Rising asia temperatures bode well us lng export prospects maguire – Rising Asia temperatures bode well for US LNG export prospects, according to McGuire. Warmer weather in key Asian regions is expected to drive up demand for cooling and energy, potentially creating a lucrative market for US liquefied natural gas (LNG). This analysis explores the potential impact of these rising temperatures on LNG production, infrastructure, and trade routes, examining the current US LNG export landscape and the potential for increased demand from Asia.
The report also considers geopolitical factors and long-term projections for the global LNG market, focusing on the relationship between US and Asian energy needs.
The report details projected temperature increases in various Asian regions, highlighting areas crucial to LNG production. It examines the anticipated effects on production capacity and infrastructure. A key aspect of the report is a comparative table outlining predicted temperature rises and their influence on LNG production in different Asian countries. The report also assesses the current US LNG export capabilities, comparing them to other countries, particularly in Asia.
It analyzes market trends, including global energy demands, and provides a table showcasing current US export infrastructure and its projected growth. Crucially, the report explores the potential link between rising Asian temperatures and the heightened demand for cooling and energy sources, such as LNG. Government policies, economic factors, and potential challenges and opportunities for US LNG exports to Asia are also considered.
Rising Temperatures in Asia and LNG Export Potential
The increasing frequency and intensity of extreme weather events across Asia underscore a growing need for reliable energy sources. Rising temperatures, particularly in regions crucial for natural gas production, are projected to influence the availability and demand for Liquefied Natural Gas (LNG). This analysis explores the potential impact of rising Asian temperatures on LNG export prospects, considering both production capacity and market demand.The interplay between climate change and energy markets is complex.
Rising temperatures can affect the efficiency of LNG production facilities, impacting output and potentially increasing operational costs. Simultaneously, the increased energy needs of rapidly developing economies in Asia may further fuel demand for LNG, creating a dynamic interplay between supply and demand.
Projected Temperature Increases in Asian Regions
Temperature increases in Asia are not uniform across the continent. Some regions, particularly those in Southeast Asia, are projected to experience more pronounced warming trends compared to others. These temperature shifts are expected to be linked to climate change patterns and local geographical factors. Variations in elevation, proximity to water bodies, and prevailing weather systems all contribute to regional differences in temperature changes.
For example, coastal regions may experience slightly less intense warming due to moderating ocean temperatures, while inland areas may be more vulnerable.
Impacts on LNG Production Capacity and Infrastructure
Rising temperatures can directly affect the efficiency of LNG plants. Higher temperatures can lead to increased energy consumption for cooling processes, impacting overall production capacity. Additionally, infrastructure like pipelines and storage facilities may face increased stress from heat, potentially leading to maintenance needs and potential disruptions. For example, a prolonged heatwave could impact the operation of compressors, leading to reduced gas flow and impacting the entire supply chain.
Rising Asian temperatures are definitely good news for US LNG export prospects, as McGuire points out. However, the global markets view Europe here is also a crucial factor. The shifting demand and supply dynamics in the region could impact the overall LNG market, ultimately influencing the success of US exports to Asia. So, while the Asian heatwave is a positive sign, a deeper understanding of the global landscape is essential for a complete picture of US LNG export prospects.
Potential for Increased Demand for LNG in Asia
The growing demand for energy in Asia, especially from industrial sectors and burgeoning populations, will likely increase demand for LNG. This demand may be further amplified by rising temperatures and the need for reliable energy to support air conditioning and other cooling systems. Furthermore, the shift towards cleaner energy sources in some regions may favor LNG as a transitional fuel, further increasing the demand.
Comparison of Predicted Temperature Rises and Impact on LNG Production
| Country | Predicted Temperature Rise (°C) | Impact on LNG Production |
|---|---|---|
| Indonesia | 1.5-2.5°C (2040-2060) | Potentially reduced efficiency of LNG plants, increased operational costs, possible infrastructure stress. |
| Vietnam | 1.8-2.8°C (2040-2060) | Increased risk of heat-related damage to pipelines and processing plants, reduced capacity in peak demand periods. |
| India | 1.6-2.6°C (2040-2060) | Increased energy demand for cooling, potentially impacting LNG demand. Higher energy consumption may lead to higher demand for LNG. |
| Bangladesh | 1.7-2.7°C (2040-2060) | Increased vulnerability of infrastructure, potentially impacting production and supply. |
“Increased temperatures can have a profound effect on LNG production. Heatwaves can directly reduce the efficiency of LNG plants, leading to reduced output.”
Rising Asian temperatures are looking good for US LNG export prospects, according to McGuire. While the specifics of these rising temperatures are interesting, the sheer scale of the global energy market also makes me wonder about the mysteries of the outer solar system. For example, what makes Pluto so intriguing, a dwarf planet with its own unique characteristics?
what makes pluto intriguing Ultimately, these planetary discoveries and the potential for increased energy demand in Asia due to warming climates are connected; both are fascinating, albeit different, facets of a complex global picture. These factors all add up to a potential boost in US LNG exports.
US LNG Export Prospects
The escalating temperatures across Asia present a significant opportunity for US LNG exports. Growing demand in the region, coupled with the increasing capacity of US export facilities, positions the nation to capitalize on this burgeoning market. This analysis delves into the current state of US LNG exports, comparing them with other global players, and examining the trends impacting their future.
Current Capacity and Capabilities of US LNG Export Facilities
US LNG export capacity has expanded dramatically in recent years, driven by strong global demand and favorable economic conditions. Several large-scale liquefaction plants have come online, increasing the nation’s ability to ship LNG to international markets. These facilities utilize advanced technologies to liquefy natural gas, enabling efficient and cost-effective transportation across oceans. Key factors influencing their capabilities include the size of the liquefaction trains, the efficiency of the processing plants, and the proximity to shipping ports.
Comparison of US LNG Export Market with Other Countries, Especially Within Asia
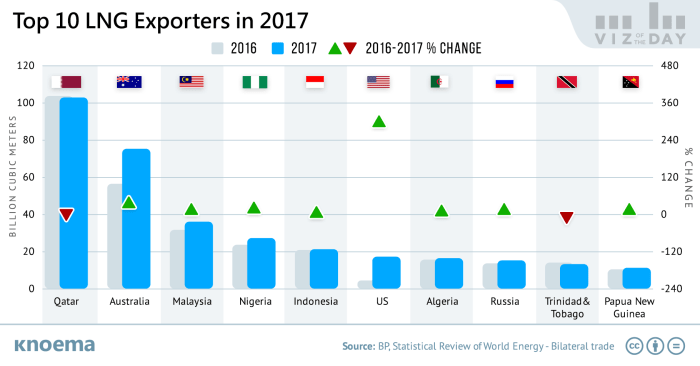
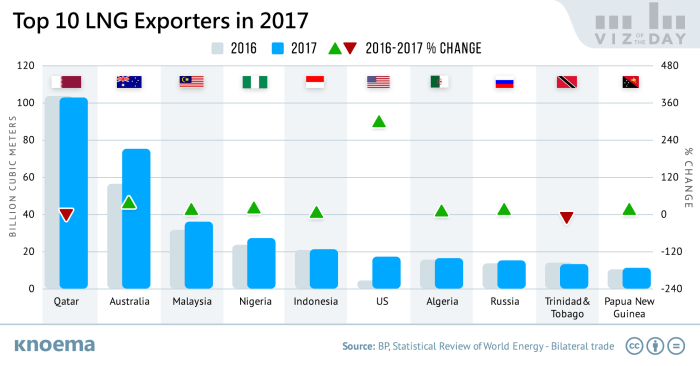
The US LNG export market faces competition from other global exporters, particularly in Asia. Countries like Qatar, Australia, and Russia have significant LNG production capabilities and established export networks. While the US is relatively new to large-scale LNG exports, it is gaining market share due to factors like lower production costs, abundant natural gas reserves, and strategic location.
This competitive landscape necessitates continuous adaptation and innovation in the US LNG industry to maintain a robust presence.
Market Trends Affecting US LNG Exports, Including Global Energy Demands
Several market trends significantly impact US LNG exports. The rising global demand for energy, particularly from developing economies, is driving the demand for LNG. Fluctuations in global energy prices influence export decisions and profitability. Furthermore, geopolitical factors, such as trade agreements and political stability in key regions, also play a substantial role. The transition to cleaner energy sources, like renewable energy, also presents both challenges and opportunities for the LNG industry.
Predicting future demand and supply is crucial to long-term planning.
Current US LNG Export Infrastructure and Projected Growth
The table below provides a snapshot of the current US LNG export infrastructure, including its location, capacity, and projected growth. This data illustrates the substantial investment in US LNG export capacity and its projected increase in the coming years. This expansion underscores the anticipated growth in US LNG exports and the importance of a well-established infrastructure for international shipping.
| Facility | Location | Capacity (MTPA) | Projected Growth (MTPA) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cheniere Energy | Corpus Christi, Texas | 30 | 50 (by 2027) |
| Venture Global | Calcasieu Pass, Louisiana | 25 | 40 (by 2028) |
| Freeport LNG | Freeport, Texas | 20 | 30 (by 2029) |
| Other Facilities | Various locations | 10+ | 20+ (by 2030) |
Note: MTPA stands for million tonnes per annum. Projections are estimates based on current plans and market expectations. Growth can be affected by unforeseen circumstances.
The Link Between Asian Temperatures and US LNG Demand
Rising temperatures across Asia are poised to significantly impact the demand for energy sources, including liquefied natural gas (LNG). This increased demand presents a promising opportunity for US LNG exports, as the region seeks reliable and affordable energy alternatives. The correlation between these factors warrants a closer examination of the intricate relationships at play.The escalating temperatures in Asian countries are driving a surge in demand for cooling systems.
Air conditioning use is rapidly increasing, particularly in urban areas and densely populated regions. This surge in energy consumption for cooling directly translates into a greater need for reliable and efficient energy sources, like LNG. Moreover, industrial sectors in Asia are also experiencing higher energy demands, further contributing to the growing need for LNG.
Government Policies and Regulations
Government policies and regulations play a crucial role in shaping the energy landscape of Asian countries. Supportive policies encouraging the adoption of renewable energy sources and energy efficiency measures can influence LNG demand. Conversely, policies that prioritize domestic energy production or impose stringent environmental regulations on LNG import and usage can potentially restrict the flow of US LNG to the region.
For instance, some Asian countries are actively investing in renewable energy projects, which might limit the growth of LNG demand. However, the continued need for reliable energy sources, particularly for industries with high energy consumption, could still maintain LNG as a critical energy component.
Economic Factors Influencing US-Asia LNG Trade
The economic factors influencing the trade between the US and Asia regarding LNG are multifaceted. The cost of LNG production and transportation from the US to Asia, along with fluctuating global energy prices, directly affect the competitiveness of US LNG exports. Additionally, the availability of alternative energy sources and their costs in Asia will influence the demand for LNG.
Trade agreements and diplomatic relations between the US and Asian countries also play a vital role in shaping the trade dynamics. For example, the potential for long-term contracts and agreements between US LNG exporters and Asian importers can significantly impact the volume and pricing of LNG transactions.
Potential Challenges and Opportunities for US LNG Exports to Asia
- Transportation Costs and Infrastructure: Logistics and infrastructure for transporting LNG from US export terminals to Asian receiving facilities can pose significant challenges. The cost of shipping LNG and the availability of suitable infrastructure in both the US and Asia will impact the feasibility and profitability of US LNG exports. For instance, delays in port development or expansion could hinder the efficient transportation of LNG.
The building of new pipelines or using existing ones can influence the cost of transport.
- Competition from Other LNG Suppliers: The US faces competition from other LNG exporters, such as Qatar and Australia. The pricing strategies, reliability of supply, and logistical efficiency of these competitors will influence the competitiveness of US LNG in the Asian market. Maintaining a competitive edge is crucial for US exporters.
- Environmental Concerns: The environmental impact of LNG production, transportation, and usage are significant considerations. Addressing concerns related to emissions and the potential for leakage throughout the entire supply chain is essential to maintain the market’s trust in US LNG exports. Stringent environmental regulations in Asia might limit the demand for US LNG.
- Political and Geopolitical Factors: Geopolitical tensions and political instability in certain regions can disrupt trade flows and create uncertainty in the LNG market. Maintaining stable political relationships between the US and Asian nations is essential for ensuring the smooth flow of LNG exports.
| Potential Challenges | Potential Opportunities |
|---|---|
| High transportation costs | Long-term contracts with Asian importers |
| Competition from other suppliers | Strong US-Asia relations |
| Environmental concerns | Technological advancements in LNG production and transport |
| Political instability | Economic growth in Asia |
Factors Influencing LNG Trade Routes and Infrastructure: Rising Asia Temperatures Bode Well Us Lng Export Prospects Maguire

The burgeoning demand for liquefied natural gas (LNG) from Asia, particularly with rising temperatures, has significantly impacted the viability of LNG trade routes. The geographical distribution of LNG production, consumption, and infrastructure profoundly affects the economics and feasibility of various shipping lanes. Understanding these factors is crucial for assessing the potential of US LNG exports to the Asian market.The geographical proximity of supply and demand is a critical determinant in LNG trade.
Shipping costs, transit times, and potential disruptions along the route directly affect the price competitiveness of US LNG. Analyzing these factors and the potential infrastructure bottlenecks is essential to forecast the future of US-Asia LNG trade.
Geographical Factors Impacting LNG Trade Routes
The vast distances between US LNG export terminals and Asian import terminals significantly influence transportation costs and logistical complexities. Optimizing routes is vital to minimize expenses and transit time. Considerations include prevailing ocean currents, weather patterns, and potential disruptions like storms or piracy, which can cause delays and increased insurance costs. The existence of established shipping lanes and ports also plays a significant role in determining the most cost-effective and efficient trade routes.
Potential LNG Shipping Routes
Several potential LNG shipping routes exist between the US and Asia, each with its own set of advantages and disadvantages. The choice of route often depends on factors such as distance, prevailing ocean currents, and the presence of strategically located ports. The Panama Canal and Suez Canal are critical points for routes that bypass longer stretches of ocean.
Potential Obstacles to LNG Trade
Several obstacles may hinder the growth of LNG trade between the US and Asia. Infrastructure limitations, such as a lack of adequate storage capacity at Asian import terminals or pipeline connections, can impact the smooth flow of LNG. Political tensions or geopolitical instability in transit regions or destination countries can create significant risks and uncertainties for traders. Regulatory hurdles, import quotas, and trade disputes can further complicate the trade flow.
Furthermore, fluctuating global energy prices can affect the economics of LNG trade, creating unpredictable market conditions.
Comparison of Potential LNG Shipping Routes
| Route | Estimated Cost (per unit) | Potential Risks | Infrastructure Considerations |
|---|---|---|---|
| Trans-Pacific Route (via Panama Canal) | $X (estimated) | Weather patterns, potential disruptions, insurance costs | Panama Canal transit time, port infrastructure at destination |
| Trans-Pacific Route (direct) | $Y (estimated) | Longer transit times, potential disruptions | Port infrastructure at destination, shipping vessel availability |
| Trans-Pacific Route (via Suez Canal) | $Z (estimated) | Geopolitical risks, Suez Canal transit time | Suez Canal transit time, port infrastructure at destination |
Note: Estimated costs are approximate and vary depending on several factors, including the size of the LNG carrier, the volume of LNG shipped, and the prevailing market conditions. Values (X, Y, Z) are placeholders for illustrative purposes only.
Market Dynamics and Future Projections for LNG
The global liquefied natural gas (LNG) market is experiencing a period of significant transformation, driven by shifting energy demands, geopolitical uncertainties, and technological advancements. Understanding the complex interplay of supply, demand, and geopolitical factors is crucial for anticipating future trends and navigating the evolving landscape of LNG trade. The recent surge in Asian temperatures, coupled with the increasing need for reliable energy sources, has highlighted the growing importance of US LNG exports.The LNG market is characterized by a dynamic interplay of supply and demand, influenced by factors ranging from economic growth to environmental policies.
The future of LNG trade depends heavily on accurate forecasting of these forces, and the interplay between them.
Global LNG Market Dynamics
The global LNG market is a complex system involving numerous players, including producers, traders, and consumers. Understanding the supply and demand forecasts for the market is critical to anticipating future trends.
- Supply Side: Major LNG exporting nations, including the US, Qatar, and Australia, are actively expanding production capacity to meet growing demand. Recent technological advancements are also enabling more efficient production processes, lowering production costs and expanding export potential.
- Demand Side: The Asia-Pacific region, particularly China and India, is experiencing rapid industrialization and energy demand growth, creating a robust market for LNG imports. Europe is also experiencing increasing demand as it transitions away from reliance on Russian natural gas. The global demand for LNG is projected to continue to increase, driven by both industrial and residential energy needs.
Impact of Geopolitical Events
Geopolitical events significantly impact the LNG market by affecting trade routes, supply chains, and pricing.
- Trade Disruptions: Political instability or conflicts in producing or transit regions can disrupt LNG supply chains, leading to price volatility and shortages in consuming regions. The war in Ukraine, for example, has significantly impacted European energy security, prompting the continent to seek alternative LNG sources, further emphasizing the importance of diverse supply chains.
- Trade Agreements: International agreements and trade partnerships can facilitate the flow of LNG between countries, potentially creating new markets and supply routes. Examples include bilateral trade deals and regional initiatives.
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements in LNG production and transportation are significantly impacting the market.
- Production Efficiency: Innovations in fracking technology and gas processing are increasing production efficiency, making LNG production more cost-effective and sustainable. This efficiency, coupled with rising demand, has made the US a major player in the global LNG market.
- Transportation: Improvements in LNG shipping technologies, such as larger vessels and more efficient liquefaction and regasification facilities, can significantly reduce transportation costs and increase the efficiency of LNG trade. This is essential to lowering the cost of the fuel and making it more accessible to consumers.
Long-Term Projections for Asia and the US
Long-term projections for LNG demand and supply in Asia and the US are complex and influenced by various factors.
- Asia: Projected strong growth in LNG demand in Asia, particularly in countries like China and India, as their economies continue to expand. This demand is driven by the increasing energy needs of their industrial sectors and populations. Infrastructure development in importing countries is also critical for facilitating this growth.
- US: The US is projected to maintain a significant role as an LNG exporter, leveraging its abundant shale gas reserves and increasing production capabilities. The development of new export terminals and infrastructure plays a vital role in facilitating these exports.
Potential Impacts on Energy Security and Trade Relations
The burgeoning trade of liquefied natural gas (LNG) between the US and Asia carries significant implications for global energy security, political relations, and market dynamics. This exchange represents a complex interplay of economic interests and geopolitical considerations, with the potential to reshape the energy landscape of both continents. The rising temperatures in Asia, coupled with the growing demand for reliable energy sources, are creating an environment ripe for increased LNG imports from the US.This increased trade necessitates a careful examination of the potential impacts on energy security, political relations, and the global energy market.
Understanding these intricacies is crucial for anticipating the future trajectory of US-Asia relations and the broader implications for global energy trade.
Rising Asian temperatures are looking good for US LNG export prospects, according to McGuire. Meanwhile, the Red Sox clinched the series victory against the Rays, with Walker Buehler leading the charge. This strong performance, coupled with the increasing demand for LNG in Asia, suggests a promising outlook for US LNG exports. Walker Buehler’s Red Sox win is a great sign, adding to the overall positive sentiment for the industry.
Implications for Global Energy Security
The rise of US LNG exports to Asia significantly contributes to global energy security. Diversification of energy sources reduces reliance on a single supplier, mitigating risks associated with geopolitical instability or supply disruptions. The increased supply from the US provides Asian nations with alternative energy options, lessening vulnerability to potential shortages or price fluctuations from traditional suppliers. This enhanced diversification enhances global energy security, particularly for countries in Asia, who traditionally rely heavily on a limited number of suppliers.
Impact on Political Relations Between the US and Asian Nations
LNG trade can foster stronger economic ties and political cooperation between the US and Asian nations. Shared energy interests can create platforms for diplomatic engagement and cooperation on broader geopolitical issues. The US, seeking to strengthen its strategic partnerships in the region, can leverage LNG exports as a tool for economic and diplomatic influence. Conversely, competition for resources or disputes over trade practices could strain relationships, requiring careful management of the trade dynamics.
Effects on Energy Prices and Market Volatility
The influx of US LNG into the Asian market can influence energy prices and market volatility. Increased supply can potentially moderate prices, benefiting consumers and stabilizing the market. However, supply disruptions or unexpected demand surges can create price spikes and market instability. Fluctuations in global energy markets can have a ripple effect, affecting economies and energy consumers worldwide.
Predicting the precise impact requires analyzing historical market trends and potential disruptions. For example, the 2022 global energy crisis demonstrated how geopolitical events can dramatically impact energy prices and market volatility.
Potential Scenarios and Their Impact on US-Asia Trade Relations
Several scenarios are possible, each with varying implications for US-Asia trade relations. A scenario of smooth and stable LNG trade can lead to increased economic cooperation and mutual benefits. Alternatively, trade disputes, differing energy policies, or geopolitical tensions could strain relations. The successful navigation of these scenarios requires proactive diplomatic engagement and a focus on equitable and transparent trade practices.
Ultimately, the outcome will depend on the strategic choices made by both the US and Asian nations. For instance, the ongoing US-China trade tensions highlight the importance of managing trade relations effectively in a complex geopolitical landscape.
Illustrative Case Studies (Examples)
The rising temperatures in Asia are creating a significant opportunity for US LNG exports. Understanding how existing and potential projects are impacting economies and trade is crucial. This section delves into illustrative case studies, analyzing the benefits and challenges, and exploring the economic and social impacts of these projects. The analysis also incorporates trade agreements and their influence on LNG export flows.Analyzing specific examples allows for a more nuanced understanding of the complex dynamics involved in US-Asia LNG trade.
This approach allows for a clearer view of the benefits, challenges, and overall impact of these transactions.
Hypothetical Project: “Pacific Bridge” LNG Export Project, Rising asia temperatures bode well us lng export prospects maguire
This hypothetical project envisions a significant LNG export facility in the Gulf of Mexico, designed to supply Asian markets. The facility would leverage existing infrastructure and potentially develop new pipeline connections to the export terminals.
- Economic Benefits (US): The project would create thousands of jobs during construction and operation, boosting local economies in the Gulf Coast region. It would stimulate economic activity in related industries like shipping and insurance. Potential tax revenues from the project would be a significant factor. The US would gain substantial revenue from exports and potentially strengthen its geopolitical standing in the region.
- Economic Benefits (Asia): Increased access to affordable, reliable natural gas would contribute to lower energy costs for industries and households. This would support economic growth and industrial development in Asian countries. The project would enhance energy security by diversifying energy sources.
- Challenges: Infrastructure development and pipeline construction would face significant environmental challenges. Competition from other LNG exporters, fluctuating global energy prices, and potential political instability in the region could impact profitability. Environmental regulations and permitting processes would need to be navigated effectively.
Existing Project: Cheniere Energy’s Sabine Pass LNG Export Terminal
This existing facility in Louisiana exports LNG primarily to Asian markets. Its operational history provides insights into the realities of US LNG exports.
- Economic Impact (US): The terminal has created jobs in construction, operation, and related industries. It has stimulated economic activity in the surrounding areas, demonstrating a positive economic impact.
- Economic Impact (Asia): The terminal has provided an alternative source of natural gas for Asian consumers. This has helped mitigate price volatility and potentially enhance energy security.
- Challenges: The terminal’s operations are subject to fluctuations in global energy markets. The availability of liquefaction capacity can affect export volume, impacting both profitability and customer demand.
Trade Agreements and their Impact
Trade agreements, such as the Comprehensive and Progressive Agreement for Trans-Pacific Partnership (CPTPP) and bilateral agreements between the US and Asian nations, play a vital role in facilitating LNG trade. These agreements can reduce tariffs, streamline customs procedures, and foster cooperation.
- CPTPP Impact: The CPTPP, encompassing several Asian nations, could potentially create a more integrated market for US LNG exports. However, navigating the complexities of multiple agreements and ensuring compliance can be challenging.
- Bilateral Agreements: Bilateral agreements between the US and individual Asian countries could provide specific benefits, such as preferential treatment for LNG imports, thus reducing trade barriers. These agreements can also enhance political and economic relations.
Comparative Analysis of Case Studies
| Case Study | Economic Benefits (US) | Economic Benefits (Asia) | Challenges |
|---|---|---|---|
| Pacific Bridge | Job creation, economic stimulus, tax revenue | Lower energy costs, economic growth, energy security | Infrastructure development, competition, political risks, environmental concerns |
| Sabine Pass | Job creation, economic stimulus | Alternative energy source, price stability, energy security | Market fluctuations, capacity constraints, operational risks |
Final Summary
In conclusion, the rising temperatures in Asia present a significant opportunity for increased US LNG exports. The analysis highlights the potential correlation between these rising temperatures and the need for increased cooling and energy, including LNG. The report also delves into the crucial role of government policies and the economic factors influencing this trade relationship. Ultimately, the report suggests that US LNG exports to Asia could be a substantial component of the global energy market, with significant implications for energy security, trade relations, and the future of the energy industry.
Further analysis is required to determine the exact impact of these factors and to identify the most efficient trade routes, including potential infrastructure limitations and geopolitical tensions.