China bristles macron linking ukraine defence taiwan threats – China bristles at Macron linking Ukraine defense to Taiwan threats, raising concerns about escalating tensions in the region. France’s President Macron’s recent comments have sparked a flurry of activity, particularly regarding China’s stance on Taiwan and the ongoing Ukraine conflict. This analysis delves into the complex interplay of geopolitical maneuvering, potential economic repercussions, and the delicate balance of power in the region.
This complex situation requires careful consideration of various factors, including China’s recent actions and statements, Macron’s role and influence, the Ukraine conflict’s impact, Taiwan’s defense posture, regional security implications, economic interdependencies, and potential diplomatic solutions. The interplay of these elements paints a vivid picture of the current geopolitical landscape and the potential for further escalation.
China’s Recent Actions and Stances
China’s recent actions and statements regarding Taiwan, the Ukraine conflict, and President Macron’s comments reflect a complex interplay of strategic interests, territorial ambitions, and economic considerations. Beijing’s assertive posture underscores its growing influence in the international arena, while simultaneously highlighting the challenges and potential risks associated with its rise. The implications of these actions extend far beyond the immediate region, impacting global trade, security, and political stability.
China’s Actions Regarding Taiwan
China views Taiwan as a breakaway province, not a sovereign nation, and its “One China” policy dictates that Taiwan must eventually be reunified with the mainland, by force if necessary. Recent military exercises and increased air and naval activity around Taiwan demonstrate a growing assertiveness in its pursuit of this goal. These actions are intended to signal China’s resolve and exert pressure on Taiwan and its international partners.
Beijing has also ramped up diplomatic pressure on countries that maintain formal or informal ties with Taiwan. This includes issuing warnings and demanding the cessation of any official contacts or support for the island.
China’s Public Pronouncements on the Ukraine Conflict
China has consistently avoided taking a direct position against Russia in the Ukraine conflict. While publicly condemning the use of force, China has refrained from explicitly condemning Russia’s invasion. Instead, China has emphasized its commitment to neutrality and has called for diplomatic solutions. This stance reflects China’s strategic interest in maintaining its economic relationship with Russia, which has grown in recent years.
China’s Stance on Macron’s Comments
President Macron’s comments regarding the Ukraine crisis and Taiwan have drawn criticism from China. Beijing’s response has been characterized by criticism of what it perceives as an attempt to interfere in China’s internal affairs and support Taiwan’s independence. China’s position emphasizes its sovereignty and territorial integrity and underscores its strong objections to any perceived challenges to these core principles.
China’s Strategic Interests in the Region
China’s strategic interests in the region are multifaceted and include:
- Maintaining its regional hegemony: China seeks to establish itself as a dominant power in the Asia-Pacific region, challenging the existing US-led order. This includes bolstering its military capabilities, expanding its economic influence, and engaging in strategic partnerships with countries in the region.
- Securing its maritime access: China’s growing maritime trade and military activities depend on secure access to crucial waterways, such as the South China Sea. This is linked to control of key resources and strategic locations. China’s assertive posture in the South China Sea is part of this strategic effort.
- Securing its economic interests: China is actively promoting its economic interests throughout the region and globally through initiatives like the Belt and Road Initiative. This includes gaining access to resources, markets, and strategic locations for investment and trade.
Potential Economic and Military Implications
China’s actions have significant implications for the global economy and military balance.
China’s response to Macron linking Ukraine defense to Taiwan threats is definitely stirring things up. It’s a complex situation, and I’ve been thinking a lot about how these geopolitical tensions play out. Interestingly, Bill Frist’s acceptance speech, a fascinating look at political strategy, might offer some insight into navigating these kinds of situations. bill frist acceptance speech Ultimately, the interconnectedness of these issues, from Ukraine to Taiwan, is raising eyebrows and potentially influencing global policy in unpredictable ways.
- Increased geopolitical tensions: China’s assertive actions in the region have increased tensions with the US and other countries, leading to a potential escalation of conflicts.
- Economic disruptions: Trade disputes, sanctions, and economic pressure could disrupt global trade flows and economic growth. Disruptions in supply chains and the flow of goods would have significant repercussions.
- Military build-up: China’s military buildup and increased assertiveness are a significant factor in the growing military competition in the region. This could lead to a military confrontation, although a large-scale conflict is not expected.
Economic Implications in Detail, China bristles macron linking ukraine defence taiwan threats
China’s actions, particularly regarding trade disputes and economic sanctions, can have substantial effects on global trade and economic growth. For instance, the trade war with the US significantly impacted global markets and disrupted supply chains. Similarly, sanctions on Russia following its invasion of Ukraine affected global energy markets and commodity prices. These disruptions highlight the interconnectedness of global economies and the potential for widespread economic consequences from escalating geopolitical tensions.
Macron’s Role and Influence
Emmanuel Macron, as President of France and a key figure in the European Union, has consistently voiced his views on China’s actions, particularly concerning Taiwan and Ukraine. His approach to these issues often stands in contrast to those of other European leaders, highlighting the complexities and nuances of the EU’s relationship with a rising global power. This analysis examines Macron’s recent statements, his diplomatic strategies, and his influence on EU policy towards China.Macron’s pronouncements on China often reflect a delicate balancing act.
China’s reaction to Macron linking Ukraine defense to Taiwan threats is noteworthy. This escalating geopolitical tension, coupled with a top Cuban official accusing the US of escalating tensions and raising concerns about conflict, highlights a complex web of global anxieties. This echoes the growing global concern regarding the escalating situation, and underscores the interconnected nature of international relations, particularly when considering how actions in one region can have far-reaching implications elsewhere.
The worry is that these actions could easily escalate, mirroring the situation in the Ukraine conflict and potentially jeopardizing regional stability. Top Cuban officials’ concerns add another layer of complexity to the already tense situation surrounding China’s response to Macron’s comments.
He recognizes China’s economic importance but also expresses concerns about its assertive foreign policy, particularly its stance on Taiwan and its actions in the South China Sea. This calculated approach is likely driven by a desire to maintain economic ties while simultaneously deterring China from further expansionist activities.
Macron’s Recent Statements
Macron’s recent statements on China, Taiwan, and Ukraine demonstrate a nuanced approach, characterized by a recognition of the complex interplay between economic interdependence and geopolitical considerations. He emphasizes the need for a strong, unified European front to address China’s actions. For instance, he has stressed the importance of maintaining a robust defense posture within Europe to deter aggression, while simultaneously advocating for maintaining open communication channels with China.
He has called for dialogue and diplomacy to manage potential conflicts.
Macron’s Diplomatic Strategies and Objectives
Macron’s diplomatic strategy towards China appears to prioritize maintaining a balance between economic engagement and geopolitical concerns. He seeks to leverage France’s influence within the EU to shape a collective response to China’s growing assertiveness. This strategy aims to encourage the EU to adopt a unified stance on key issues, rather than fragmented responses from individual member states. His diplomatic objectives include fostering a stronger EU position in international affairs, and promoting multilateralism.
Macron’s Influence on EU Policy Towards China
Macron’s influence on EU policy towards China is significant, albeit not always decisive. He has been a vocal advocate for a more strategic and assertive approach to China, particularly regarding trade imbalances and human rights issues. His efforts have contributed to a growing consensus within the EU that a more cautious and critical approach to China is necessary.
This includes calls for greater scrutiny of Chinese investments and closer cooperation on issues like cybersecurity and technology.
Comparison to Other European Leaders’ Perspectives
While some European leaders share Macron’s concerns about China’s actions, others may prioritize economic ties more strongly. For example, some EU member states have a greater dependence on Chinese markets, influencing their stance on China’s actions. Macron’s approach emphasizes a more comprehensive, balanced strategy that integrates economic interests with geopolitical considerations, in contrast to some other leaders who may prioritize economic gains above all else.
Macron’s Possible Motivations
Macron’s motivations for his statements likely stem from a combination of factors. A key driver is undoubtedly France’s national interests, seeking to maintain a prominent role in European and global affairs. Further, a desire to shape a stronger EU stance on global issues, including China’s rise, also plays a significant role. Lastly, Macron may be driven by a belief in the importance of multilateralism and international cooperation to address global challenges.
The Ukraine Conflict and its Relation
The escalating conflict in Ukraine has profound implications for global geopolitics, particularly affecting China’s regional strategy and its relationship with other nations. The war’s impact on international trade, investment, and security necessitates careful consideration of its ripple effects. China’s stance on the conflict, alongside its ambitions in Taiwan, complicates an already complex global landscape.The Ukraine conflict serves as a potent reminder of the intertwined nature of global affairs.
China’s response to Macron linking Ukraine defense to Taiwan threats is certainly noteworthy. The recent unrest in France following PSG’s victory, with two dead and over 500 arrested during celebrations here , offers a starkly different perspective on global tensions. However, the underlying issue of China’s stance on Taiwan remains a significant geopolitical concern, regardless of the localized French disturbances.
Events in one region often have far-reaching consequences for others, influencing economic stability, political alignments, and the overall security environment. China’s response to the Ukrainian crisis, coupled with its evolving posture regarding Taiwan, further underscores this interconnectedness.
Impact on China’s Regional Strategy
The war in Ukraine has prompted a reassessment of global power dynamics, forcing nations to re-evaluate their security postures and alliances. China’s regional strategy, which includes its assertive posture toward Taiwan, is undeniably influenced by the evolving geopolitical landscape. China observes the West’s response to the conflict and potentially adjusts its own actions and rhetoric accordingly.
Connections between China’s Taiwan Actions and the Ukraine Situation
Some analysts posit a potential link between China’s increasingly assertive actions regarding Taiwan and the situation in Ukraine. The perceived success of Russia’s military approach, despite unforeseen challenges, might tempt China to adopt a similar strategy. However, the unique circumstances of Taiwan, including its democratic governance and global economic ties, suggest that any direct comparison is overly simplistic.
Geopolitical Implications of the Ongoing War
The ongoing war in Ukraine has significant geopolitical implications, particularly concerning the future of international order. The conflict highlights the fragility of international agreements and the challenges of maintaining a stable global environment. The response to the war will significantly shape future international relations and security architecture.
Influence on Relationships between China, France, and Other European Nations
The Ukraine conflict has strained relations between some European nations and Russia, influencing their interactions with China. France, a prominent European player, faces the challenge of balancing its economic ties with China against its security concerns regarding the conflict. This complex dynamic requires careful diplomacy to navigate potential conflicts of interest.
Potential Impacts on Global Trade and Investment
The war in Ukraine has disrupted global supply chains and created uncertainty in international trade. The conflict’s effects are particularly pronounced in sectors reliant on Ukrainian resources or European markets. The ongoing uncertainty hinders investment and economic growth, affecting countries across the globe.
Taiwan’s Situation and Defense
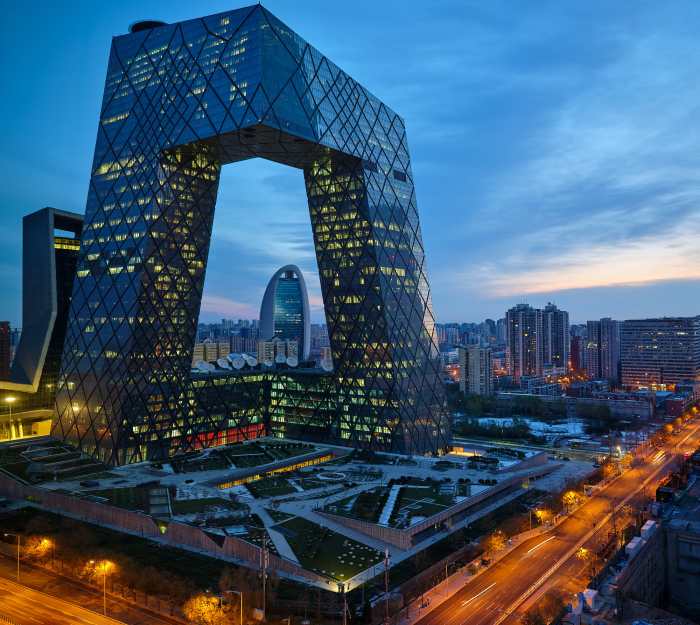

Taiwan, a self-governing island democracy, faces a complex geopolitical situation. Its close relationship with the United States, coupled with its vibrant economy and democratic values, makes it a strategically important area. However, China considers Taiwan a breakaway province and a potential threat to its national sovereignty, leading to ongoing tensions and a potential military conflict. Understanding Taiwan’s defense posture, economic significance, and political status is crucial to grasping the potential consequences of China’s actions.
Taiwan’s Defense Posture and International Relations
Taiwan maintains a robust defense posture, actively developing its military capabilities. This includes advanced air defense systems, naval forces, and a strong ground component. The island nation has also forged alliances with several countries, particularly the United States, to enhance its defensive capabilities. These partnerships involve the exchange of military equipment, training, and intelligence. Taiwan’s defense strategy emphasizes deterrence and is designed to deter potential aggression from China.
This involves not just military strength but also the ability to project resolve and a commitment to self-defense.
Taiwan’s Economic Significance in the Region
Taiwan is a key player in the global economy, particularly in the semiconductor industry. Its advanced manufacturing sector and skilled workforce contribute significantly to the regional and global economy. Taiwan’s economic prosperity is intertwined with its political stability. A disruption in Taiwan’s operations would have profound repercussions throughout the global supply chain, impacting major economies and industries reliant on Taiwanese components and technology.
The loss of Taiwanese manufacturing capabilities could lead to significant price increases and shortages in critical electronic goods.
Taiwan’s Political Status and Stability Risks
Taiwan’s political status remains a contentious issue. While Taiwan enjoys a high degree of self-governance, its status as an independent nation is not internationally recognized. This ambiguity fuels uncertainty and tension in the region. China’s claim to Taiwan creates significant risks to the island’s stability, as China has repeatedly asserted its right to unify Taiwan, even by force if necessary.
This unresolved political status increases the likelihood of a potential conflict, with unpredictable outcomes.
Potential Consequences of China’s Actions on Taiwan’s Future
China’s actions and rhetoric regarding Taiwan carry significant implications for the island’s future. Any military intervention could lead to a major regional conflict, potentially impacting global stability. Such an intervention could disrupt the global economy, impacting markets and trade routes. Taiwan’s future prosperity and democratic values are directly threatened by China’s actions. A loss of sovereignty could lead to a suppression of democratic freedoms and cultural expression.
Taiwan’s Potential Response Strategies
Taiwan’s response to potential Chinese threats will be multifaceted, encompassing military, economic, and diplomatic strategies. A robust defense posture, coupled with a strong international alliance system, is crucial to deterring potential aggression. Diversifying its economic partnerships and strengthening its technological capabilities are essential to mitigating economic vulnerabilities. A continued commitment to democratic values and a robust international diplomatic presence will bolster Taiwan’s position in the face of Chinese pressure.
Ultimately, Taiwan’s strategy is focused on maintaining its independence, safeguarding its economy, and defending its democratic way of life.
Regional Security Implications: China Bristles Macron Linking Ukraine Defence Taiwan Threats
The complex interplay of China’s growing assertiveness, France’s diplomatic efforts, and Taiwan’s defense posture creates a volatile regional security landscape. The Ukraine conflict serves as a stark reminder of the potential for escalation when competing national interests clash, highlighting the critical need for diplomatic solutions and a careful assessment of potential responses. The situation surrounding Taiwan presents a similar dynamic, with implications for the broader Indo-Pacific region.
Security Concerns Comparison
Understanding the unique security concerns of each nation is crucial in assessing potential conflicts and their regional impact. The following table compares the security concerns of China, France, and Taiwan.
| Country | Concern | Explanation | Potential Impact |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Taiwan’s independence | China views Taiwan as a breakaway province and a threat to its sovereignty. Its claim to Taiwan is a long-standing geopolitical issue. | Potential military conflict, economic sanctions, and disruption of regional trade. |
| France | Maintaining its influence in the Indo-Pacific | France seeks to maintain its global influence and strategic presence, particularly in the face of growing Chinese influence in the region. | Potential for diplomatic tensions and increased competition with China in international forums. |
| Taiwan | Defense against potential invasion | Taiwan faces the imminent threat of invasion from China, and its primary concern is ensuring its security and defense against military aggression. | Direct military conflict, displacement of population, and significant economic damage. |
Escalation Potential
The current geopolitical climate presents significant risks of escalation. China’s increasing military presence in the region, coupled with its assertive rhetoric towards Taiwan, raises concerns about miscalculation and unintended consequences. France’s efforts to counterbalance Chinese influence might be perceived as provocative by China, potentially leading to further tension. Taiwan’s reliance on international support and its own defense capabilities will be critical in determining the course of events.
Historical conflicts, such as the Korean War, demonstrate how regional conflicts can escalate rapidly and impact global stability.
Responses of Other Regional Actors
Several regional countries, including Japan and the United States, are closely monitoring the situation and have articulated their responses.
- Japan: Japan, a close ally of the US and a key player in the region, is likely to increase its defense spending and strengthen its security partnerships to counter potential threats. The country’s focus on maintaining regional stability is likely to influence its approach to the escalating tensions. Japan’s experience with historical conflicts in the region, like the Sino-Japanese War, informs its approach to conflict resolution and defense strategies.
- United States: The US is likely to maintain its commitment to Taiwan’s defense, likely through increased military presence and arms sales. This commitment is crucial in deterring potential Chinese aggression. The US’s involvement in the Ukraine conflict has demonstrated its willingness to engage in international conflicts and support allies.
Potential Responses from International Actors
The international community’s reaction to the situation will be critical.
| Country | Response | Rationale | Potential Outcome |
|---|---|---|---|
| United States | Increased military support to Taiwan, strengthened alliances in the region | Maintaining regional stability and deterring Chinese aggression. | Escalation of tensions, potential for conflict, or diplomatic resolution. |
| European Union | Increased diplomatic pressure on China, economic sanctions | Responding to China’s actions and supporting Taiwan’s sovereignty. | Economic repercussions for China, potential for further escalation, or diplomatic solutions. |
| Russia | Potential support for China, aligning with geopolitical interests | Seeking to counterbalance US influence and maintain its own geopolitical interests. | Further destabilizing the region, potential for international conflict, or diplomatic maneuvering. |
Timeline of Events
A detailed timeline of events related to the actions and statements of these countries is crucial for understanding the evolution of the situation. Tracking these events helps to illustrate the progression of the crisis.
- 2023-Present: Continued Chinese military exercises and assertive rhetoric toward Taiwan, increasing tensions in the region. International actors have reacted with various responses, including increased diplomatic engagement and security cooperation. This period shows the escalating nature of the situation and the reactions of other actors.
Economic Interdependencies
The intricate web of economic relationships between China, France, and Taiwan is a significant factor in the current geopolitical climate. These connections, while offering potential benefits, also create vulnerabilities and expose all parties to potential risks. Understanding these interdependencies is crucial for assessing the possible outcomes of escalating tensions and navigating the complex challenges ahead.
Economic Ties Between China, France, and Taiwan
China’s economic rise has created substantial trade and investment links with France and Taiwan. France, a significant European power, has substantial economic interests in China, particularly in sectors like technology and infrastructure. Taiwan, a vital player in the global electronics supply chain, is heavily reliant on China for some components and markets. This intricate network of economic ties is a double-edged sword, presenting both opportunities and threats.
Potential Economic Risks and Rewards of China’s Actions
China’s actions, particularly regarding Taiwan, carry substantial economic risks. Any disruption to the status quo, including military action or economic pressure, could severely impact global trade and investment. This could lead to supply chain disruptions, market volatility, and potentially a global recession. Conversely, a peaceful resolution and continued economic engagement could yield significant rewards for all parties involved, fostering economic growth and stability.
Geopolitical Tensions and Global Trade
Geopolitical tensions stemming from the China-Taiwan issue and broader global power dynamics are already impacting global trade and investment. Uncertainty about the future of the region is discouraging foreign investment and creating a climate of apprehension. Companies are re-evaluating their supply chains, seeking diversification to reduce dependence on specific regions. This trend is already visible in the increasing interest in Southeast Asian manufacturing hubs.
Potential Economic Consequences
| Country | Impact | Sector | Mitigation Strategy |
|---|---|---|---|
| China | Potential economic slowdown due to international sanctions or trade disruptions. | Export-oriented industries, technology, infrastructure. | Diversifying export markets, investing in domestic consumption, developing alternative supply chains. |
| France | Disruption of trade relations with China and supply chain vulnerabilities. | Technology, luxury goods, agriculture. | Strengthening trade relationships with other partners, diversifying supply chains, supporting European integration initiatives. |
| Taiwan | Increased risk of military conflict, disruption to the global electronics supply chain, economic isolation. | Electronics manufacturing, semiconductor production, export-oriented industries. | Strengthening defense capabilities, diversification of manufacturing bases, establishing alternative trade agreements. |
Economic Vulnerabilities of Each Nation
Each nation involved possesses unique economic vulnerabilities. China’s economy is heavily reliant on exports, making it susceptible to global trade disruptions. France’s economy is intertwined with international trade, and its reliance on specific supply chains presents a vulnerability. Taiwan’s economy is particularly vulnerable due to its dependence on China for components and markets. These vulnerabilities underscore the importance of strategic planning and diversification to mitigate risks.
Possible Diplomatic Solutions
Navigating the complex web of geopolitical tensions requires a multifaceted approach, recognizing that diplomatic solutions are often the most sustainable pathways to de-escalation. This section explores potential strategies for fostering dialogue, identifying key actors, and establishing frameworks for meaningful negotiations, while acknowledging the inherent challenges in achieving peaceful resolutions to these conflicts.The path to resolving international disputes is rarely straightforward.
Success hinges on a combination of carefully crafted diplomatic strategies, a nuanced understanding of the motivations of all parties, and a willingness to compromise. This necessitates a comprehensive analysis of the historical context, current dynamics, and potential future implications of any proposed solution.
Potential Diplomatic Strategies for De-escalation
A variety of diplomatic strategies can be employed to de-escalate tensions. These range from direct negotiations between conflicting parties to the involvement of international mediators and organizations. Successful de-escalation strategies often rely on establishing clear communication channels, building trust, and fostering a shared understanding of the issues at hand.
- Direct Negotiations: Direct engagement between opposing parties, facilitated by neutral intermediaries, can lead to concrete agreements. The success of such negotiations depends heavily on the willingness of all sides to engage in good faith and compromise.
- International Mediation: Experienced mediators, often from international organizations or countries with established diplomatic traditions, can play a crucial role in facilitating dialogue and fostering mutual understanding. The success of mediation efforts is contingent upon the credibility and impartiality of the mediator, as well as the willingness of all parties to accept their role and advice.
- Confidence-Building Measures: Implementing confidence-building measures, such as reciprocal reductions in military activities or increased transparency in military deployments, can help reduce anxieties and foster a climate conducive to dialogue. Examples of these measures can be seen in arms control agreements and confidence-building measures implemented in various regional conflicts.
Examples of Successful International Negotiations
Examining past successes in international negotiations provides valuable insights into the strategies and approaches that have proven effective.
- The Camp David Accords (1978): The Camp David Accords, brokered by US President Jimmy Carter, demonstrated the potential of direct negotiations between previously hostile nations. The success of the Accords stemmed from the personal commitment of the leaders involved and the active mediation efforts of the US President.
- The Oslo Accords (1993): These accords, facilitating a breakthrough in Israeli-Palestinian relations, highlight the role of third-party mediation in complex conflicts. The active involvement of Norway played a crucial role in facilitating the dialogue and negotiations between the two parties.
- The Iran nuclear deal (2015): The Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action (JCPOA), although ultimately abandoned, provides an example of complex international negotiations involving multiple parties. The negotiations were characterized by lengthy discussions and compromises across different nations, demonstrating the complexity of reaching agreements in a multi-faceted international context.
Key Actors and Their Potential Roles in Negotiations
The involvement of various actors can influence the outcome of negotiations.
- National Leaders: National leaders play a critical role in initiating and sustaining negotiations. Their commitment to the process, coupled with the support of their constituents, is essential to securing progress.
- International Organizations: International organizations, such as the United Nations, can act as neutral platforms for dialogue and mediation, facilitating communication and fostering cooperation.
- Regional Powers: Regional powers, with their vested interests and influence within the affected region, can play a crucial role in mediating between opposing sides, fostering cooperation, and influencing outcomes.
Framework for Potential Talks Between Involved Parties
A potential framework for talks could involve a phased approach.
- Phase 1: Establish a communication channel and agree on a neutral venue for initial talks. This initial phase should focus on building trust and establishing a common ground for dialogue.
- Phase 2: Engage in discussions to identify areas of common ground and potential compromises. This phase requires active listening and a willingness to consider alternative solutions.
- Phase 3: Develop concrete proposals and agreements based on identified common ground. This requires flexibility and a willingness to adapt to changing circumstances. This stage requires a comprehensive understanding of the needs and concerns of all parties.
Role of International Organizations in Conflict Resolution
International organizations possess valuable tools and experience in facilitating conflict resolution.
- Facilitating Dialogue: International organizations can act as neutral platforms for dialogue, bringing together opposing sides to engage in constructive communication.
- Providing Support: These organizations often offer technical expertise, resources, and logistical support to facilitate the process.
- Monitoring and Enforcement: International organizations can monitor agreements and enforce compliance to ensure lasting peace.
End of Discussion
In conclusion, China’s response to Macron’s comments highlights the delicate balance of power in the region, and the potential for escalation. The interconnected nature of the Ukraine conflict, Taiwan’s defense, and China’s ambitions makes this a critical juncture for global diplomacy. Further analysis is needed to assess the long-term consequences of these evolving events.






