals significant disparities. While renewable energy technologies often enjoy dedicated and substantial incentives, the nuclear sector often relies on broader tax codes and R&D provisions. This disparity may contribute to the slower pace of nuclear energy development compared to some renewables. Factors such as the inherent complexities of nuclear technology and the historical regulatory environment surrounding it likely contribute to the differences.
Current Tax Credit Structure
The current tax credit structure is complex and varies significantly based on the specific energy source and project type. A comprehensive overview requires detailed consideration of individual programs and their respective eligibility criteria.
| Energy Source | Tax Credit Type | Amount | Duration |
|---|---|---|---|
| Solar | Investment Tax Credit (ITC) | Varying, often significant | Typically, several years |
| Wind | Production Tax Credit (PTC) | Varying, often substantial | Limited duration, subject to renewal |
| Advanced Nuclear | R&D tax credits, potential future dedicated credits | Variable, often less substantial | Dependent on program and project |
Arguments for Keeping Energy Tax Credits

Fueling innovation in advanced nuclear energy is crucial for a sustainable future. Tax credits play a vital role in supporting these nascent technologies, encouraging investment, and driving job creation. These incentives are essential for bridging the gap between promising research and widespread adoption, thereby contributing to a cleaner energy landscape.Maintaining these credits fosters a competitive market and incentivizes companies to develop cutting-edge nuclear reactor designs.
These designs hold the potential to deliver clean energy with higher efficiency and safety standards, a critical aspect for addressing the climate crisis.
Stimulating Innovation with Tax Credits
Tax credits for advanced nuclear energy companies provide substantial financial incentives, enabling companies to invest in research and development. This support encourages the development of innovative reactor designs, potentially leading to substantial improvements in efficiency, safety, and cost-effectiveness. For example, companies can dedicate resources to advanced materials, reactor designs, and safety systems, fostering innovation and reducing risks associated with new technologies.
This crucial investment in R&D translates into tangible improvements and potentially groundbreaking advancements in nuclear power generation.
Economic Benefits of Maintaining Tax Credits
These credits stimulate economic activity by encouraging investment in advanced nuclear facilities. This investment creates high-paying jobs in engineering, construction, and related industries. The economic benefits extend beyond direct employment to include indirect impacts on local economies, supporting businesses that supply goods and services to these projects. A flourishing nuclear energy sector can drive economic growth and development.
Job Creation through Tax Credits
The development of advanced nuclear technologies is labor-intensive. Tax credits directly encourage the growth of the sector by lowering the financial barriers for investment. Consequently, this leads to the creation of numerous high-skilled jobs. These jobs span a range of disciplines, from engineering and design to construction and operation, benefiting both the national economy and local communities.
Advanced nuclear companies and others are urging the Senate to keep energy tax credits, highlighting the crucial role they play in bolstering domestic clean energy innovation. Meanwhile, Japan’s confirmation that China’s aircraft carrier sailed east of Iwo Jima for the first time ( japan confirms chinas aircraft carrier sailed east iwo jima first time ) raises important geopolitical questions, potentially impacting global energy security.
Ultimately, the focus should remain on supporting the development of advanced nuclear technologies, crucial for a sustainable future, and maintaining these tax credits is a necessary step in that direction.
Moreover, a robust nuclear industry can support a wider range of related jobs in education, training, and service industries.
Summary of Arguments for Maintaining Energy Tax Credits
| Argument | Supporting Evidence | Impact | Counterargument |
|---|---|---|---|
| Stimulates Innovation | Financial incentives drive R&D, leading to improved reactor designs and cost-effectiveness. | Faster development of advanced nuclear technologies, leading to cleaner energy solutions. | Potential for misallocation of funds if not properly managed. |
| Generates Economic Benefits | Investment in advanced nuclear facilities creates high-paying jobs and boosts local economies. | Increased GDP, job creation, and improved infrastructure. | Concerns about potential job displacement in other sectors. |
| Creates Jobs | Growth in the advanced nuclear sector necessitates skilled labor across various disciplines. | High-skilled employment opportunities in engineering, construction, and operations. | Potential for a slower rate of job creation in other sectors. |
Arguments Against Keeping Energy Tax Credits
The allure of advanced nuclear energy is undeniable. However, proponents of tax credits must acknowledge potential downsides. These incentives, while aiming to foster innovation, could have unforeseen consequences and may not always be the most efficient allocation of taxpayer funds. Careful consideration of alternative uses for those resources is vital.Critics of these tax credits raise concerns about their potential for inequities and inefficiencies.
Arguments against maintaining these credits often focus on the potential for misallocation of resources, disproportionate benefits to specific industries, and the overall cost-effectiveness compared to other government priorities.
Potential for Misallocation of Resources
Tax credits, while intended to encourage innovation, can inadvertently channel resources away from other equally or potentially more impactful areas of research and development. For example, funds allocated to advanced nuclear energy may divert funding from other renewable energy sources or even from established, mature technologies that have demonstrated more immediate and tangible results. This can result in a slower overall progress toward energy independence and sustainability.
The potential for a delayed return on investment compared to alternative technologies is a valid concern.
Disproportionate Benefits to Specific Industries
One key argument against the credits is the potential for undue favoritism toward specific industries or companies. Tax credits, if not carefully designed and monitored, could disproportionately benefit large, established corporations with greater financial resources to leverage these incentives, leaving smaller, emerging companies at a disadvantage. This could potentially stifle competition and innovation in the long run. For example, a large corporation might be better positioned to absorb the initial financial risks and costs associated with the development of advanced nuclear technology, while a smaller competitor might be hindered by the financial burden.
Cost-Effectiveness Compared to Other Government Priorities
A critical question is whether the cost of these tax credits outweighs the benefits and aligns with other government priorities. Funds allocated to advanced nuclear tax credits may be better utilized in addressing other pressing societal needs. The opportunity cost of these incentives, measured against investments in education, healthcare, or infrastructure, deserves careful evaluation. For example, the cost of the tax credits could potentially fund the construction of crucial infrastructure, leading to greater long-term economic growth.
Comparison with Other Government Priorities
| Argument | Supporting Evidence | Impact | Rebuttal |
|---|---|---|---|
| Reduced funding for other energy research | Competition for research grants and funding may be exacerbated. | Slows overall energy transition progress. | Alternative energy sources may require a similar level of support to remain competitive. |
| Disproportionate benefit to large corporations | Established firms with greater financial resources gain more from the credits. | Lessens competitive landscape for emerging technologies. | Stringent criteria and transparency in credit allocation can mitigate the effect. |
| Opportunity cost of alternative investments | Funds could be better allocated to infrastructure or other societal needs. | Reduces effectiveness of broader government initiatives. | Demonstrate a clear cost-benefit analysis that outweighs potential alternatives. |
| Uncertain long-term cost-benefit | The feasibility and profitability of advanced nuclear technologies remain uncertain. | Risk of substantial financial burden on taxpayers. | Robust cost-benefit analysis and thorough regulatory oversight can address uncertainty. |
Potential Unintended Consequences
A thorough evaluation of the potential unintended consequences is crucial. The credits could inadvertently encourage the development of technologies that have unforeseen environmental or safety implications, requiring significant post-implementation remediation. Furthermore, the credits might incentivize projects that do not align with broader societal goals for energy sustainability. For example, focusing solely on advanced nuclear might hinder the development of other potentially more sustainable solutions like solar or wind energy.
The potential for unforeseen environmental or safety concerns warrants thorough consideration.
Alternatives to Tax Credits
Incentivizing the development of advanced nuclear energy requires a multifaceted approach beyond just tax credits. While tax credits play a role, other funding mechanisms and policies can provide equally effective, or even superior, avenues for supporting this crucial technology. This exploration examines alternative approaches, drawing comparisons with existing tax credits and highlighting successful models in other countries.Alternative approaches to incentivizing advanced nuclear energy development offer diverse pathways to support the industry.
These strategies often provide flexibility and adaptability, responding to evolving market conditions and technological advancements. By diversifying funding sources, policymakers can reduce reliance on a single approach, increasing the robustness and sustainability of the energy sector.
Alternative Funding Mechanisms, Advanced nuclear companies others urge senate keep energy tax credits
Government funding, through direct grants, subsidies, and loan guarantees, can provide a substantial boost to advanced nuclear energy development. These mechanisms offer a degree of control over project direction and ensure projects align with national priorities. Dedicated research funds and public-private partnerships are additional avenues for bolstering innovation and reducing the financial risk associated with new technologies.
Policy Incentives Beyond Tax Credits
Beyond funding, supportive policies can further encourage the adoption of advanced nuclear technologies. Streamlined permitting processes, accelerated regulatory timelines, and clear safety standards can significantly reduce project lead times and costs. The establishment of specialized training programs for the workforce, coupled with workforce development initiatives, can ensure the availability of qualified personnel to operate and maintain these complex facilities.
Advanced nuclear companies and others are pushing the Senate to maintain energy tax credits, highlighting the crucial role of these incentives in fostering innovation. Meanwhile, the Australian case of the accused mushroom murders, where the suspect reportedly searched for a deadly strain before the deaths ( australian accused mushroom murders searched deadly strain before deaths court ), serves as a stark reminder of the importance of responsible energy development.
This underscores the need for continued support for sustainable energy sources, which is precisely why maintaining these credits for advanced nuclear companies is vital.
Examples of Successful Alternative Approaches
Many countries have employed alternative approaches to fostering the development of innovative energy technologies. France, for example, has a robust nuclear energy program, relying heavily on government support and public funding to maintain and advance the sector. Likewise, countries like South Korea and China have utilized direct subsidies and government-backed loans to support the growth of their renewable energy industries, which serves as a model for supporting advanced nuclear.
Comparison of Tax Credits and Alternative Methods
| Incentive Type | Mechanism | Pros | Cons |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tax Credits | Reduced tax liabilities for investments in advanced nuclear energy | Indirect support for the sector; potentially wider reach | Complex administration; potential for unintended consequences; can be influenced by broader tax policy changes |
| Direct Grants | Direct financial support for specific projects | Targeted support; greater control over project direction | Limited reach; potential for political influence; administrative burden |
| Loan Guarantees | Government backing for loans to advance nuclear companies | Facilitates access to capital; reduced risk for investors | Potential for government liability; need for rigorous assessment processes |
| Public-Private Partnerships | Collaboration between government agencies and private companies | Leverages private sector expertise; fosters innovation | Potential for conflicts of interest; complex negotiation processes |
Impact on the Energy Sector
The fate of advanced nuclear energy, a promising solution to global energy needs, hinges significantly on the continuation of supportive government policies. Decisions regarding energy tax credits will have a profound ripple effect throughout the energy sector, impacting everything from research and development to job creation and international collaborations.The energy sector is poised at a crucial juncture. Investment in advanced nuclear technologies will determine whether we can achieve substantial progress toward cleaner, more sustainable energy sources.
Conversely, a lack of support could severely hamper this crucial development. This makes the decision about energy tax credits a pivotal moment for the entire energy landscape.
Overall Impact of Keeping or Removing Credits
The continued availability of energy tax credits will likely foster significant investment in advanced nuclear research and development. This financial incentive encourages private sector participation and accelerates the timeline for commercialization. Conversely, the removal of these credits could significantly reduce investment, potentially delaying or even halting the development of advanced nuclear technologies. The impact will be felt across the entire energy sector, influencing the future of energy production and consumption.
Projections for the Future of Advanced Nuclear Energy
The future of advanced nuclear energy depends on the level of support received. Optimistic projections envision advanced nuclear technologies becoming a substantial part of the global energy mix within the next few decades. These technologies, with their potential for higher efficiency and lower waste production, offer a pathway toward a more sustainable energy future. However, these projections are contingent on substantial investment, consistent government support, and overcoming technological hurdles.
Examples of similar technologies that saw accelerated development and widespread adoption due to government support include solar panel technology and certain types of wind turbines. These examples demonstrate the potential for government investment to drive innovation and market penetration.
Potential Implications for Job Creation and Economic Growth
The development of advanced nuclear technologies holds significant potential for job creation and economic growth. Construction of new plants, research and development, and maintenance activities will generate employment opportunities across various sectors. Furthermore, the creation of new industries related to advanced nuclear technology could spur significant economic activity, potentially creating new jobs and industries in areas such as manufacturing, engineering, and technical support.
The economic impact of a large-scale adoption of advanced nuclear technologies could rival that of the early days of the semiconductor industry, with its significant ripple effect across other industries.
Potential for International Collaboration and Trade
Advanced nuclear technologies are inherently complex and require international collaboration for their development and deployment. The sharing of knowledge, expertise, and resources among nations is essential for the successful advancement of these technologies. International collaboration can lead to the development of standardized technologies, shared research facilities, and coordinated deployment strategies. This could also foster increased trade in advanced nuclear components and services, potentially generating significant economic benefits for participating nations.
Examples of international cooperation in scientific and technological fields can be found in the development of the internet and the exploration of space. These showcase how international collaboration can lead to unprecedented advancements.
Summary of Various Perspectives and Potential Outcomes
There are diverse perspectives on the role of energy tax credits in the advancement of advanced nuclear energy. Supporters emphasize the critical role these incentives play in fostering innovation, job creation, and economic growth. Opponents, on the other hand, often raise concerns about the cost and potential risks associated with these incentives. The potential outcomes of keeping or removing the credits vary widely, ranging from significant progress toward a sustainable energy future to a substantial setback in the development of this crucial technology.
The long-term impact will depend heavily on the decisions made today regarding these crucial incentives.
Final Conclusion: Advanced Nuclear Companies Others Urge Senate Keep Energy Tax Credits
In conclusion, the debate over energy tax credits for advanced nuclear companies is complex, with strong arguments on both sides. While these credits offer a potential pathway to a cleaner energy future, concerns about their cost-effectiveness and potential unintended consequences must also be considered. Ultimately, the decision on whether to maintain or adjust these credits will have a substantial impact on the future of the energy sector, and the ongoing push for cleaner, sustainable energy solutions.

